Difference between revisions of "Cytology Q&A 12"
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Template:Manson}} | + | {{Template:Manson |
| + | |book = Cytology Q&A}} | ||
| − | [[Image:|centre|500px]] | + | [[Image:Cytology 12.JPG|centre|500px]] |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
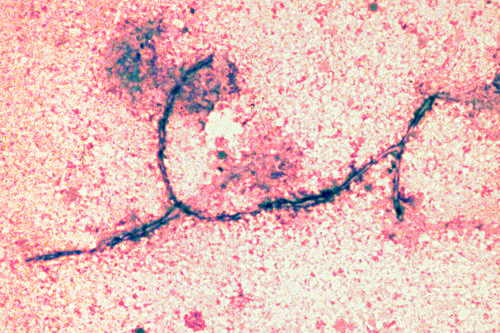
The microphotograph illustrates a hyphal structure compatible with Aspergillus species. Nasal aspergillosis is therefore the likely diagnosis.<br><br> | The microphotograph illustrates a hyphal structure compatible with Aspergillus species. Nasal aspergillosis is therefore the likely diagnosis.<br><br> | ||
This infection is more common in dogs than in cats, particularly long-nosed breeds (e.g. Collies). | This infection is more common in dogs than in cats, particularly long-nosed breeds (e.g. Collies). | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1=Aspergillosis |
|q2=What other diagnostic tests can be performed to support this diagnosis? | |q2=What other diagnostic tests can be performed to support this diagnosis? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
It should be noted that for cytological examination, material obtained via a nasal flush or biopsy is preferred to nasal secretions, which may not contain the organism. | It should be noted that for cytological examination, material obtained via a nasal flush or biopsy is preferred to nasal secretions, which may not contain the organism. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2=Aspergillosis#Diagnosis |
|q3=What treatment can be recommended? | |q3=What treatment can be recommended? | ||
|a3=Oral fluconazole or itraconazole can be administered; topical infusion of an antifungal drug such as clotrimazole has been shown to be effective in dogs, and may clear infections more successfully than systemic therapy. <br><br> | |a3=Oral fluconazole or itraconazole can be administered; topical infusion of an antifungal drug such as clotrimazole has been shown to be effective in dogs, and may clear infections more successfully than systemic therapy. <br><br> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
Nasal flushings can be very frustrating because they may reflect nonspecific inflammation and may not contain diagnostic features. Client education regarding the possibility of a nonrepresentative specimen and the possible need to progress to nasal biopsy is recommended. <br><br> | Nasal flushings can be very frustrating because they may reflect nonspecific inflammation and may not contain diagnostic features. Client education regarding the possibility of a nonrepresentative specimen and the possible need to progress to nasal biopsy is recommended. <br><br> | ||
Nasal biopsy specimens taken from multiple locations may be needed and aggressive sampling is recommended to obtain specimens that will give the clinician and pathologist confidence in making a diagnosis. | Nasal biopsy specimens taken from multiple locations may be needed and aggressive sampling is recommended to obtain specimens that will give the clinician and pathologist confidence in making a diagnosis. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3=Aspergillosis#Treatment |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 27 September 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Cytology Q&A. |
A 13-year old neutered male DSH cat presents with inspiratory dyspnoea, frequent sneezing, congestion, weight loss and partial anorexia of three months’ duration. Physical examination reveals bilateral mucopurulent nasal discharge. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid has been administered unsuccessfully. Vaccinations are up-to-date and the cat is free roaming. A smear is prepared from a nasal flush (Wright’s, ×40). Cranial radiographs do not reveal any osteolytic lesions or evidence of a mass.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is your diagnosis based on cytological observation? | The microphotograph illustrates a hyphal structure compatible with Aspergillus species. Nasal aspergillosis is therefore the likely diagnosis. |
Link to Article | |
| What other diagnostic tests can be performed to support this diagnosis? |
|
Link to Article | |
| What treatment can be recommended? | Oral fluconazole or itraconazole can be administered; topical infusion of an antifungal drug such as clotrimazole has been shown to be effective in dogs, and may clear infections more successfully than systemic therapy. Note: Aspergillus organisms in cytological preparations are usually observed as uniform, septate hyphae of 3–6 microns in width with 45-degree angle (dichotomous) branching. |
Link to Article | |