- Epidemiology:
- Saprophyte in soil
- Endospore formation allows persistence and spread
- Endospores survive decades in the soil
- Outbreaks in herbivores grazing pastures contaminated by spores from buried carcases
- Infection usually by ingestion of spores and penetration through damaged mucosa
- Pathogenesis and pathogenicity:
- Spores germinate at site of entry and spread via lymphatics to bloodstream, where they multiply and produce toxin
- Capsule and toxin (encoded by separate plasmids) required for virulence
- Capsule composed of homopolymer of D-isomer of glutamic acid allows survival in the body by resisting phagocytosis
- Capsule stains mauve with polychrome methylene blue in the MacFadyean's reaction - identify anthrax in blood samples
- Bacilli appear as chains of dark blue, square-ended rods surounded with the capsule
- Extracellular toxin (holotoxin) composed of oedema factor, protective antigen and lethal factor
- Oedema factor is an adenylate cyclase which increases intracellular cAMP concetrations, causing fluid accumulation and damaging neutrophils
- Lethal factor causes release of cytokines from macrophages
- Protective antigen binds to the cell receptor to allow action of the other factors
- The toxin kills phagocytes, increases capillary permeability and interferes with clotting cascade
- Capillary thrombosis; leakage of fluid through damaged capillary endothelium
- Systemic shock from circulatory collapse, haemorrhagic disease and oedema lead to death of the animal
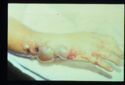
- Severe systemic disease that can result in enteritis
- Causes tissues to darken and swell due to oedema and necrosis
- Causes severe systemic disease that can result in enteritis.
- Peritonitis in pigs