Difference between revisions of "East Coast Fever"
| (21 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
Also Known As: '''''[[Theileriosis - Cattle |Theileriosis]] — Corridor Disease — January Disease — [[Theileria|Theileria parva]] — Exotic Theileriosis — Zimbabwe Theileriosis — Fortuna Disease — Murimu wa ngai''''' (African) — '''''Ol tegana''''' (African) | Also Known As: '''''[[Theileriosis - Cattle |Theileriosis]] — Corridor Disease — January Disease — [[Theileria|Theileria parva]] — Exotic Theileriosis — Zimbabwe Theileriosis — Fortuna Disease — Murimu wa ngai''''' (African) — '''''Ol tegana''''' (African) | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
==Signalment== | ==Signalment== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Mainly cattle. Also possibly buffalo. | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
==Clinical Signs== | ==Clinical Signs== | ||
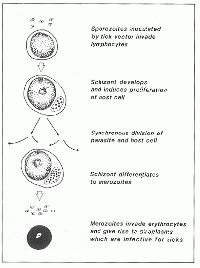
[[File:Theileria lifecycle.gif|thumb|200px|right|''Theileria'' lifecycle]] | [[File:Theileria lifecycle.gif|thumb|200px|right|''Theileria'' lifecycle]] | ||
| − | Early clinical signs include marked '''pyrexia''', '''leucopaenia''', ''' | + | Early clinical signs include marked '''pyrexia''', '''leucopaenia''', '''inappetence''', decrease in milk production, '''lymphadenopathy''' and '''palpably hot [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph nodes]]'''. |
As disease progresses, multisystemic signs develop: | As disease progresses, multisystemic signs develop: | ||
| − | '''Cardiovascular'''– Tachycardia, Petechiae and Ecchymoses, [[Anaemia]] | + | '''Cardiovascular''' – Tachycardia, Petechiae and Ecchymoses, possibly [[Anaemia]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''Respiratory''' - Nasal discharge, Dyspnoea, Cough |
| − | ''' | + | '''Gastrointestinal''' – [[Diarrhoea]] with mucus and/or blood, Inappetance, Hypomotility, Constipation |
| − | ''' | + | '''Opthalmological''' – Blindness, Corneal opacity, Discharge, Photophobia, Increased lacrimation |
| − | ''' | + | '''Reproductive''' – Abortion, Stillbirths, Agalactia |
| − | '''Other'''– Sudden death, [[Icterus]], Marked Pyrexia, Neurological signs, Emaciation | + | '''Other''' – Sudden death, [[Icterus]], Marked Pyrexia, Neurological signs, Emaciation |
The clinical phase usually lasts '''2-3 weeks''', but death occasionally occurs within a week. | The clinical phase usually lasts '''2-3 weeks''', but death occasionally occurs within a week. | ||
| − | Sub-lethal acute disease may be followed by complete recovery or continue as chronic emaciation and decreased productivity and performance. | + | Sub-lethal acute disease may be followed by complete recovery or more usually continue as chronic emaciation and decreased productivity and performance. |
===Corridor Disease=== | ===Corridor Disease=== | ||
| − | Acute and usually fatal form of East Coast Fever that occurs when ''T. parva'' is transmitted from '''African buffalo''' to cattle. Buffalo appear to be asymptomatic carriers | + | Acute and usually fatal form of East Coast Fever that occurs when ''T. parva'' is transmitted from '''African buffalo''' to cattle. Buffalo appear to be asymptomatic carriers. |
===January Disease=== | ===January Disease=== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 42: | ||
Also Known As – '''''Zimbabwe theileriosis''''' – '''''Fortuna disease''''' | Also Known As – '''''Zimbabwe theileriosis''''' – '''''Fortuna disease''''' | ||
| − | Acute '''strictly seasonal''' fatal form of ''T. parva'' in Zimbabwe. Occurs only from '''December to May''' due to the distribution of its vector, ''[[Rhipicephalus spp.|Rhipicephalus]] appendiculatus''. | + | Acute '''strictly seasonal''' fatal form of ''T. parva'' in Zimbabwe. Occurs only from '''December to May''', or more commonly January to March, due to the distribution of its vector, ''[[Rhipicephalus spp.|Rhipicephalus]] appendiculatus''. |
Chronic signs such as emaciation and diarrhoea are rarely seen in Corridor disease and January disease due to the short disease course before death. | Chronic signs such as emaciation and diarrhoea are rarely seen in Corridor disease and January disease due to the short disease course before death. | ||
| Line 51: | Line 49: | ||
On post-mortem examination, the lymphoid system is severely damaged and respiratory changes are marked. | On post-mortem examination, the lymphoid system is severely damaged and respiratory changes are marked. | ||
| − | Froth is often present in the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles due to pneumonia and pulmonary oedema. | + | Froth is often present in the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles due to pneumonia and pulmonary oedema. Necrosis of the lymphoid tissue may be seen. |
Lymph nodes and spleen may be hyperplastic. | Lymph nodes and spleen may be hyperplastic. | ||
The heart is commonly petechiated and ecchymotic. | The heart is commonly petechiated and ecchymotic. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 55: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| − | '''Buparvaquone/Parvaquone''' and '''Halofuginone''' chemotherapy drugs | + | '''Buparvaquone/Parvaquone''' and '''Halofuginone''' chemotherapy drugs can be effective but their cost often makes them prohibitive. |
| − | '''Tetracyclines''' | + | '''Tetracyclines''' may also be effective against schizonts. |
'''Immunisation''' with cryopreserved sporozoites is also possible but carries a risk of causing patent disease. | '''Immunisation''' with cryopreserved sporozoites is also possible but carries a risk of causing patent disease. | ||
==Control== | ==Control== | ||
| − | Vaccination with '''cryopreserved sporozoites''' derived from crushed ticks is possible but expensive and not without risks. | + | Vaccination with '''cryopreserved sporozoites''' derived from crushed ticks is possible but expensive and not without risks. Vaccination is followed by treatment with long acting oxytetracycline - the so called '''Infection and Treatment Method (ITM)'''. |
Control of tick vectors and use of tick resistant breeds is also valuable. | Control of tick vectors and use of tick resistant breeds is also valuable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[East Coast Fever Flashcards]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | + | {{CABI source | |
| + | |datasheet = [http://www.cabi.org/ahpc/?compid=3&dsid=62109&loadmodule=datasheet&page=2144&site=160 East Coast fever] | ||
| + | |date =2 June 2011 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Nick Lyons | ||
| + | |date = 25 March 2012 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Lymphoreticular and Haematopoietic Diseases - Cattle]] | [[Category:Lymphoreticular and Haematopoietic Diseases - Cattle]] | ||
| − | [[Category:CABI Expert Review]] | + | [[Category:CABI Expert Review Completed]][[Category:CABI AHPC Pages]] |
| + | [[Category:Nick Lyons reviewed]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:54, 17 August 2012
Also Known As: Theileriosis — Corridor Disease — January Disease — Theileria parva — Exotic Theileriosis — Zimbabwe Theileriosis — Fortuna Disease — Murimu wa ngai (African) — Ol tegana (African)
Introduction
East Coast fever is a form of theileriosis caused by Theileria parva.
Signalment
Mainly cattle. Also possibly buffalo.
Distribution
Mainly in tropical regions due to reliance upon tick vectors.
Clinical Signs
Early clinical signs include marked pyrexia, leucopaenia, inappetence, decrease in milk production, lymphadenopathy and palpably hot lymph nodes. As disease progresses, multisystemic signs develop:
Cardiovascular – Tachycardia, Petechiae and Ecchymoses, possibly Anaemia
Respiratory - Nasal discharge, Dyspnoea, Cough
Gastrointestinal – Diarrhoea with mucus and/or blood, Inappetance, Hypomotility, Constipation
Opthalmological – Blindness, Corneal opacity, Discharge, Photophobia, Increased lacrimation
Reproductive – Abortion, Stillbirths, Agalactia
Other – Sudden death, Icterus, Marked Pyrexia, Neurological signs, Emaciation
The clinical phase usually lasts 2-3 weeks, but death occasionally occurs within a week.
Sub-lethal acute disease may be followed by complete recovery or more usually continue as chronic emaciation and decreased productivity and performance.
Corridor Disease
Acute and usually fatal form of East Coast Fever that occurs when T. parva is transmitted from African buffalo to cattle. Buffalo appear to be asymptomatic carriers.
January Disease
Also Known As – Zimbabwe theileriosis – Fortuna disease
Acute strictly seasonal fatal form of T. parva in Zimbabwe. Occurs only from December to May, or more commonly January to March, due to the distribution of its vector, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus.
Chronic signs such as emaciation and diarrhoea are rarely seen in Corridor disease and January disease due to the short disease course before death.
Diagnosis
On post-mortem examination, the lymphoid system is severely damaged and respiratory changes are marked. Froth is often present in the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles due to pneumonia and pulmonary oedema. Necrosis of the lymphoid tissue may be seen. Lymph nodes and spleen may be hyperplastic. The heart is commonly petechiated and ecchymotic. Petechiae may also be seen throughout the intestines and abomasums in ruminants.
Treatment
Buparvaquone/Parvaquone and Halofuginone chemotherapy drugs can be effective but their cost often makes them prohibitive.
Tetracyclines may also be effective against schizonts.
Immunisation with cryopreserved sporozoites is also possible but carries a risk of causing patent disease.
Control
Vaccination with cryopreserved sporozoites derived from crushed ticks is possible but expensive and not without risks. Vaccination is followed by treatment with long acting oxytetracycline - the so called Infection and Treatment Method (ITM).
Control of tick vectors and use of tick resistant breeds is also valuable.
| East Coast Fever Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
East Coast Fever Flashcards |
References

|
This article was originally sourced from The Animal Health & Production Compendium (AHPC) published online by CABI during the OVAL Project. The datasheet was accessed on 2 June 2011. |
| This article has been expert reviewed by Nick Lyons MA VetMB CertCHP MRCVS Date reviewed: 25 March 2012 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt698caaaf4f4f43_10482728 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt698caaaf5684a3_28645315 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt698caaaf5c5985_12073544
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |