Difference between revisions of "Hair - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{toplink |
| + | |backcolour = FFCCCC | ||
| + | |linkpage =Integumentary - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |linktext =INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM | ||
| + | |maplink = Integumentary System (Content Map) - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
| + | |||
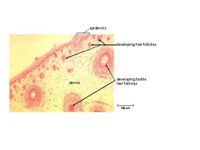
[[image: Section of Foetal Cat Skin.jpg|thumb|200px|right|A section of foetal cat skin showing developing hair follicles. ©RVC2008]] | [[image: Section of Foetal Cat Skin.jpg|thumb|200px|right|A section of foetal cat skin showing developing hair follicles. ©RVC2008]] | ||
| − | Hair germs begin from an aggregation of keratinocytes in the stratum basale of the [[Skin - Anatomy & Physiology#Epidermis|epidermis]]. The initiating factor is the underlying | + | Hair germs begin from an aggregation of keratinocytes in the stratum basale of the [[Skin - Anatomy & Physiology#Epidermis|epidermis]]. The initiating factor is the underlying dermal fibroblast cells. The keratinocytes elongate, divide and relocate to the dermis. Dermal fibroblasts then form a dermal papilla beneath the hair germ. This causes stimulation of the basal stem cells to up-regulate their cycle, producing cells that will keratinise and form the hair shaft. Two swellings form on the shaft, one containing stem cells for follicle regeneration, the other becomes a [[Skin - Anatomy & Physiology#Glands|sebaceous gland]] which will secrete sebum onto the hair shaft. The follicles develop from an ectodermal bud which invades the mesenchyme during embryonic development. The mesoderm also condenses during the development creating an outer mesodermal component to the embedded part of the hair. |
==Structure and Function== | ==Structure and Function== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Hair Types=== | ===Hair Types=== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 20: | ||
[[image: Rex rabbit.jpg|thumb|175px|left|The short, fine and densely packed guard hairs of a rex rabbit giving the coat a "velvet" appearance. ©Rachael Wallace2008]] | [[image: Rex rabbit.jpg|thumb|175px|left|The short, fine and densely packed guard hairs of a rex rabbit giving the coat a "velvet" appearance. ©Rachael Wallace2008]] | ||
| − | These are generally | + | These are generally stiff and straight and form the outer haircoat of an animal. They are uniformly distributed across the skin surface and give the haircoat a smooth appearance. The smoothness of the coat is important in allowing rain to fall from the surface without penetrating deeper to the epidermis and causing loss of body temperature. The oily coating of the haircoat comes from the secretions of the sebaceous glands in the epidermis, associated with the hair follicle. This also contributes to the ‘waterproofing’ of the haircoat. Each hair consists of an outer cuticle, with a cortex and innermost medulla. It is composed of highly keratinised, dead epithelial cells, with the arrangement into the 3 layers conferring flexibility. |
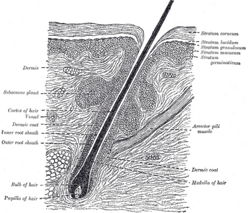
[[image: Section of hair follicle.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Section of skin showing a hair follicle. From Gray's Anatomy]] | [[image: Section of hair follicle.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Section of skin showing a hair follicle. From Gray's Anatomy]] | ||
| − | The '''''arrector pili''''' muscle is attached to the proximal end of the follicle and the dermis close to the point at which the hair is externalised. Involuntary contraction of this muscle in cold ambient temperatures causes | + | The '''''arrector pili''''' muscle is attached to the proximal end of the follicle and the dermis close to the point at which the hair is externalised. Involuntary contraction of this muscle in cold ambient temperatures causes erection of the hairs to trap warm air against the skin, thus providing [[Thermoregulation in Skin - Anatomy & Physiology|insulation]]. This can also be induced by the ‘fight or flight’ mechanism of the '''sympathetic nervous system'''. |
| + | |||
| + | Hairs have a finite life span and are shed and replaced at varying frequencies, depending on species. The most noticeable is seasonal shedding and growth. An increase in ambient temperature causes a slowing of the growth of existing hairs. This is termed the '''catagen phase'''. Atrophy of the papillae and hair matrix occurs and growth ceases in the '''telogen phase'''. The follicle shortens, pushing the hair further from the surface. When growth resumes, the follicle retreats deeper into the epidermis, leaving the old hair unattached and thus it falls out. '''Anagen phase''' is where a new matrix produced and another hair grows in the place of the old one. | ||
*'''Wool hairs''' | *'''Wool hairs''' | ||
| − | These are thin, wavy, soft hairs that form the | + | These are thin, wavy, soft hairs that form the undercoat of animals. They are often much more numerous than the tough guard hairs and usually shorter. Wool hairs often share a single follicle with guard hairs, although this is not common to all species. |
*'''Tactile hairs''' | *'''Tactile hairs''' | ||
| Line 56: | Line 35: | ||
[[image: Long vibrissae.jpg|thumb|250px|left|Long vibrissae of a domestic cat. ©Rachael Wallace2008]] | [[image: Long vibrissae.jpg|thumb|250px|left|Long vibrissae of a domestic cat. ©Rachael Wallace2008]] | ||
| − | Tactile hairs are associated with a sensory function and are much | + | Tactile hairs are associated with a sensory function and are much thicker and stiffer than other hairs. They are mainly found on the face and can also be referred to as '''''whiskers''''' or '''''vibrissae'''''. Their follicles are much deeper into the subcutis than guard or wool hairs and possess a venous sinus and nerve endings with mechanoreceptors. During embryonic development, they appear before other hair types. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Test yourself with the Integumentary System Flashcards== |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Integumentary_System_-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology_-_Flashcards#Hair_Flashcards|Hair Flashcards]] | |
| − | + | [[Integumentary_System_-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology_-_Flashcards#Ear_Flashcards|Ear Flashcards]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Integumentary System | + | [[Category:Integumentary System]] |
Revision as of 15:23, 22 August 2010
|
|
Development
Hair germs begin from an aggregation of keratinocytes in the stratum basale of the epidermis. The initiating factor is the underlying dermal fibroblast cells. The keratinocytes elongate, divide and relocate to the dermis. Dermal fibroblasts then form a dermal papilla beneath the hair germ. This causes stimulation of the basal stem cells to up-regulate their cycle, producing cells that will keratinise and form the hair shaft. Two swellings form on the shaft, one containing stem cells for follicle regeneration, the other becomes a sebaceous gland which will secrete sebum onto the hair shaft. The follicles develop from an ectodermal bud which invades the mesenchyme during embryonic development. The mesoderm also condenses during the development creating an outer mesodermal component to the embedded part of the hair.
Structure and Function
Hair Types
- Guard hairs
These are generally stiff and straight and form the outer haircoat of an animal. They are uniformly distributed across the skin surface and give the haircoat a smooth appearance. The smoothness of the coat is important in allowing rain to fall from the surface without penetrating deeper to the epidermis and causing loss of body temperature. The oily coating of the haircoat comes from the secretions of the sebaceous glands in the epidermis, associated with the hair follicle. This also contributes to the ‘waterproofing’ of the haircoat. Each hair consists of an outer cuticle, with a cortex and innermost medulla. It is composed of highly keratinised, dead epithelial cells, with the arrangement into the 3 layers conferring flexibility.
The arrector pili muscle is attached to the proximal end of the follicle and the dermis close to the point at which the hair is externalised. Involuntary contraction of this muscle in cold ambient temperatures causes erection of the hairs to trap warm air against the skin, thus providing insulation. This can also be induced by the ‘fight or flight’ mechanism of the sympathetic nervous system.
Hairs have a finite life span and are shed and replaced at varying frequencies, depending on species. The most noticeable is seasonal shedding and growth. An increase in ambient temperature causes a slowing of the growth of existing hairs. This is termed the catagen phase. Atrophy of the papillae and hair matrix occurs and growth ceases in the telogen phase. The follicle shortens, pushing the hair further from the surface. When growth resumes, the follicle retreats deeper into the epidermis, leaving the old hair unattached and thus it falls out. Anagen phase is where a new matrix produced and another hair grows in the place of the old one.
- Wool hairs
These are thin, wavy, soft hairs that form the undercoat of animals. They are often much more numerous than the tough guard hairs and usually shorter. Wool hairs often share a single follicle with guard hairs, although this is not common to all species.
- Tactile hairs
Tactile hairs are associated with a sensory function and are much thicker and stiffer than other hairs. They are mainly found on the face and can also be referred to as whiskers or vibrissae. Their follicles are much deeper into the subcutis than guard or wool hairs and possess a venous sinus and nerve endings with mechanoreceptors. During embryonic development, they appear before other hair types.