Difference between revisions of "Pseudomonas species - Overview"
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| + | {{Taxobox | ||
| + | |name =''Pseudomonas'' | ||
| + | |phylum =Proteobacteria | ||
| + | |class =Gamma Proteobacteria | ||
| + | |order =Pseudomonadales | ||
| + | |family =Pseudomonadaceae | ||
| + | |genus =Pseudomonas | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | [[File:Pseudomonas.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center> | + | |
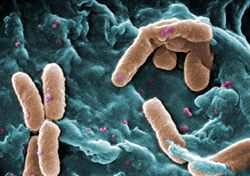
| + | [[File:Pseudomonas.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center> Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a number of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' bacteria.( Janice Haney Carr 2008, Wikimedia commons)</center></small>]] | ||
The ''Pseudomonas'' species are Gram-negative rods. They are obligate aerobes and are oxidase and catalase positive. | The ''Pseudomonas'' species are Gram-negative rods. They are obligate aerobes and are oxidase and catalase positive. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 17: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | Krieg, Noel (1984). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume 1. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. [[ | + | Krieg, Noel (1984). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume 1. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. |
| − | [[Category: | + | |
| + | <big>'''[[:Category:Pseudomonas and Burkholderia species|See here for a list of ''Pseudomonas'' species]]'''</big> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Pseudomonas_and_Burkholderia_species|D]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:40, 18 July 2012
| Pseudomonas | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Proteobacteria |
| Class | Gamma Proteobacteria |
| Order | Pseudomonadales |
| Family | Pseudomonadaceae |
| Genus | Pseudomonas |
The Pseudomonas species are Gram-negative rods. They are obligate aerobes and are oxidase and catalase positive.
The Pseudomonas species are motile by polar flagellae and cause opportunistic infections. Most Pseudomonas species are resistant to antibiotics due to their efflux pumps, which pump out the antibiotics before they can act. They contain porins in their cell wall that allows them to survive harsh conditions.
References
Krieg, Noel (1984). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume 1. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
See here for a list of Pseudomonas species
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a30d097b8039_50488360 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a30d098c3c95_05203489 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a30d099ad3b8_08635498
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |