Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 03
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Veterinary Dentistry Q&A. |
| Question | Answer | Article | |
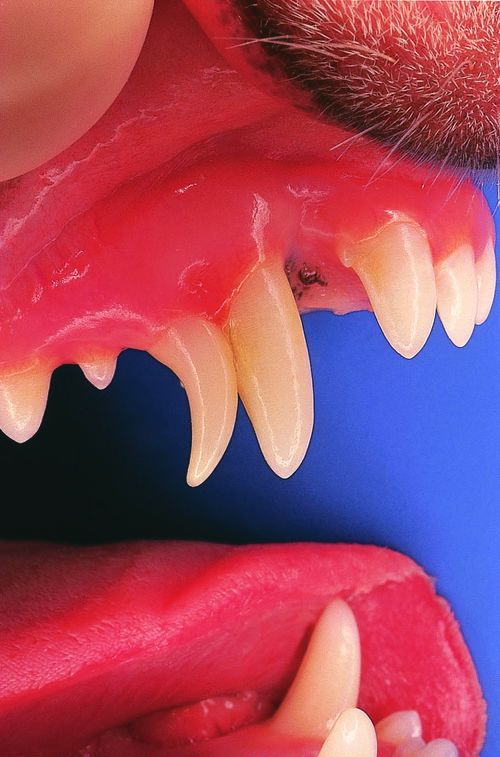
| What is the developmental abnormality seen in this one-year-old dog? | A persistent deciduous canine on the right maxilla. Although the term retained deciduous canine is more commonly used for this condition, persistent is more correct. ‘Retained’ strictly-speaking refers to failure to erupt (retentio dentis), while ‘persistent’ in this context means failure to exfoliate. |
Link to Article | |
| What is the clinical importance of this condition? | In most cases the permanent tooth develops normally, although the time and direction of eruption are influenced by the persistent deciduous tooth. Persistent deciduous canines may cause linguoversion of the erupting mandibular canines and facial deviation of the maxillary canines. Furthermore, persistent deciduous teeth alter the gingival contour, which results in plaque and debris accumulating between the deciduous and permanent teeth. |
Link to Article | |
| What is the identification of this tooth using the Triadan system and the anatomic identification system? | The right maxillary deciduous canine is tooth 504 in the Triadan system and is abbreviated anatomically as c1. |
Link to Article | |