Difference between revisions of "Hard Palate"
(→Links) |
(→Links) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | Click here for the [[Cleft Palate|Pathology of Cleft Palate]] | + | Click here for the [[Cleft Palate|Pathology of Cleft Palate]] |
| + | |||
{{OpenPages}} | {{OpenPages}} | ||
[[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:54, 7 May 2016
Overview
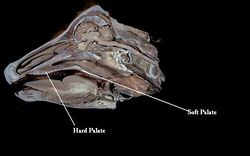
The hard palate (palatum durum) forms the rostral roof of the oral cavity. It merges caudally with the soft palate where a connective tissue aponeurosis replaces the bone.
Structure and Function
The hard palate is the bony shelf of the palatine processes of the incisive, maxillary and palatine bones. Failure of the palatine bones to fuse results in cleft palate. There are 6-8 fixed transverse ridges to direct food caudally. The hard palate is flat and has incisive papilla (small median swelling) behind the incisive teeth and smaller papillae ducts branching to the nasal cavity and vomeronasal organ.
Histology
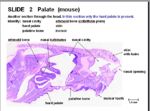
The palate is formed by thick mucosa and keratinised stratified squamous epithelium.
Species Differences
Herbivores
Herbivores have a more heavily keratinised hard palate.
Feline
Felines have short a hard palate.
Links
Click here for the Pathology of Cleft Palate
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a459e69b0764_85886991 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a459e6a22552_71566546 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a459e6a82bd9_26862037
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |