Difference between revisions of "Stomatitis"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (40 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Introduction== | |
| − | |||
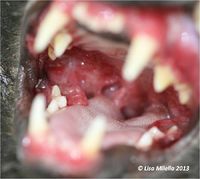
| − | + | [[File:Stomatitis.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Stomatitis in a cat <small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | |
| − | + | Stomatitis is the inflammation of the mucosa lining any structures within the mouth. This may include the lips, cheeks, [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] and [[Gingiva#Structure and Function of the Gingiva|gingiva]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | </ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Stomatitis is the inflammation of the mucosa lining any structures within the mouth. This may include the lips, cheeks, tongue and gingiva. | ||
Several different types of stomatitis have been described in the dog: | Several different types of stomatitis have been described in the dog: | ||
| − | + | Chronic ulcerative paradental stomatitis which is seen on the buccal mucosa that overlie the teeth, especially in the area of the maxillary canine tooth, fourth premolar and the lateral edge of the tongue. Severe ulceration can occur together with gingival recession. | |
| − | + | Ulcerative stomatitis which presents as ulcerations on the margins of the tongue that are common together with a secondary lip-fold dermatitis due to excessive salivation. | |
| − | + | Necrotizing stomatitis which is a very painful condition in dogs that may be caused by opportunistic invasion of normal oral flora. Suspected causative organisms include [[Fusobacterium necrophorum|''Fusobacterium'']] and [[:Category:Spirochaetes|spirochaetes]]. Invasion of these organisms is thought to be associated with reduced host resistance. | |
| − | + | Uraemic stomatitis which occurs as a result of [[uraemia]] due to renal disease. Severe stomatitis and ulceration of the oral mucosa as well as the margins of the tongue are seen with this condition. The lesions occur due to the bacterial degradation of urea to form ammonia together with dehydration and drying of the oral mucosa that results from renal disease. | |
Stomatitis in the cat: | Stomatitis in the cat: | ||
| − | + | Only one form of the disease which is [[Feline Lymphoplasmacytic Gingivitis Stomatitis Complex|Feline lymphoplasmacytic gingivitis stomatitis complex]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Signalment== | ||
| + | Both dogs and cats can develop this condition. | ||
| + | Breeds of dog predisposed include the Greyhound, Maltese, Cavalier King Charles, Miniature Schnauzer and Labrador Retriever. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| − | |||
===Clinical Signs=== | ===Clinical Signs=== | ||
| − | + | Include severe halitosis, hypersalivation, thick, ropey saliva, anorexia caused by pain, malaise, pyrexia, weight loss and ulceration and bleeding of the gingiva. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Oral Examination=== | ===Oral Examination=== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 35: | ||
===Biopsy=== | ===Biopsy=== | ||
| − | Often indicated to rule out other diseases such as [[ | + | Often indicated to rule out other diseases such as [[Pemphigus|pemphigus]] or other immunopathies. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Pathology=== | ||
| + | Starts as hyperaemia and oedema of the [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] or pharynx with mucoid exudate on the surface. | ||
| + | Lymphoid follicles on the [[Soft Palate|soft palate]] may enlarge and proliferate. | ||
| + | Often see white spots due to epithelial hyperplasia and increased mucous secretion, these can be scraped off to leave ordinary mucosa underneath. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment is both symptomatic to control the clinical signs as well as specific to the cause of the condition. The underlying cause should be sought and treated appropriately. | Treatment is both symptomatic to control the clinical signs as well as specific to the cause of the condition. The underlying cause should be sought and treated appropriately. | ||
| − | + | Thorough teeth cleaning is necessary as well as systemic [[Antibiotics|antibiotics]] (effective against aeobes and anaerobes). | |
| − | + | Oral rinses such as chlorhexidine may also be useful. | |
| − | + | [[Steroids|Corticosteriods]] have been suggested with cases of chronic ulcerative paradental stomatitis. | |
| − | + | Diet modification in cases of renal disease to reduce blood urea levels. | |
| − | + | Tooth extraction in the most severely affected area has been suggested. | |
| − | + | Resistent lesions in cats have been shown to respond to bovine lactoferrin in some cases. | |
| − | |||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
Depends on the underlying cause. | Depends on the underlying cause. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/Content/Disease/dis00627.asp, Ulcerative stomatitis] | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 17]] | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22Stomatitis%22)&fq=sc:%22ve%22 Stomatitis publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22stomatitis%22)+AND+od:(dogs) Stomatitis in dogs publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22stomatitis%22)+AND+od:(cats) Stomatitis in cats publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22stomatitis%22)+AND+od:(horses) Stomatitis in horses publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22stomatitis%22)+AND+od:(cattle) Stomatitis in cattle publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22stomatitis%22)+AND+od:(sheep) Stomatitis in sheep publications] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title:(%22stomatitis%22)+AND+od:(pigs) Stomatitis in pigs publications] | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | Merck & Co (2008) '''The Merck Veterinary Manual''' | |
| − | + | Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) '''Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition)''' ''Mosby Elsevier'' | |
| − | + | Tutt, C., Deeprose, J. and Crossley, D. (2007) '''BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dentistry (3rd Edition)''' ''BSAVA'' | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
| − | + | ==Webinars== | |
| − | === | + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/gastroenterology-and-nutrition/webinars/feed</rss> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Oral_Cavity_and_Gingiva_-_Pathology]] | [[Category:Oral_Cavity_and_Gingiva_-_Pathology]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Oral Diseases - Cat]][[Category:Oral Diseases - Dog]] |
| + | [[Category:Expert_Review - Small Animal]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Periodontal Conditions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:09, 9 January 2023
Introduction
Stomatitis is the inflammation of the mucosa lining any structures within the mouth. This may include the lips, cheeks, tongue and gingiva.
Several different types of stomatitis have been described in the dog: Chronic ulcerative paradental stomatitis which is seen on the buccal mucosa that overlie the teeth, especially in the area of the maxillary canine tooth, fourth premolar and the lateral edge of the tongue. Severe ulceration can occur together with gingival recession.
Ulcerative stomatitis which presents as ulcerations on the margins of the tongue that are common together with a secondary lip-fold dermatitis due to excessive salivation.
Necrotizing stomatitis which is a very painful condition in dogs that may be caused by opportunistic invasion of normal oral flora. Suspected causative organisms include Fusobacterium and spirochaetes. Invasion of these organisms is thought to be associated with reduced host resistance.
Uraemic stomatitis which occurs as a result of uraemia due to renal disease. Severe stomatitis and ulceration of the oral mucosa as well as the margins of the tongue are seen with this condition. The lesions occur due to the bacterial degradation of urea to form ammonia together with dehydration and drying of the oral mucosa that results from renal disease.
Stomatitis in the cat:
Only one form of the disease which is Feline lymphoplasmacytic gingivitis stomatitis complex.
Signalment
Both dogs and cats can develop this condition. Breeds of dog predisposed include the Greyhound, Maltese, Cavalier King Charles, Miniature Schnauzer and Labrador Retriever.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
Include severe halitosis, hypersalivation, thick, ropey saliva, anorexia caused by pain, malaise, pyrexia, weight loss and ulceration and bleeding of the gingiva.
Oral Examination
A thorough oral examination under general anaesthesia is often required to aid the diagnosis. Diagnosis is usually made by gross visualisation of the lesions. The mandibular lymph nodes may also be enlarged.
Laboratory Tests
Clinical pathology may be carried out to assess renal function in the case of uraemic stomatitis. Culture and sensitivity tests may be required to aid diagnosis and enable specific treatment.
Biopsy
Often indicated to rule out other diseases such as pemphigus or other immunopathies.
Pathology
Starts as hyperaemia and oedema of the tongue or pharynx with mucoid exudate on the surface. Lymphoid follicles on the soft palate may enlarge and proliferate. Often see white spots due to epithelial hyperplasia and increased mucous secretion, these can be scraped off to leave ordinary mucosa underneath.
Treatment
Treatment is both symptomatic to control the clinical signs as well as specific to the cause of the condition. The underlying cause should be sought and treated appropriately.
Thorough teeth cleaning is necessary as well as systemic antibiotics (effective against aeobes and anaerobes). Oral rinses such as chlorhexidine may also be useful. Corticosteriods have been suggested with cases of chronic ulcerative paradental stomatitis. Diet modification in cases of renal disease to reduce blood urea levels. Tooth extraction in the most severely affected area has been suggested. Resistent lesions in cats have been shown to respond to bovine lactoferrin in some cases.
Prognosis
Depends on the underlying cause.
| Stomatitis Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 17 |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Stomatitis publications
Stomatitis in dogs publications Stomatitis in cats publications Stomatitis in horses publications Stomatitis in cattle publications |
References
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual
Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition) Mosby Elsevier
Tutt, C., Deeprose, J. and Crossley, D. (2007) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dentistry (3rd Edition) BSAVA
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/gastroenterology-and-nutrition/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS