Difference between revisions of "Pseudomonas species - Overview"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{review}} | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Taxobox | ||
| + | |name =''Pseudomonas'' | ||
| + | |phylum =Proteobacteria | ||
| + | |class =Gamma Proteobacteria | ||
| + | |order =Pseudomonadales | ||
| + | |family =Pseudomonadaceae | ||
| + | |genus =Pseudomonas | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
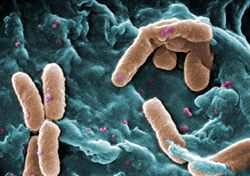
[[File:Pseudomonas.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center> Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a number of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' bacteria.( Janice Haney Carr 2008, Wikimedia commons)</center></small>]] | [[File:Pseudomonas.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center> Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a number of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' bacteria.( Janice Haney Carr 2008, Wikimedia commons)</center></small>]] | ||
Revision as of 10:33, 29 July 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
| Pseudomonas | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Proteobacteria |
| Class | Gamma Proteobacteria |
| Order | Pseudomonadales |
| Family | Pseudomonadaceae |
| Genus | Pseudomonas |
The Pseudomonas species are Gram-negative rods. They are obligate aerobes and are oxidase and catalase positive.
The Pseudomonas species are motile by polar flagellae and cause opportunistic infections. Most Pseudomonas species are resistant to antibiotics due to their efflux pumps, which pump out the antibiotics before they can act. They contain porins in their cell wall that allows them to survive harsh conditions.
References
Krieg, Noel (1984). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume 1. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.