Difference between revisions of "Parascaris equorum"
(Created page with '=== ''PARASCARIS EQUORUM'' === ==== General ==== *Ascarid, small intestine. *Mostly in young horses, especially foals <6months old. ==== Morphology ==== *Stout worms, up to 50cm…') |
|||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | |
| − | ==== | + | {{Taxobox |
| − | + | |name = ''Parascaris equorum | |
| − | + | |kingdom = | |
| + | |phylum = | ||
| + | |class = [[Nematodes|Nematoda]] | ||
| + | |sub-class = | ||
| + | |order = | ||
| + | |super-family = [[:Category:Ascaridoidea|Ascaridoidea]] | ||
| + | |family = | ||
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus = | ||
| + | |species = ''Parascaris equorum | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==Introduction== |
| − | + | [[Image:Parascaris equorum.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Parascaris equorum'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | |
| − | + | [[Image:Parascaris equorum2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Parascaris equorum'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | |
| + | [[Image:Parascaris equorum3.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Parascaris equorum'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Parascaris equorum4.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Parascaris equorum'' - Joaquim Castellà Veterinary Parasitology Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona]] | ||
| + | ''P. equorum'' is a [[Nematodes|nematode]] that primarily affects younger horses, usually under two years of age, as their immune response is not as developed as older horses. | ||
| − | + | Predilection site: '''Small intestine | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ==Hosts== |
| − | + | Horses and donkeys. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Identification== |
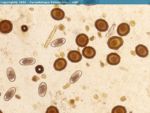
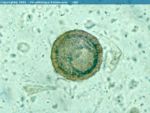
| − | '' | + | ''P. equorum'' is a large stout nematode, with the female capable of growing up to 40cm in length. The adults have a mouth surrounded by three large lips. The egg is spherical, brown and has a thick outer shell. |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Life-Cycle == | |
| − | + | The adults live unattached in the small intestine. In heavy infections, they may form large balls, which can cause intestinal obstruction. Under optimal conditions L2 can develop in 14 days. The host ingests the embryonated egg. L2 larvae then pass through the intestinal wall, and transform into L3. The larvae then migrate to the liver via the hepatic portal vein, where they stay for around a week. They enter the vena cava and travel to the pulmonary alveoli, where they transform to L4. | |
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | The larvae travel up bronchi to the trachea and are coughed up and swallowed. Finally they return to the stomach and small intestine, where they mature into adults. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The prepatent period of ''P. equorum'' is 10-16 weeks. | |
| + | |||
| + | May cause [[Ascarid Impaction - Horse|'''Ascarid Impaction''']] in horses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Horse_Nematode_Flashcards|Horse Nematode Flashcards]] | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=%22Parascaris+equorum%22&occuring1=title&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&x=32&y=11&publishedstart=yyyy&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all ''Parascaris equorum'' publications] | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/search?s=nematode Nematodes] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Ascaridoidea]][[Category:Horse_Nematodes]] | [[Category:Ascaridoidea]][[Category:Horse_Nematodes]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Respiratory Parasitic Infections]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:49, 4 June 2016
| Parascaris equorum | |
|---|---|
| Class | Nematoda |
| Super-family | Ascaridoidea |
| Species | Parascaris equorum |
Introduction
P. equorum is a nematode that primarily affects younger horses, usually under two years of age, as their immune response is not as developed as older horses.
Predilection site: Small intestine
Hosts
Horses and donkeys.
Identification
P. equorum is a large stout nematode, with the female capable of growing up to 40cm in length. The adults have a mouth surrounded by three large lips. The egg is spherical, brown and has a thick outer shell.
Life-Cycle
The adults live unattached in the small intestine. In heavy infections, they may form large balls, which can cause intestinal obstruction. Under optimal conditions L2 can develop in 14 days. The host ingests the embryonated egg. L2 larvae then pass through the intestinal wall, and transform into L3. The larvae then migrate to the liver via the hepatic portal vein, where they stay for around a week. They enter the vena cava and travel to the pulmonary alveoli, where they transform to L4.
The larvae travel up bronchi to the trachea and are coughed up and swallowed. Finally they return to the stomach and small intestine, where they mature into adults.
The prepatent period of P. equorum is 10-16 weeks.
May cause Ascarid Impaction in horses.
| Parascaris equorum Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Horse Nematode Flashcards |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Parascaris equorum publications |
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt698d8fe3c31c22_48015061 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt698d8fe3e07a22_89896839 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt698d8fe404b5a5_25726026
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |