Difference between revisions of "Sarcoptes"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
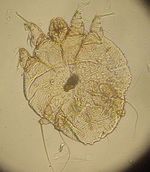
[[Image:Sarcoptes scabei.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Sarcoptes scabei.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
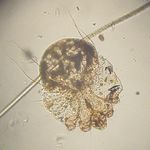
[[Image:Sarcoptes scabei 2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Sarcoptes scabei 2.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Sarcoptes scabei'' - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| − | [[Image:Scabies human skin pruritis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Scabies on human skin resulting in | + | [[Image:Scabies human skin pruritis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Scabies on human skin resulting in pruritus - Wikimedia Commons]] |
==Recognition== | ==Recognition== | ||
Revision as of 09:59, 2 June 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
File:Scabies human skin pruritis.jpg
Scabies on human skin resulting in pruritus - Wikimedia Commons
Recognition
- Small, round mite
- Short legs
- Project only a short distance from body margin
- Dorsal spines
- Arranged in rows
- Terminal anus
- Male is about 250μm in length and the female about 400-430μm in length
Life cycle
- 3 week life cycle
- Female lays eggs in epidermis in an egg laying pocket
- Female feeds on liquid oozing from damaged tissue
- The eggs hatch in 1 week
- 6 legged larvae released which crawl to skin surface
- The larvae then burrow back into the epidermis into moulting pockets
- Larvae moult to become 8 legged nymphs
- Nymphs moult twice before becoming adults
- Adult males emerge and look for females to mate
Cause Sarcoptic Mange