Difference between revisions of "Carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Primary Liver Tumours== | ==Primary Liver Tumours== | ||
| − | |||
===Hepatocytic=== | ===Hepatocytic=== | ||
| − | |||
*more in dogs and cats | *more in dogs and cats | ||
=====Gross===== | =====Gross===== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
*can be very variable appearing as sheets or cords of neoplastic cells | *can be very variable appearing as sheets or cords of neoplastic cells | ||
*cells generally smaller with a higher nucleus to cytoplasmic ratio | *cells generally smaller with a higher nucleus to cytoplasmic ratio | ||
| − | |||
===Cholangiocellular - bile duct=== | ===Cholangiocellular - bile duct=== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 52: | ||
*Or diffuse sheet of undifferentiated cells | *Or diffuse sheet of undifferentiated cells | ||
| + | ==Endocrine Pancreatic== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Larger than adenomas | ||
| + | *Multilobular | ||
| + | *Invasive into parenchyma and surrounding tissue | ||
| + | *Metastasis into [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph nodes]], [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]] mesentery, omentum | ||
| + | *Few mitotic figures | ||
[[Category:Liver,_Primary_Tumours]] | [[Category:Liver,_Primary_Tumours]] | ||
[[Category:Liver,_Secondary_Tumours]] | [[Category:Liver,_Secondary_Tumours]] | ||
[[Category:Pancreas_-_Hyperplastic_and_Neoplastic_Pathology]] | [[Category:Pancreas_-_Hyperplastic_and_Neoplastic_Pathology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Endocrine_System_-_Pathology]] | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 9 June 2010
Primary Liver Tumours
Hepatocytic
- more in dogs and cats
Gross
- can be difficult to distinguish grossly from adenomas
- usually one single large mass and additional smaller masses (intrahepatic metastases)
- may have features of malignancy such as internal necrosis and haemorrhage
Microscopically
- can be very variable appearing as sheets or cords of neoplastic cells
- cells generally smaller with a higher nucleus to cytoplasmic ratio
Cholangiocellular - bile duct
- more common than adenoma
- reported in all species (mostly dogs and cats)
Gross
- usually multiple whitish umbilicated nodules that are present diffusely throughout the liver
- actually look as though they were secondary tumours
- firm on cut surface
- due to fibrosis
Microscopically
- distinctly adenocarcinomatous
- ductal and acinar proliferation in abundant fibrous tissue
- sometimes papillary formations
Secondary Liver Tumours
- from a variety of origins
Pancreatic
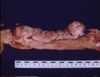
Image of haemorrhage and pancreatic carcinoma in a cat from Cornell Veterinary Medicine
- In older dogs, more common in Airedale terriers, rare in cats, other species too
- Tend to arise centrally in the gland
- Highly invasive and infiltrative
- Metastases to the liver, visceral serosa, abdominal lymph nodes, spleen, adrenals etc.
- Similar to malignant ovarian tumours - implant on the peritoneum
Gross appearance
- Usually spherical nodules with adhesions to nearby structures
- Single or multiple, variable size
- Greyish or yellow fibrous tissue - firm on cutting
- May show internal necrosis and haemorrhage
- Some tumours may contain cysts wih mucinous content
- Adhesions may occur
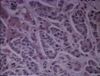
Microscopic appearance
- May be well differentiated with normal acini and ducts
- Or diffuse sheet of undifferentiated cells
Endocrine Pancreatic
- Larger than adenomas
- Multilobular
- Invasive into parenchyma and surrounding tissue
- Metastasis into lymph nodes, liver mesentery, omentum
- Few mitotic figures