Difference between revisions of "Gingiva"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
LisaMilella (talk | contribs) |
LisaMilella (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Gingiva is mucosal tissue over [[Enamel Organ#Alveolar Bone|alveolar bone]]. It has a stratified squamous epithelium, with some keratinisation. It resists friction of food during [[Mastication|mastication]] by being tightly bound to the underlying bone. It recedes with age, exposing the cervical part of the tooth. It is usually salmon pink in healthy animals. A colour change indicates pathology. | Gingiva is mucosal tissue over [[Enamel Organ#Alveolar Bone|alveolar bone]]. It has a stratified squamous epithelium, with some keratinisation. It resists friction of food during [[Mastication|mastication]] by being tightly bound to the underlying bone. It recedes with age, exposing the cervical part of the tooth. It is usually salmon pink in healthy animals. A colour change indicates pathology. | ||
| − | ===Mucogingival | + | ===Mucogingival junction=== |
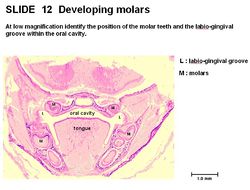
[[Image:Labiogingival Groove Histology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Labiogingival Groove Histology - Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Labiogingival Groove Histology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Labiogingival Groove Histology - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | The '''mucogingival | + | The '''mucogingival junction''' is the junction between the '''attached gingiva''' and '''the free alveolar mucosa''' |
==Vasculature and Innervation of the Gingiva== | ==Vasculature and Innervation of the Gingiva== | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 4 August 2014
Introduction
Gingiva is the oral mucosa surrounding the neck of each tooth forming the gums.
Structure and Function of the Gingiva
Gingiva is mucosal tissue over alveolar bone. It has a stratified squamous epithelium, with some keratinisation. It resists friction of food during mastication by being tightly bound to the underlying bone. It recedes with age, exposing the cervical part of the tooth. It is usually salmon pink in healthy animals. A colour change indicates pathology.
Mucogingival junction
The mucogingival junction is the junction between the attached gingiva and the free alveolar mucosa
Vasculature and Innervation of the Gingiva
The gingiva is supplied by the superior and inferior alveolar arteries.
Innervation is from the trigeminal nerve (CN V).
Species Differences
Canine
Some breeds of dog have dark gums, e.g. chow chow.
| Gingiva Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Teeth and Gingiva Flashcards |
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology tutorial on the oral cavity |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a256f1b6cca4_63688246 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a256f1c5e5a9_54030367 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a256f1d33d41_56091572
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |