Monogastric Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology
Overview
The enlarged swelling of the gastrointestinal tract between the oesophagus and the duodenum is called the stomach. It is a simple structure in carnivores and a compound structure in ruminants.
The stomach functions as a reservoir of food where digestion occurs through chemical and mechanical processes. This allows food to be broken down further and absorbed.
Development
The gut tube is formed from the folding of the splanchnopleure (mesoderm and endoderm). The mesoderm forms the skeletal muscle, (oesophagus and anus), smooth muscle (lateral plate mesoderm) and connective tissue layers form around the inner endoderm. The endoderm is the inner layer forming the epithelia and glands.
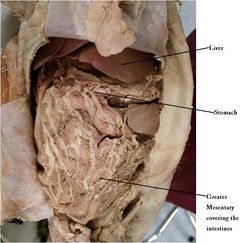
The region enlarges. Swelling indicates where the stomach will form. The dorsal surface becomes convex to form the greater curvature of the stomach and the ventral surface becomes concave to form the lesser curvature. Two rotations of 90 degrees occur along the longitudinal axis and then then the dorso-ventral axis. The dorsal mesogastrium becomes elongated (with the spleen) and expands into a large fold along the ventral abdominal wall. This becomes the greater omentum which covers all the abdominal organs. It is a superficial structure which is free to move. The ventral mesogastrium becomes the lesser omentum. It is in between the stomach and the liver. The rest of the ventral mesentry degenerates.
Structure and Function
The stomach is split into the regions: cardia, fundic, body and pyloric parts. The entire stomach is motile. It has a pH of 0.9 to 1.5.
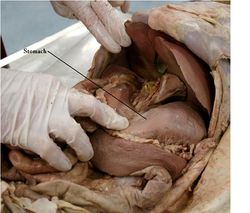
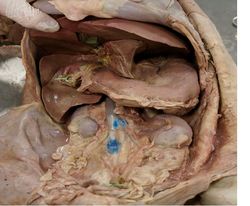
The larger part of the stomach lies to the left of the midline, under cover from the ribcage and in contact with the liver and diaphragm. The oesophagus opens into it at the cardiac sphincter. The smaller part of the stomach has thicker walls and passes to the right of the midline into the duodenum at the pyloric sphincter. The angular point between the two parts of the stomach is called the angular notch (incisura)
The fundus is a blind dome rising above the cardia; The body extends from the cardia ventrally; The pyloric part is on the right divided into a more muscular and a less muscular half. The serosa (external peritoneum) covers the entire organ.
Contractions start near the cardia and spread distally, accelerating and becoming more vigorous as they reach the pylorus region. The pyloric sphincter is open for 1/3 of the time during contractions. The empty stomach lies completely within the rib cage and does not contact the abdominal floor. Little secretion is produced and only small peristaltic contractions occur. Once food is offered or anticipated, the secretions begin.
The stomach is supported by 4 folds of peritoneum; The Gastrophrenic ligament- from the greater curvature of the stomach to the crura of the diaphragm; The Lesser omentum- connecting the lesser curvature of the stomach and the initial segment of duodenum to the liver in the region of the hepatic porta; The Gastrosplenic ligament- connecting the greater curvature of the stomach to the spleen by a double fold of peritoneum and the Greater omentum- connceting the greater curvature of the stomach to the duodenum and dorsal body wall.
Vasculature
Vasculature of the stomach includes the coeliac artery (which is a branch of the dorsal aorta). The coeliac artery splits into the hepatic artery supplying the liver, pancreas and stomach (right gastric and right gastro-epiploic arteries). The coeliac artery also splits into the splenic artery which supplies the spleen and the stomach (left gastro-epiploic artery), it also splits into the left gastric artery supplying the stomach.
The gastro-epiploic arteries supply the greater curvature of the stomach and the gastric arteries supply the lesser curvature of the stomach. The numerous veins join the portal vein.
Innervation
Sympathetic fibres run with the arteries. Parasympathetic fibres from the vagus nerve (CN X) are within the two vagal trunks. In the proximal region of the stomach, vagal stimulation suppresses muscular contraction (VIP); In the distal region, vagal stimulation increases muscular activity (ACh).
Histology
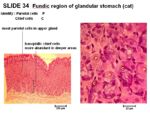
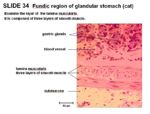
- Columnar epithelium
- Folded mucosa forming longitudinal rugae
- Invaginations called gastric pits which are continuous with gastric glands
- The 4 layers of the stomach wall are:
- Serosa/adventitia
- Tunica muscularis
- Submucosa
- Mucosa
- Chief (zygomatic) cells secreting pepsinogen
- Secreted in response to vagus and gastrin
- Basophilic
- More abundant in base of glands
- Pepsinogen unfolds and cleaves itself (autocatalyses) in response to hydrochloric acid
- Only active in acidic envrionments
- Goblet cells secreting mucous
- Protects against autodigestion
- Parietal (oxyntic) cells secreting hydrochloric acid in gastric pits
- Aids digestion
- Activates gastric enzymes, e.g. pepsinogen to pepsin
- Kills microorganisms and enzymes that enter with food
- Secreted in response to vagus or pepsin
- Large, pyramid shaped
- More abundant in upper region of glands
- Gastrin from pyloric G cells
- Somatostatin from pyloric D cells
- Histamine from Enterochromaffin-like cells (ECL cells)
- 3 layers of lamina muscularis: the outer longitudinal, middle circular and inner oblique.
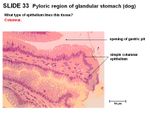
- Glands are short, coiled, branched tubular. Need to be replaced due to wear and tear. Only in mucosal layer.
- Cardia is a narrow muscle strip
- Pyloric sphincter is thickened tunica muscularis from the middle circular smooth muscle layer
- In fundic region, tunica muscularis is thinner, glands are straight and gastric pits are shallow. Abundance of parietal and cheif cells in gland.
- In pyloric region, tunica muscularis is thicker, glands are coiled and gastric pits are deep.
- Lymphatic vessels are present in the submucosa
Digestive Enzymes
The digestive enzymes include;
Proteases
An inactive zymogen, activated by hydrochloric acid. Active pepsin is produced and completed near the brush border to generate small peptides and individual amino acids. It starts in the stomach and continues into the small intestine.
Carbohydrases
E.g. amylase. Salivary and pancreatic secretions to produce disaccharides. Disaccharides are converted to monosaccharides near the brush border. Cellulases are formed from symbiotic micro-organisms (ruminant stomachs).
Lipases
Lipases are assisted by bile salts which neutralise stomach acids and emulsifies fats. It generates free fatty acids, monoglycerides and diglycerides.
Control of secretions
The control of gastric secretions is under hormonal (gastrin), paracrine (histamine) and neural (ACh) mediators in the cephalic and gastric phases. Gastric secretions are inhibited during the intestinal phase by CCK and secretin.
For more information, see control of secretions.
Species Differences
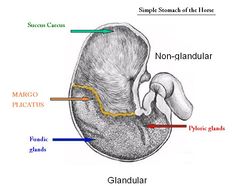
The size of the non-glandular region in the simple stomach varies between species. It is largest in the horse, pig and then smallest in the dog.
Equine
A region called the margo plicatus is present which separates the glandular and non-glandular parts of the equine stomach. The non-glandular area is lined with squamous epithelium (not columnar). The stomach is relatively small (10% GIT) with a strong cardiac sphincter which prevents the animal from vomiting. The equine stomach is rarely empty and retention time is short as expulsion into the duodenum stops when feeding stops. A 500kg horse can produce 30ml of gastric juice in 24 hours.
Canine
The stomach is of variable size ranging from 0.5 to 6L according to breed. A full stomach can touch the bladder. The Subglandular layer of fibroblasts and collagen fibres are for protection, e.g. from consuming bones. It is between the glands and the lamina muscularis. A 25kg dog can produce 0.5 to 1L gastric juice in 24 hours.
Porcine
The cardia is thickened, taking up nearly half the area of the stomach. The internal diverticulum is present, which can be seen externally.
Links
Test yourself with the Stomach Flashcards
Click here for Stomach Pathology.
Click here for Control of Feeding.
Video links:
2.Lateral View of the Equine Abdomen
3.Left Sided topography of the Equine abdomen
4.Right sided topography of the Equine Abdomen
6.Left sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen and Thorax