Difference between revisions of "Giardia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
*Infections often asymptomatic in domestic animals | *Infections often asymptomatic in domestic animals | ||
| − | **Can cause | + | **Can cause villous atrophy leading to malabsorption |
**Infection can persist for weeks to months if not treated | **Infection can persist for weeks to months if not treated | ||
==Epidemiology== | ==Epidemiology== | ||
| − | *Infection via direct oral-faecal route or through contaminated water source (water- | + | *Infection via direct oral-faecal route or through contaminated water source (water-borne) |
*Wild animals may act as a source of infection for humans | *Wild animals may act as a source of infection for humans | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
**Cysts need to be distinguished from pollen grains and yeasts | **Cysts need to be distinguished from pollen grains and yeasts | ||
| − | * | + | *Cyst excretion is intermittent |
**Faeces need to be collected over a 3 day period | **Faeces need to be collected over a 3 day period | ||
*Cysts are '''heavy''' | *Cysts are '''heavy''' | ||
| − | **Needs higher density | + | **Needs higher density flotation fluids |
**Do not float well in saturated sodium chloride solution | **Do not float well in saturated sodium chloride solution | ||
*Immunoassays | *Immunoassays | ||
| − | ** | + | **Detect cyst antigen in faeces |
==Control and Treatment== | ==Control and Treatment== | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
**Minimise risk of human infection | **Minimise risk of human infection | ||
| − | *Boil (or sterilise through other means) drinking water in regions of the world where drinking water may be | + | *Boil (or sterilise through other means) drinking water in regions of the world where drinking water may be contaminated |
*Avoid uncooked foodstuffs | *Avoid uncooked foodstuffs | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
*[[Vaccines - WikiBlood|Vaccination]] | *[[Vaccines - WikiBlood|Vaccination]] | ||
**Killed trophozoites | **Killed trophozoites | ||
| − | ** | + | **Available in the USA for cats and dogs |
**Decreases the excretion and viability of cysts | **Decreases the excretion and viability of cysts | ||
**Decreases environmental pressure | **Decreases environmental pressure | ||
Revision as of 09:11, 7 January 2009
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Recognition
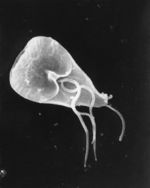
- Flagellate protozoa
- Found in the intestine of humans
- Associated with chronic diarrhoea
- Found in both wild and domestic animals
- 15-20μm long
- Pear-shaped
- 8 flagella
- 6 flagellae are free
- Large adhesive discs to hold onto intestinal mucosa
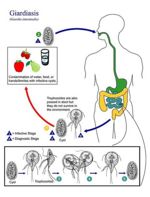
Life Cycle
- Simple and direct
- Trophozoites attach to intestinal wall
- Reproduce by binary fission
- Form cysts of 10μm
- Multi-nucleate cysts formed intermittently
- Immediately infective when passed in faeces
- Prepatent period of 5-6 days
Pathogenesis
- Commonest cause of protozoal diarrhoea of man in the UK
- Common in domesticated animals
- Infections often asymptomatic in domestic animals
- Can cause villous atrophy leading to malabsorption
- Infection can persist for weeks to months if not treated
Epidemiology
- Infection via direct oral-faecal route or through contaminated water source (water-borne)
- Wild animals may act as a source of infection for humans
- E.g. Beavers
- Divided into 7 species
- G. duodenalis most commonly infects humans
- Some subspecies are zoonotic
- G. duodenalis most commonly infects humans
Diagnosis
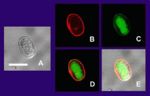
- Faecal examination
- Cysts need to be distinguished from pollen grains and yeasts
- Cyst excretion is intermittent
- Faeces need to be collected over a 3 day period
- Cysts are heavy
- Needs higher density flotation fluids
- Do not float well in saturated sodium chloride solution
- Immunoassays
- Detect cyst antigen in faeces
Control and Treatment
- Sanitation and hygiene
- Minimise risk of human infection
- Boil (or sterilise through other means) drinking water in regions of the world where drinking water may be contaminated
- Avoid uncooked foodstuffs
- Contaminated by washing
- Drug Treatments
- Metronidazole
- Flagyl, Torgyl
- Fenbendazole
- Panacur
- Metronidazole
- Vaccination
- Killed trophozoites
- Available in the USA for cats and dogs
- Decreases the excretion and viability of cysts
- Decreases environmental pressure