Difference between revisions of "Recognition of Microorganisms"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Rjfrancisrvc (talk | contribs) |
(Created page with "thumb|right|150px|Pattern Recognition Receptors - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008 * The innate immune system recognises components of pathogens which are intrinsically ...") |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:PRRs.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Pattern Recognition Receptors - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:PRRs.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Pattern Recognition Receptors - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | The | + | * The innate immune system recognises components of pathogens which are intrinsically foreign (i.e. not present on normal mammalian cells), such as: |
| − | *Lipopolysaccharides of gram-negative | + | **Lipopolysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria |
| − | *Peptidoglycans of gram-positive bacteria | + | **Peptidoglycans of gram-positive bacteria |
| − | *Mannose sugars | + | **Mannose sugars |
| − | *D-isoform amino acids | + | **D-isoform amino acids |
| − | + | *These are given away as foreign by expressing '''pathogen-associated molecular patterns''' (PAMPs) | |
| − | These are | + | * PAMPs are recognised by '''pattern recognition receptors''' (PRRs) expressed on mammalian cells |
| − | *Recognition of pathogens via the cellular PRRs results in phagocytosis and inflammation | + | ** Pattern recognition receptors are expressed on many different cell types, not just on phagocytes |
| − | *Recognition of pathogens via the humoral PRRs results in various killing mechanisms | + | ** Not all are expressed by all cells: different cell types express a different range of PRRs |
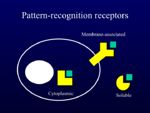
| − | + | ** PRRs are either intracellular, membrane-associated or soluble: | |
| − | + | *** Recognition of pathogens via the cellular PRRs results in phagocytosis and inflammation | |
| − | + | *** Recognition of pathogens via the humoral PRRs results in various killing mechanisms | |
| − | * ''' | + | * Engagement of PRRs by PAMPs triggers: |
| − | * The expression of ''' | + | ** '''Phagocytosis''' |
| − | + | ** The expression of '''cytokines''', which brings about [[Inflammation - WikiBlood|inflammation]] and other immune responses | |
| + | |||
| − | |||
<big><center>'''''Examples of Pattern Recognition Receptors'''''</center></big> | <big><center>'''''Examples of Pattern Recognition Receptors'''''</center></big> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| TLR3 | | TLR3 | ||
| − | | Cell Membrane | + | | Cell Membrane |
| dsRNA of RNA viruses (e.g. avian influenza) | | dsRNA of RNA viruses (e.g. avian influenza) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| TLR9 | | TLR9 | ||
| − | | Cell Membrane | + | | Cell Membrane |
| Bacterial DNA (CpG DNA) | | Bacterial DNA (CpG DNA) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
| Carbohydrates, all bacteria, dead cells | | Carbohydrates, all bacteria, dead cells | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | fmlf |
| Soluble | | Soluble | ||
| Formyl peptides (i.e. all bacteria) | | Formyl peptides (i.e. all bacteria) | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
| ds RNA of RNA viruses | | ds RNA of RNA viruses | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Innate Immune System]] | [[Category:Innate Immune System]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:42, 13 August 2010
- The innate immune system recognises components of pathogens which are intrinsically foreign (i.e. not present on normal mammalian cells), such as:
- Lipopolysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria
- Peptidoglycans of gram-positive bacteria
- Mannose sugars
- D-isoform amino acids
- These are given away as foreign by expressing pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
- PAMPs are recognised by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) expressed on mammalian cells
- Pattern recognition receptors are expressed on many different cell types, not just on phagocytes
- Not all are expressed by all cells: different cell types express a different range of PRRs
- PRRs are either intracellular, membrane-associated or soluble:
- Recognition of pathogens via the cellular PRRs results in phagocytosis and inflammation
- Recognition of pathogens via the humoral PRRs results in various killing mechanisms
- Engagement of PRRs by PAMPs triggers:
- Phagocytosis
- The expression of cytokines, which brings about inflammation and other immune responses
| Receptor | Location | Ligands |
|---|---|---|
| TLR2 (Toll-like receptor) | Cell Membrane | Peptidoglycan of gram +ve bacteria |
| TLR3 | Cell Membrane | dsRNA of RNA viruses (e.g. avian influenza) |
| TLR4 | Cell Membrane | Lipoplysaccharide from gram-negative bacteria (e.g. E. coli, Salmonella) |
| TLR5 | Cell Membrane | Bacterial flagellin |
| TLR9 | Cell Membrane | Bacterial DNA (CpG DNA) |
| C-type lectins | Soluble | Carbohydrates, all bacteria, dead cells |
| fmlf | Soluble | Formyl peptides (i.e. all bacteria) |
| Complement receptors | Soluble | Fixed complement components (e.g. iC3b) |
| NOD2 | Cytoplasm | Peptidoglycan of gram +ve bacteria |
| dsRNA-dependent Protein Kinase Receptor | Cytoplasm | ds RNA of RNA viruses |