Difference between revisions of "Aelurostrongylus abstrusus"
m (Text replace - "Category:To_Do_-_Max" to "") |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | |||
Also known as: '''''Cat lungworm | Also known as: '''''Cat lungworm | ||
| + | Causes: '''''Aelurostrongylosis''''' | ||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
|name = ''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus | |name = ''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|species =''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus | |species =''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | Aelurostrongylosis is the disease caused by the cat lungworm ''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus'', which is found in many parts of Europe, the USA and Australia. | ||
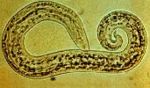
[[Image:Aeurostrongylus abstrusus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Aeurostrongylus abstrusus'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | [[Image:Aeurostrongylus abstrusus.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Aeurostrongylus abstrusus'' - Courtesy of the Laboratory of Parasitology, University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine]] | ||
==Hosts== | ==Hosts== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
==Life Cycle== | ==Life Cycle== | ||
| − | This is an indirect lifecyle, involving two intermediate hosts, and a definitive host. | + | This is an indirect lifecyle, involving two intermediate hosts, and a definitive host. The female is ovo-viviparous, and passes L1 within the host faeces. The L1 then infect the molluscs, and later develop into L2, then infective L3. The paratenic host ingests the molluscs. The cat, acting as the definitive host then ingests the L3, and becomes infected with the parasite. |
| + | |||
| + | The larvae then travel to the lungs via the lymphatic system or the bloodstream. These can be seen as nodules on the lungs. They then hatch out, and are coughed up and swallowed. The parasite enters the alimentary tract, and is passed out in the faeces. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The parasite affects pulmonary parenchyma and causes aelurostrongylosis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Clinical Signs== | ||
| + | The disease is often '''asymptomatic''', and serious respiratory problems usually occur due to a deficient immunity, following [[FIV]] infection for example. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Respiratory signs are usually '''progressive and worstening'''. Heavy infections can cause '''severe bronchopneumonia''', with cats presenting with '''open-mouth breathing''' and abdominal effort. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There might also be '''coughing and sneezing''' and systemic signs such as '''anorexia, lethargy and wasting'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| + | '''Radiography''' may reveal a diffuse interstitial pattern with focal peribronchial densities. An alveolar pattern may appear in severe cases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bronchial lavage''' may reveal characteristic coiled larvae with an undulating tail and spine and eosinophilic inflammation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Haematology''' may reveal [[eosinophilia]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Post mortem examination''' may reveal greenish nodules in the lungs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Microscopically, eggs and larvae in the alveolar spaces cause a foreign body type reaction (surrounded by mononuclear cells and giant cells). There is submucosal gland hypertrophy and smooth muscle hypertrophy in airway and vessel walls. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Treatment and Prevention== | ||
| + | Treatment is difficult and '''not often necessary''' unless the cat is showing clinical signs, as the disease is usually self-limiting. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Fenbendazole''' for 21 consecutive days is usually effective. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Imidacloprid with moxidectin''', '''emodepsid''', and '''selamectin are also effective''' according to Sandra Sawchuk's capsule report <ref>Sawchuk, S (2014) Best Practices for Lungworm Prevention & Treatment in Clinician's Brief, volume 12 number 1, January 2014, p 54</ref>, which reviews a selamectin lungworm efficacy study.<ref>Iannino F, Iannetti L, Paganico D, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of selamectin spot-on in cats infested with ''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus'' (Strongylida, Filariodidae) in a Central Italy cat shelter. ''Vet Parasitol'' 2013;197:258-262. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23743419 PubMed link ]</ref> ) | ||
| − | + | Ivermectin has also been used in some cases. | |
| − | + | '''Control''' is only by prevention of hunting by cats. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Cytology Q&A 05]] | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=%22Aelurostrongylus+abstrusus%22&occuring1=title&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&x=57&y=15&publishedstart=yyyy&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all ''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus'' publications] | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/search?s=nematode Nematodes] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ==References== | |
| − | + | <references /> | |
| − | |||
| + | * Merck and Co (2008) '''Merck veterinary Manual''' ''Merial'' | ||
| + | * Bowman, D. (2002) '''Feline Clinical Parasitology''' ''Wiley-Blackwell'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Expert Review - Small Animal]] | ||
[[Category:Angiostrongylidae]][[Category:Cat_Nematodes]] | [[Category:Angiostrongylidae]][[Category:Cat_Nematodes]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:46, 4 June 2016
Also known as: Cat lungworm
Causes: Aelurostrongylosis
| Aelurostrongylus abstrusus | |
|---|---|
| Class | Nematoda |
| Super-family | Metastrongyloidea |
| Family | Angiostrongylidae |
| Species | Aelurostrongylus abstrusus |
Introduction
Aelurostrongylosis is the disease caused by the cat lungworm Aelurostrongylus abstrusus, which is found in many parts of Europe, the USA and Australia.
Hosts
Intermediate hosts: Molluscs, including snails and slugs, as well as paratenic hosts, including rodents, birds, amphibians, and reptiles.
Definitive host: Cat.
Identification
A. abstrusus are small parasites of the family Angiostrongylidae, measuring around 1cm in length. The worms are long and thing, and the male has a bursa, but it is small and poorly developed.
Life Cycle
This is an indirect lifecyle, involving two intermediate hosts, and a definitive host. The female is ovo-viviparous, and passes L1 within the host faeces. The L1 then infect the molluscs, and later develop into L2, then infective L3. The paratenic host ingests the molluscs. The cat, acting as the definitive host then ingests the L3, and becomes infected with the parasite.
The larvae then travel to the lungs via the lymphatic system or the bloodstream. These can be seen as nodules on the lungs. They then hatch out, and are coughed up and swallowed. The parasite enters the alimentary tract, and is passed out in the faeces.
The parasite affects pulmonary parenchyma and causes aelurostrongylosis.
Clinical Signs
The disease is often asymptomatic, and serious respiratory problems usually occur due to a deficient immunity, following FIV infection for example.
Respiratory signs are usually progressive and worstening. Heavy infections can cause severe bronchopneumonia, with cats presenting with open-mouth breathing and abdominal effort.
There might also be coughing and sneezing and systemic signs such as anorexia, lethargy and wasting.
Diagnosis
Radiography may reveal a diffuse interstitial pattern with focal peribronchial densities. An alveolar pattern may appear in severe cases.
Bronchial lavage may reveal characteristic coiled larvae with an undulating tail and spine and eosinophilic inflammation.
Haematology may reveal eosinophilia.
Post mortem examination may reveal greenish nodules in the lungs.
Microscopically, eggs and larvae in the alveolar spaces cause a foreign body type reaction (surrounded by mononuclear cells and giant cells). There is submucosal gland hypertrophy and smooth muscle hypertrophy in airway and vessel walls.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment is difficult and not often necessary unless the cat is showing clinical signs, as the disease is usually self-limiting.
Fenbendazole for 21 consecutive days is usually effective.
Imidacloprid with moxidectin, emodepsid, and selamectin are also effective according to Sandra Sawchuk's capsule report [1], which reviews a selamectin lungworm efficacy study.[2] )
Ivermectin has also been used in some cases.
Control is only by prevention of hunting by cats.
| Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Cytology Q&A 05 |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus publications |
References
- ↑ Sawchuk, S (2014) Best Practices for Lungworm Prevention & Treatment in Clinician's Brief, volume 12 number 1, January 2014, p 54
- ↑ Iannino F, Iannetti L, Paganico D, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of selamectin spot-on in cats infested with Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Strongylida, Filariodidae) in a Central Italy cat shelter. Vet Parasitol 2013;197:258-262. PubMed link
- Merck and Co (2008) Merck veterinary Manual Merial
- Bowman, D. (2002) Feline Clinical Parasitology Wiley-Blackwell
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a19e84d1ff60_40256448 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a19e84dd8c28_30301420 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a19e84e2aaa4_94050821
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |