Difference between revisions of "Jejunum - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
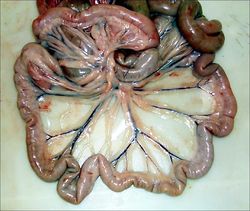
[[Image:jejunumphoto.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Jejunum(Dog) - © RVC 2008]] | [[Image:jejunumphoto.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Jejunum(Dog) - © RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | + | Jejunum occupies the ventral part of the abdominal cavity, filling those parts that are not occupied by other viscera. This produces species variation (see [[#Species Differences|species differences]]). It lies on the abdominal floor, separated from the parietal [[Peritoneal Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|peritoneum]] by the greater omentum. It is suspended by the mesentery (mesojejunum). This conveys the blood vessels and nerves and houses lymph nodes. The mesentery converges to its root. This is where the cranial mesenteric artery branches off from the aorta. | |
==Vasculature== | ==Vasculature== | ||
| − | The cranial mesenteric artery, a branch of the abdominal aorta, supplies blood to the jejunum, [[Ileum - Anatomy & Physiology|ileum]], [[Caecum - Anatomy & Physiology|caecum]], [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|ascending colon]] and part of the [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|transverse colon]]. It branches greatly within the | + | The cranial mesenteric artery, a branch of the abdominal aorta, supplies blood to the jejunum, [[Ileum - Anatomy & Physiology|ileum]], [[Caecum - Anatomy & Physiology|caecum]], [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|ascending colon]] and part of the [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|transverse colon]]. It branches greatly within the mesentery of the jejunum. There are many anastomoses within the mesentery, which ensure that the intestine can survive even if a major division of the cranial mesenteric artery is damaged. The cranial mesenteric vein drains blood from the jejunum and enters the portal vein. It is rich in the products of digestion following a meal. The portal vein enters the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]]. |
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
===Ruminant=== | ===Ruminant=== | ||
| − | The jejunum is pushed entirely to the right side of the abdomen by the [[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]] which is on the left. Coils of the jejunum usually lie within the supraomental recess; although this can vary between individuals depending on fullness of the [[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]] and size of the [[ | + | The jejunum is pushed entirely to the right side of the abdomen by the [[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]] which is on the left. Coils of the jejunum usually lie within the supraomental recess; although this can vary between individuals depending on fullness of the [[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]] and size of the [[Uterus - Anatomy & Physiology|uterus]]. |
===Porcine=== | ===Porcine=== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Click here for information on [[Intestines, Small and Large - Pathology|pathology of the Small and Large Intestines]]''' | '''Click here for information on [[Intestines, Small and Large - Pathology|pathology of the Small and Large Intestines]]''' | ||
| − | + | {{Template:Learning | |
| − | + | |flashcards = [[Jejunum - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards|Jejunum anatomy]] | |
| − | + | |videos = [[Video: Ruminant small and large intestine potcast|Ruminant small and large intestine potcast]]<br>[[Video: Ruminant abdomen potcast|Ruminant abdomen potcast]]<br>[[Video: Foal gastrointestinal tract potcast|Foal gastrointestinal tract potcast]]<br>[[Video: Lateral view of the feline thorax and abdomen potcast|Lateral view of the feline thorax and abdomen potcast]]<br>[[Video: Female dog abdomen dissection|Female dog abdomen dissection]]<br>[[Video: Abdominal viscera of the horse dissection|Abdominal viscera of the horse dissection]]<br>[[Video: Equine left-sided abdominal and thoracic topography dissection|Equine left-sided abdominal and thoracic topography dissection]]<br>[[Video: Equine left-sided abdominal and thoracic topography dissection 2|Equine left-sided abdominal and thoracic topography dissection 2]]<br>[[Video: Ovine large and small intestine dissection|Ovine large and small intestine dissection]]<br>[[Video: Porcine abdomen dissection|Porcine abdomen dissection]] | |
| − | + | |powerpoints = [[Gastrointestinal Tract Histology resource|Histology of the jejunum - see part 1]] | |
| − | + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/Content/Disease/dis02601.asp Ileus] | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Webinars== | ||
| + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/gastroenterology-and-nutrition/webinars/feed</rss> | ||
[[Category:Small Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Small Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:A&P Done]] |
Latest revision as of 15:08, 4 January 2023
Introduction
The jejunum continues from the duodenum and leads into the ileum. It is the longest part of the small intestine and is highly coiled. It has digestive and absorptive functions.
Structure
Jejunum occupies the ventral part of the abdominal cavity, filling those parts that are not occupied by other viscera. This produces species variation (see species differences). It lies on the abdominal floor, separated from the parietal peritoneum by the greater omentum. It is suspended by the mesentery (mesojejunum). This conveys the blood vessels and nerves and houses lymph nodes. The mesentery converges to its root. This is where the cranial mesenteric artery branches off from the aorta.
Vasculature
The cranial mesenteric artery, a branch of the abdominal aorta, supplies blood to the jejunum, ileum, caecum, ascending colon and part of the transverse colon. It branches greatly within the mesentery of the jejunum. There are many anastomoses within the mesentery, which ensure that the intestine can survive even if a major division of the cranial mesenteric artery is damaged. The cranial mesenteric vein drains blood from the jejunum and enters the portal vein. It is rich in the products of digestion following a meal. The portal vein enters the liver.
Species Differences
The position of the jejunum is variable between species as it lies in that part of the abdomen not occupied by other viscera.
Canine
The jejunum lies roughly symmetrically about the midline. It contacts the liver, stomach and spleen cranially and urinary bladder ventrally.
Equine
The jejunum is confined to the left dorsal part of the abdomen. It is restricted to this position by the large caecum on the right, and ascending colon ventrally on both sides.
Ruminant
The jejunum is pushed entirely to the right side of the abdomen by the rumen which is on the left. Coils of the jejunum usually lie within the supraomental recess; although this can vary between individuals depending on fullness of the rumen and size of the uterus.
Porcine
The jejunum lies in the caudoventral aspect of the abdominal cavity, mainly to the right of the midline. This is due to the presence of the ascending colon on the left.
Links
Click here for information on pathology of the Small and Large Intestines
| Jejunum - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Jejunum anatomy |
 Selection of relevant videos |
Ruminant small and large intestine potcast Ruminant abdomen potcast Foal gastrointestinal tract potcast Lateral view of the feline thorax and abdomen potcast Female dog abdomen dissection Abdominal viscera of the horse dissection Equine left-sided abdominal and thoracic topography dissection Equine left-sided abdominal and thoracic topography dissection 2 Ovine large and small intestine dissection Porcine abdomen dissection |
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology of the jejunum - see part 1 |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/gastroenterology-and-nutrition/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS