Knemidocoptes
| Knemidocoptes | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Class | Arachnida |
| Sub-class | Acari |
| Order | Acariformes |
| Sub-order | Sarcoptiformes (Astigmata) |
| Family | Knemidokoptidae |
| Genus | Knemidocoptes |
| Species | K. mutans, K.gallinae, K. pilae |
Also known as: Cnemidocoptes
Causes: Knemidocoptiasis — Depluming Itch — Scaly Leg — Scaly Beak — Scaly Face
Overview
Knemidocoptes are burrowing mites of avian species. There are a number of important species infecting both production birds and pet animals. The mites tend to infect unfeathered areas of birds and so commonly cause scale as a clinical sign. Spread of these mites occurs from prolonged close contact between birds, such as occurs between a mother and unfeathered young.
Knemidocoptes is the only genus of burrowing mite found in birds. There are three main species of Knemidocoptes that affect birds and these are K. mutans, K. gallinae and K. pilae, which all cause different disease manifestations and clinical signs.
Identification
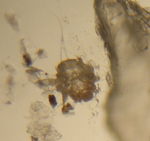
Knemidocoptes are small round mites found in different locations on avian species dependent on the species of mite present. They have a stumpy legged appearance as their coxa are sunk into the body and a U-shaped chitinous bar found behind the head.
Unlike other burrowing mites, that have pediculated suckers, the tarsal portions of Knemidocoptes mites have claw like structures and tactile hairs. They may look similar to Sarcoptes spp. however they lack pegs and have dorsal striations instead. The mites breath through their cuticles and therefore are astigmata. The presence of a terminal anus can also be used as a distinguishing feature.
Life Cycle
The entire life cycle takes place on a single host and takes between 14 and 21 days to complete. The mite is spread by close contact with an infected animal, however it can survive for a limited time off the host. Mating occurs on the host, a mature male will leave its moulting pocket and seek a female either on the skin or in a moulting pocket. The females are ovo-viviparous meaning that they give birth to live larval young. Once fertilised the female will create a burrow in the upper layers of the epidermis, the larvae will be laid in this burrow and move to the skin surface.
Larvae
Knemidocoptes mites have hexapod larvae. They burrow into the skin creating moulting pockets and undergo two nymphal stages before reaching maturity.
Clinical Signs
Signs are dependent on which mite is present:
K. gallinae
The disease associated with this mite is called depluming itch. Mites burrow into the feather shafts and cause intense pruritus and pain, so much so that the bird will pull out its feathers. Therefore clinical signs include loss of feathers by self trauma, depression, intense pre-occupation in pulling out feathers. The bird will often not eat and will appear to lose weight.
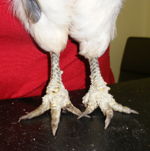
K. mutans
The disease caused by this mite is called scaly leg. This specie of mite burrows beneath leg scales and causes them to loosen and rise. Clinical signs will include the bird having distorted legs and claws and may appear lame. The bird may also be paying particular attention to their legs and may show signs of pruritus.
K. pilae
The disease associated with this mite is called scaly beak (scaly face in psittacine birds) and is caused when the mites burrow into feathered parts of the beak and into the lightly feathered areas of the face and body. Clinical signs will include loss of feathers and scaliness around the base of the beak and spreading over the face. There may be mild pruritus but not as severe as other forms in the genus.
Not all infections of Knemidocoptes mite result in clinical signs, some may lay dormant for until the animal is stressed or is otherwise immunocompromised.
Diagnosis
History and clinical signs are very suggestive of the disease. A deep skin scraping is required to identify the mites and this should be performed by scraping the skin until capillary blood is seen. Feather pluck may also prove useful.
Treatment and Control
There are few licensed acaracidal treatments for poultry. Repeated treatment with one of the licensed treatments is necessary to cure this disease. Prophylactic acaracidal treatment can be used for prevention.
| Knemidocoptes Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Mites Flashcards |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Knemidocoptes publications |
References
Jordan, F, Pattison, M, Alexander, D, Faragher, T, (1999) Poultry Disease (Fifth edition), W.B. Saunders
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition), Merial
Randell, C.J, (1985) Disease of the Domestic Fowl and Turkey, Wolfe Medical Publication Ltd
Saif, Y.M, (2008) Disease of Poultry (Twelfth edition) Blackwell Publishing
Taylor, M A, Coop, R L & Wall, R L (2007) Veterinary Parasitology Blackwell Publishing
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69469077d4c589_02367951 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69469077e1bd22_49223364 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69469077ed7e59_92779345
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |