Difference between revisions of "Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{toplink |
| + | |backcolour =BCED91 | ||
| + | |linkpage =Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |linktext =Alimentary System | ||
| + | |maplink = | ||
| + | |subtext1=STOMACH AND ABOMASUM | ||
| + | |sublik1=Stomach and Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | The omasum is the third chamber in the ruminant stomach. It lies within the intrathoracic part of the abdomen so cannot be palpated manually. Instead it is examined by ausculation. The omasum has biphasic contractions which squeeze fluid out of the food before allowing the ingesta to continue into the [[Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology|abomasum]]. Absorption of [[Volatile Fatty Acids|volatile fatty acids]] continues in the omasum. | + | The omasum is the third chamber in the ruminant stomach. It lies within the intrathoracic part of the abdomen so cannot be palpated manually. Instead it is examined by ausculation. |
| + | |||
| + | The omasum has biphasic contractions which squeeze fluid out of the food before allowing the ingesta to continue into the [[The Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology|abomasum]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Absorption of [[Volatile Fatty Acids - Anatomy & Physioogy|volatile fatty acids]] continues in the omasum. | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | [[Image:Omasum Anatomy Sheep.jpg|thumb|right| | + | |
| − | + | [[Image:Omasum Anatomy Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Omasum Anatomy (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | |
| + | *Right of the midline | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[The Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|Rumen]] and [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] to the left, liver and body wall to the right | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Covered by lesser omentum | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Bilaterally flattened | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Ribs 8-11 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lower pole has an extensive connection to fundic region of the [[The Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology|abomasum]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Omasal canal present | ||
| + | **Known as the omasal groove | ||
| + | **Floor smooth except for low ridges and projections around the upper opening | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Opening to the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] at the cranial end of the omasal canal | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Opening to the [[The Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology|abomasum]] at the caudal end of the omasal canal. It is a large oval opening, partly covered by overhanging abomasal folds. | ||
| + | |||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | + | *Absorption | |
| + | |||
| + | *Food enters omasum at second biphasic reticular contraction | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Biphasic contractions | ||
| + | |||
| + | *First contraction expels fluid by squeezing the ingesta from the omasal canal between the lamellae | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Second contraction expels solids by mass contraction of the omasum | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Contractions are slower than the rumenoreticular contractions (see [[Rumination - Anatomy & Physiology|rumination]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Food squeezed between lamellae | ||
| + | |||
==Vasculature== | ==Vasculature== | ||
| − | + | *Cranial mesenteric artery | |
| + | |||
| + | *Caudal mesenteric artery | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Left gastric and left gastroepiploic arteries | ||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | + | *Dorsal vagus nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN X]]) (most important) | |
| + | |||
| + | *Ventral vagus nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN X]]) | ||
==Lymphatics== | ==Lymphatics== | ||
| − | + | *Numerous small lymph nodes are scattered in the omasal curvatures | |
| + | |||
| + | *The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the cardia and the omasum, then to the cistera chyli | ||
| + | |||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
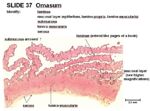
| − | [[Image:Omasum Histology Sheep.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Omasum Histology Sheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Omasum Histology (Sheep) - Copyright RVC 2008]] |
| − | + | *Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium | |
| + | |||
| + | *Lamellae thrown into leaves | ||
| + | **Different sizes | ||
| + | **Divides the lumen into narrow and uniform recesses | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Firm | ||
| + | |||
| + | *No glands | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Papillae | ||
| + | **Most small and lenticular | ||
| + | **Some large and [[Oral Cavity - Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology#Types of Papillae|conical]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cicrular tunica muscularis extends into papillae of long laminae | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lamina muscualris extends into papillae encircling tunica muscularis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *3 smooth muscle layers in papillae so they are very motile | ||
| − | |||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
===Small Ruminant=== | ===Small Ruminant=== | ||
| − | + | *Smaller omasum | |
| + | |||
| + | *Omasum is bean shaped | ||
===Bovine=== | ===Bovine=== | ||
| − | + | *Lower pole of omasum contacts the the abdominal floor below the costal arch | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Test yourself with the stomachs of the ruminant flashcards== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[The Stomachs of the Ruminant - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards#The Omasum|The Omasum Flashcards]] | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | + | [[The Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|The Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology]] | |
| + | |||
| + | [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[The Abomasum - Anatomy & Physiology|The Abomasum- Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Video''' |
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/bovine/Pot0052.mp4 Pot 52 Lateral view of the Abdomen of a young Ruminant] | |
| + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/bovine/pot0175.mp4 Pot 175 Sections of the Ruminant Stomach] | ||
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/ovine/Pot0047.mp4 Pot 47 Ovine Omasum and Abomasum] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/LeftSideTopography.mp4 Left sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen and Thorax] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/RightSideTopography.mp4 Right sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen] | |
| + | |||
| + | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Frean/sheep/RuminantStomachStructure.mp4 Structure of the ruminant forestomachs] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Alimentary System]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Alimentary | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 31 August 2010
|
|
Introduction
The omasum is the third chamber in the ruminant stomach. It lies within the intrathoracic part of the abdomen so cannot be palpated manually. Instead it is examined by ausculation.
The omasum has biphasic contractions which squeeze fluid out of the food before allowing the ingesta to continue into the abomasum.
Absorption of volatile fatty acids continues in the omasum.
Structure
- Right of the midline
- Covered by lesser omentum
- Bilaterally flattened
- Ribs 8-11
- Lower pole has an extensive connection to fundic region of the abomasum
- Omasal canal present
- Known as the omasal groove
- Floor smooth except for low ridges and projections around the upper opening
- Opening to the reticulum at the cranial end of the omasal canal
- Opening to the abomasum at the caudal end of the omasal canal. It is a large oval opening, partly covered by overhanging abomasal folds.
Function
- Absorption
- Food enters omasum at second biphasic reticular contraction
- Biphasic contractions
- First contraction expels fluid by squeezing the ingesta from the omasal canal between the lamellae
- Second contraction expels solids by mass contraction of the omasum
- Contractions are slower than the rumenoreticular contractions (see rumination)
- Food squeezed between lamellae
Vasculature
- Cranial mesenteric artery
- Caudal mesenteric artery
- Left gastric and left gastroepiploic arteries
Innervation
- Dorsal vagus nerve (CN X) (most important)
- Ventral vagus nerve (CN X)
Lymphatics
- Numerous small lymph nodes are scattered in the omasal curvatures
- The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the cardia and the omasum, then to the cistera chyli
Histology
- Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
- Lamellae thrown into leaves
- Different sizes
- Divides the lumen into narrow and uniform recesses
- Firm
- No glands
- Papillae
- Most small and lenticular
- Some large and conical
- Cicrular tunica muscularis extends into papillae of long laminae
- Lamina muscualris extends into papillae encircling tunica muscularis
- 3 smooth muscle layers in papillae so they are very motile
Species Differences
Small Ruminant
- Smaller omasum
- Omasum is bean shaped
Bovine
- Lower pole of omasum contacts the the abdominal floor below the costal arch
Test yourself with the stomachs of the ruminant flashcards
Links
The Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology
The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology
The Abomasum- Anatomy & Physiology
Video
Pot 52 Lateral view of the Abdomen of a young Ruminant
Pot 175 Sections of the Ruminant Stomach
Pot 47 Ovine Omasum and Abomasum
Left sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen and Thorax