Difference between revisions of "Type III Hypersensitivity"
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = FFE4E1 | ||
| + | |linkpage =Immunology | ||
| + | |linktext =IMMUNOLOGY | ||
| + | |sublink1 =Hypersensitivity - WikiBlood | ||
| + | |subtext1 =HYPERSENSITIVITY | ||
| + | |pagetype =Blood | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
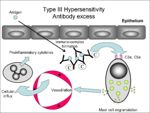
[[Image:Type III hypersensitivity antibody excess.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Type III hypersensitivity antibody excess-Brian Catchpole RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Type III hypersensitivity antibody excess.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Type III hypersensitivity antibody excess-Brian Catchpole RVC 2008]] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 33: | ||
4. Arthritis | 4. Arthritis | ||
| − | 5. [[Glomerulonephritis]] | + | 5. [[Kidney Glomerular Disease - Pathology|Glomerulonephritis]] |
* Can occur as an adverse effect of antibody response to infection if there is significant levels of antigen in the circulation. Examples of diseases that can cause this are: | * Can occur as an adverse effect of antibody response to infection if there is significant levels of antigen in the circulation. Examples of diseases that can cause this are: | ||
| − | ** | + | ** Leishmaniasis |
| − | ** | + | ** Lymes disease |
| − | ** | + | ** African swine fever |
| Line 46: | Line 57: | ||
2. [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus|Systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)]]- antigen is a self antigen (autoimmune disease of dogs and cats) | 2. [[Systemic Lupus Erythematosus|Systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)]]- antigen is a self antigen (autoimmune disease of dogs and cats) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 14:43, 11 August 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Introduction
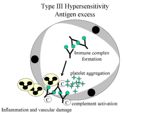
In the normal animal, immune complexes (lattice of soluble antigen and antibodies) are formed and removed all the time. They are broken up by complement, transported to the spleen by RBC's and phagocytosed. When the amount of immune complexes formed (due to rapid influx of antigen) does not equal the amount that are being cleared it causes type III hypersensitivity (an excess of immune complexes).
Location of the immune complexes:
Locally:
1. Inhaled antigen leads to hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Farmers lung (humans) - inhalation of fungal spores
- Pigeon fancier's disease - repeated inhalation of dried pigeon faeces
- Mouldy hay containing Micropolyspora felis
2. Intradermal and subcutaneous injection of antigen (with high levels of circulating antibody) leads to localised immune complexes which cause acute inflammation.
3. Vasculitis - due to antigen deposition in blood vessels.
4. Arthritis
- Can occur as an adverse effect of antibody response to infection if there is significant levels of antigen in the circulation. Examples of diseases that can cause this are:
- Leishmaniasis
- Lymes disease
- African swine fever
Systemically:
Due to increased quantities of antigen systemically.
Generalised effects:
- Vasculitis
- Erythema
- Oedema
- Neutropaenia
- Proteinuria (caused by of kidney damage)
1. Drug reactions (eg. penicillins and sulphonamides)
2. Systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)- antigen is a self antigen (autoimmune disease of dogs and cats)