Difference between revisions of "Sublingual Gland - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "Category:Alimentary System" to "Category:Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology") |
m (Text replace - "Oral Cavity - Salivary Glands - Anatomy & Physiology" to "Salivary Glands - Anatomy & Physiology") |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|linktext =Alimentary System | |linktext =Alimentary System | ||
|maplink = | |maplink = | ||
| − | |sublink1= | + | |sublink1=Salivary Glands - Anatomy & Physiology#Major Salivary Glands |
|subtext1=MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS | |subtext1=MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 16:16, 4 September 2010
|
|
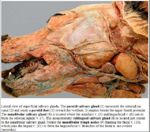
Sublingual Salivary Gland
- Merocrine secretion
- Smaller than parotid gland
- Consists of monostomatic compact part drained by a single duct. Located over rostral mandibluar gland in dog. Duct runs with mandibluar gland duct and opens at the sublingual caruncle.
- Consists of polystomatic diffuse part drained by numerous smaller ducts. Thin strip below mucosa of the floor of oral cavity and duct opens beside the frenulum.
Histology
- Tubulo-acinar gland
- Mucous cells (stain lighter)
- Serous demilunes (stain darker)
- Demilunes secrete into lumen by canaliculi between mucous cells
Species Differences
Ruminant and Pig
Equine
- Diffuse part is the only part of the sublingual salivary gland present