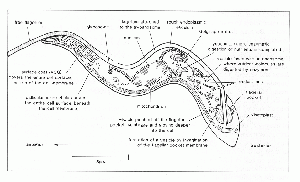
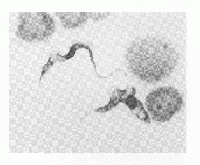
Trypanosomosis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Also Known As
Pathogenesis
- Salivarian
- Causes wasting disease in cattle (nagana)
- Sleeping sickness in humans
- Stercorarian
- T. cruzi most important in veterinary medicine
- Occurs in South America
- Infects armadillos, possums and humans
- Causes Chagas' Disease
- Transmitted by a triatomid (kissing) bug
- Chronic infections are often fatal causing heart failure
- Non-pathogenic species are transmitted by tabanids and keds
- T. theileria and T. melophagium
- T. cruzi most important in veterinary medicine
- Enlarged lymph nodes and spleen
- Causes lymphoid exhaustion
- Associated with plasma cell hypertrophy and hypergammaglobulinaemia
- Due to an increase in IgM
- With infections of increased duration, the lymph nodes and spleen shrink due to exhaustion of their cellular elements
- Anaemia
- Red blood cells are removed from circulation (haemolytic)
- Is a cardinal feature of the disease
- Degeneration and inflammation of multiple organs
- E.g. Skeletal muscle, myocardium and CNS
Clinical Signs
- In ruminants:
- Anaemia
- Enlargement of the lymph nodes
- Progressive loss of body condition
- Fever and appetite loss occur during parasite peaks
- Chronic disease usually terminates in death of the animal if untreated
- Can cause abortion, infertility and decreased growth in herds
- In horses:
- Acute or chronic infections of T. brucei
- Oedema of the limbs and genitalia
- In pigs:
- T. congolense infections are mild or chronic
- T. simiae infections are hyperacute usually leading to death from pyrexia in a few days
- In dogs and cats:
- T. brucei and T. congolese
- Acute infections
- Fever, anaemia, myocarditis, corneal opacity
- Occasionally neurological signs present, such as increased aggression, ataxia and convulsions
- In donkeys:
- T. brucei in skin infections
Epidemiology
- Vector distribution
- Tsetse flies found in riverine, savannah and forest habitats
- Up to 20% flies infected
- Flies infected for life
- Parasite virulence
- Some parasitaemic animals survive for long periods of time
- E.g. T. brucei and T. congolense
- Increases the opportunity for infection of flies
- Some trypanosomes kill their host in 1-2 weeks
- E.g. T. vivax
- Decreases the chances of fly infection
- Trypanosomes avoid host immune defences by altering glycoprotein coat (surface antigen) before host antibody response
- Antigenic variation can occur many times over several months causes relapsing parasitaemia
- Some parasitaemic animals survive for long periods of time
- Host response
- Trypanotolerant wild animals remain parasitaemic for prolonged periods without showing clinical signs of disease
- Cause lasting reservoirs of infection
- Most domestic livestock are susceptible to trypanosomosis
- Some local breeds of sheep, goats and cattle are trypanotolerant
- E.g. Bos indicus
- Trypanotolerant wild animals remain parasitaemic for prolonged periods without showing clinical signs of disease
Diagnosis
- Demonstrate trypanosomes in blood
- Giemsa stained smears
- Fresh blood films
- Motile trypanosomes
- Haematocrit tube
- Motile trypanosomes at the plasma/buffy coat interface
Control
- Tsetse fly control
- Spraying and trapping
- Prophylactic drug treatment
- Change drug group periodically to decrease the chances of resistance occurring
- May lead to protective immunity but livestock will still be susceptible to heterologous challenges
- Barrier fences and buffer zones
- Separate livestock and wild animals
- Trypanotolerant livestock
Other trypanosomes
- Mechanically transmitted by biting flies
- E.g. Surra affecting horses and camels in North Africa, Asia and South America
- T. equinum in South America
- T. evansi in Asia
- Venereally transmitted
- E.g. Dourine
- Transmitted by T. equiperdum
- Causes genital and abdominal oedema, emaciation and CNS signs
- Affects horses and donkeys in Africa, Asia, Central and South America
- E.g. Dourine
- Non-pathogenic species occur in the UK
- In sheep caused by T. melophagium
- In cattle caused by T. theileri
- Myositis
- Infrequent muscle lesions with mononuclear infiltrates
- Dogs, cats and pigs are affected
- Parasites lie between myofilaments
- May cause fibre degeneration