Difference between revisions of "Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology"
(→Links) |
|||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{Template:Learning | {{Template:Learning | ||
|quiz = [[Oropharyngeal anatomy]] | |quiz = [[Oropharyngeal anatomy]] | ||
| − | |flashcards = [[ | + | |flashcards = [[Oropharynx Anatomy & Physiology Flashcards]] |
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 30 June 2011
Introduction
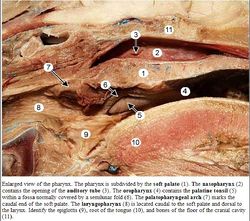
The pharynx is the chamber connecting the oral cavity, nasal cavity, oesophagus and larynx. The pharynx is divided into the nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngeal pharynx which all have different functions, innervation and develop differently. The oropharynx is the oral section of the pharynx.
Structure and Function
The last molar borders rostrally and the epiglottis caudally. The tongue borders ventrally and the soft palate dorsally. It is derived from endoderm.
The oropharynx is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX). It is divided by the glossopalatine arch from the laryngeal pharynx.
Histology
The oropharynx has a stratified squamous epithelium. It is keratinised in ruminants. The lamina propria contains aggregates of lymphoid tissue (called tonsils) in several parts of the oropharynx.
Musculature
Constrictors
The constrictor muscles include the hyopharyngeus, thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus.
Dilators
The dilator muscle is the stylopharyngeus.
The pterygopharyngeus muscle shortens the oropharynx and the palatopharyngeus muscle closes the pharyngeal arch.
Innervation
Muscles from the pharyngeal arch are innervated by the vagus nerve (CN X). The stylopharyngeus from the pharyngeal arch is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
| Oropharynx - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Multiple choice quizzes |
Oropharyngeal anatomy |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Oropharynx Anatomy & Physiology Flashcards |