Difference between revisions of "Taenia solium"
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | |||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
|name = ''Taenia solium | |name = ''Taenia solium | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
==Hosts== | ==Hosts== | ||
| − | '''Intermediate host''': Pig, and | + | '''Intermediate host''': Pig (natural intermediate host), man (accidental intermediate host) and very exceptionally the dog. |
'''Definitive host''': Man. | '''Definitive host''': Man. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 25: | ||
==Life Cycle== | ==Life Cycle== | ||
| − | The life-cycle is similar to that of [[Taenia saginata|''T. saginata'']], except now the pig is the intermediate host. Gravid segments, containing the parasite eggs are passed in faeces. The oncospheres are then ingested by the intermediate host, in this case the pig, and pass into the blood system, infecting striated muscles. The cysticerci may also develop in the | + | The life-cycle is similar to that of [[Taenia saginata|''T. saginata'']], except now the pig is the intermediate host. Gravid segments, containing the parasite eggs are passed in faeces. The oncospheres are then ingested by the intermediate host, in this case the pig, and pass into the blood system, infecting striated muscles. The cysticerci may also develop in the lungs, liver, kidney and the brain. Like ''T. saginata'', humans, which are the definitive hosts, become infected via ingestion of poorly cooked meat containing viable cysticerci. |
| + | Contrary to ''T. saginata'', humans can also act as intermediate host. Cysticerci can develop in several tissues, including the central nervous system, causing neurocysticercosis in man. | ||
| − | == | + | {{Learning |
| + | |flashcards = [[Cestodes_Flascards|Cestodes Flashcards]] | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=title:(%22Taenia+solium%22)+OR+title:(%22Cysticercus+cellulosae%22)+&occuring1=freetext&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&publishedstart=2000&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all&x=48&y=8 ''Taenia solium'' publications since 2000] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ==References== | |
| + | Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) '''Veterinary Parasitology''' ''Blackwell Publishing'' | ||
| − | + | Ito A et al. Dogs as alternative intermediate hosts of ''Taenia solium'' in Papua (Irian Jaya), Indonesia confirmed by highly specific ELISA and immunoblot using native and recombinant antigens and mitochondrial DNA analysis. J Helminthol. 2002 Dec;76(4):311-4. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{OpenPages}} | |
| − | |||
[[Category:Taeniidae]] | [[Category:Taeniidae]] | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Zoonoses]] | |
| − | |||
[[Category:Expert_Review]] | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:46, 18 July 2012
| Taenia solium | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Platyhelminthes |
| Class | Cestoda |
| Order | Cyclophyllidea |
| Family | Taeniidae |
| Genus | Taenia |
| Species | T. solium |
Also known as: Cysticercus cellulosae — Human pork tapeworm
Hosts
Intermediate host: Pig (natural intermediate host), man (accidental intermediate host) and very exceptionally the dog.
Definitive host: Man.
Identification
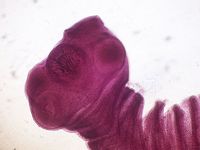
The adults are 3-5m in length, have a scolex, and several rows of hooks.
Life Cycle
The life-cycle is similar to that of T. saginata, except now the pig is the intermediate host. Gravid segments, containing the parasite eggs are passed in faeces. The oncospheres are then ingested by the intermediate host, in this case the pig, and pass into the blood system, infecting striated muscles. The cysticerci may also develop in the lungs, liver, kidney and the brain. Like T. saginata, humans, which are the definitive hosts, become infected via ingestion of poorly cooked meat containing viable cysticerci. Contrary to T. saginata, humans can also act as intermediate host. Cysticerci can develop in several tissues, including the central nervous system, causing neurocysticercosis in man.
| Taenia solium Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Cestodes Flashcards |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Taenia solium publications since 2000 |
References
Taylor, M.A, Coop, R.L., Wall,R.L. (2007) Veterinary Parasitology Blackwell Publishing
Ito A et al. Dogs as alternative intermediate hosts of Taenia solium in Papua (Irian Jaya), Indonesia confirmed by highly specific ELISA and immunoblot using native and recombinant antigens and mitochondrial DNA analysis. J Helminthol. 2002 Dec;76(4):311-4.
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a13db941b277_08426422 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a13db94a7285_59967589 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a13db9523181_76610969
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |