Trypanosomosis
Also Known As — Nagana—Typanosomiasis
Introduction
Trypanosomosis is a disease caused by protozoan pathogens of the genus Trypanosoma.
Trypanosomosis causes a wasting disease in cattle and sleeping sickness in humans.
T. cruzi is the most important species in veterinary medicine.
Causative Organisms
T. cruzi occurs in South America where it is transmitted by a triatomid bug and infects armadillos, possums and humans. It is known as Chagas’ Disease.
T. brucei and T. Equiperdum affect horses, the latter causing venereal dourine.
T. simiae causes fatal pyrexia in pigs while T. Congolense is milder in the same species.
T. brucei and T. Congolense can also affect dogs and cats causing acute fever, anaemia and neurological signs.
T. brucei causes skin infections in donkeys.
T. melophagum and T. Theileri are non-pathogenic species present in the UK.
Transmission
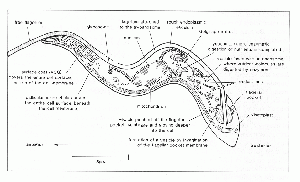
Trypanosomiasis is spread by Tsetse flies.
Clinical Signs
Clinical disease varies widely with death occurring from 1 week to months after infection. T. vivax is known for is rapid mortality while T. brucei and T. congolense hosts often survive for prolonger periods. Infection of large numbers of insect vectors is common in these circumstances
Ruminants
Enlarged lymph nodes and spleen. Later in the disease course the lymph nodes and spleen shrink due to lymphoid exhaustion.
Haemolytic anaemia is a cardinal feature.
Chronic infection causes heart failure and associated signs and death.
Plasma cell hypertrophy and hypergammaglobulinaemia are evident on haematology and biochemistry.
Emaciation
Abortion and infertility
Horses
Oedema of the limbs and genitalia. Dourine – genital and abdominal oedema and neurological signs.
Donkeys
Dogs and Cats
Pyrexia, myocarditis, myositis, corneal opacity and neurological signs.
Diagnosis
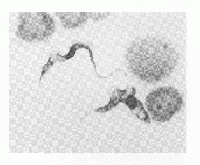
Microscopic identification on trypanosome parasites in the host blood on a smear with Giemsa staining.
Motile trypanosomes may be demonstrable in a haematocrit tube at the plasma: buffy coat interface.
Treatment
A variety of drugs can be used to treat trypanosomiasis including diminazene, homidium, isometadium, suramin and melarsomine.
Control
Separation of livestock and wild animals is effective but difficult.
Use of trypanotolerant livestock breeds. Tsetse fly control by sprays, traps etc
Prophylactic drug therapy with quinapyramine or homidium is effective.
References
Merck Veterinary Manual, Tetse-transmitted Trypanosomiasis accessed online 03/06/2011 @ http://www.merckvetmanual.com/mvm/index.jsp?cfile=htm/bc/10413.htm