Insecta
Revision as of 17:04, 22 December 2008 by Rmeikle (talk | contribs) (→Alimentary and Excretary System)
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Classification
The phylum arthropoda is divided into several subphylums including Chelicerata (which includes the arachnids), Myriapoda, Hexapoda (which includes the insecta), Crustacea and Trilobitomorpha. These are then divided into many classes. The two of major veterinary importance are the insecta and arachnida classes.
Structure and Function
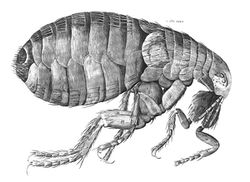
Insect Body
- Covered by an exoskeleton
- Provides support and protection to the living tissues
- Acellular so is secreted by underlying epidermis
- The outer layer is called the epicuticle which is composed of proteins and covered by a waxy layer
- The inner layers are the endocuticle and exocuticle which are composed of protein and chitin
- Body is metameric (divided into segments)
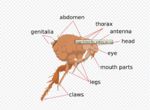
- Divided into head, body and abdomen
- Articular membranes link segments allowing movement
Insect Head
- Capsule of fused plates at the anterior end of the body
- One large pair of compound eyes
- Honeycomb like corneal facets
- Three simple ocelli
- Dorsal to compound eyes
- One pair of antennae
Antennae
- Form varies amongst insecta
- E.g. long and segmented, short and squat etc.
- Hairs sometimes present
- Aristae (bristles) sometimes present
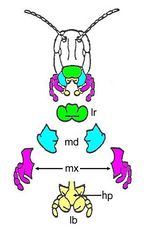
Mouthparts
- Modification depending on feeding method
- Insects which suck up liquified food have an expanded sponge like labellae
- Cannot penetrate skin
- Palps are also present which are sensory structures
- Insects which suck blood have long slender mouthparts for piercing skin
- Hypopharynx
- Mandibles
- Labrum
- Maxillae
- Larval mouthparts are prominent
- One pair of hooks
- Cephalo-pharyngeal skeleton
- Mouthparts help identify larvae
Insect Thorax
- Divided into three segments
- Prothorax, mesothorax and metathorax
- Each segment has one pair of legs attached
- One or two pairs of wings may be present on the mesothorax and metathorax
Leg
- Leg is attached to the body by coxa
- Trochanter
- Femur
- Tibia
- Tarsus, which is composed of several segments
- Claw
- Usually six-segmented
Wing
- Insects usually posess two pairs of wings
- Diptera have a reduced second pair of wings called halteres for balance
- Membranous outgrowth of the integument
- Strengthened by a network of veins comprising breathing tubes (trachea) and blood vessels
- The wing venation can be used for identification
- Longitudinal veins
- Cross veins
- Open cells
- Closed cells
Insect Abdomen
- Segmented
- Soft
- Appendages present
- Copulatory claspers
- Ovipositor
- External genitalia
Respiratory System
- Branching trachea strengthened by spiral thickenings in the walls
- Trachea communicate with outside via spiracles
- Spiracles on side of body
- Chitinous openings
- Muscular control so can open and close at will
- Mounted on stigmatic plates
- Lead to trachea
- Muscular contactions of the body wall produce respiratory movements
- Shape of spiracles and stigmatic plates used for species identification
Alimentary and Excretary System
- The precise shape of the gut varies between arthropods
- The Alimentary canal is divided into fore, mid and hind gut
- Foregut:
- Oesophagus
- Crop for temporary food storage
- Proventriculus
- Gizzard present in insects which eat solid food
- Muscular wall and teeth on inner surface
- Midgut:
- Stores food
- Secretes enzymes for digestion
- Outlet for malpighian tubules (equivalent of the mammalian kidney)
- Hindgut:
- Water resorption
Circulatory System
- Branching blood vessels
- Haemocoele
- General body cavity
- Equivalent to the capillary circulation in mammals
- Contains haemolymph
- Ostia (openings) in the blood vessel walls allow return of blood to the heart
Nervous System
- Small brain above the oesophagus
- Chain of fused ganglia running along the floor of the abdomen and thorax
- Nerves are given off from chain
- Complex nervous system
- Well developed visual senses
Fat Body
- Large structure
- Cells containing fat vacuoles
- Lines the body cavity and internal organs
- Equivalent to the visceral and parietal peritoneum in mammals
- Food reservoir during hibernation or starvation periods
Reproductive System
- Most insects have seperate sexes
- Reproductive organs are analogous to mammals
- Spermatheca present in females
- Accessory female sex organ
- Recepticle for spermatozoa
- Sperm remains viable for most of the female's life cycle
Life cycles
- Most adult female insects are oviparous
- Lay eggs which hatch after deposition
- Some adult female insects are viviparous
- Lay larvae or nymphs
- Eggs rupture in female reproductive tract
Simple Metamorphosis
- Hemimetabolous
- Nymph emerges from the egg which resembles the adult but is sexually immature
- Nymph grows and undergoes several ecdyses (moults)
- Nymph becomes an adult (imago)
- E.g. Lice
Complex Metamorphosis
- Holometabolous
- Larva emerges from the egg and does not resemble the adult
- Larva feeds, grows and undergoes several ecdyses
- Larvae undergoes a quiescent stage where the outer cuticle hardens to form a pupa
- Some species have a silken cocoon
- Adult develops inside the pupal case before emerging
- E.g. Fleas and dipteran flies