| This article is still under construction. |
| Leishmania spp. | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Eukaryota |
| Phylum | Euglenozoa |
| Class | Kinetoplastea |
| Order | Trypanosomatida |
| Family | Trypanosomatidae |
| Genus | Leishmania |
| Species | L. infantum, L. donovani, L.chagasi |
Overview
Leishmania spp. are intracellular parasites of macrophages from the same family as Trypanosoma spp.. These organisms parasitise human, dogs and wild animals throughout southern Europe, Africa, Asia and South America. The infection is transmitted by sandflies. Infection can cause both cutaneous and visceral disease. Three types of Leishmania spp. are described;
- Hypoplaria - found in lizards that ingest the sandfly intermediate host. Development occurs in the hindgut of the fly.
- Peripylaria - found in mammals and lizards, development occurs in the fore- and hindgut of the fly.
- Suprpylaria - found only in mammals transmitted by the bite of a sandfly, development occurs in the fore- and midgut of the fly.
Recognition
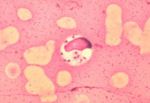
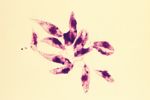
Leishmania spp. are ovoid shaped parasites containing a rod shaped 'kinetoplast'. The kinetoplast is associated with a rudimentary flagellum that does not extened beyond the cell margin. The position of the kinetoplast changes as the parasite changes between life stages. Once ingested by a sand fly the parasite takes the promastigote form and the kinetoplast moves the the posterior of the cell.
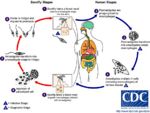
Life Cycle
The life cycle of Leishamania spp. requires transmission between mammalian (and occasionally reptile) hosts by a blood sucking fly. The sand flies is the intermediate host, in the Old World the flies are of the genus Phlebotomus and in the New World they are of the genus Lutzomyia. The amastigote form which lacks a flagella is found in he vertebrate hosts macrophages. The amistgote is ingested by the sand fly whilst it feeds on the host, once ingested the Leishamnia will transform into the flagellated promastigote form in the insect gut. Replication by binary fission occurs in the insects gut followed by migration to the proboscis of the insect. The presence of Leishamnia in the insects proboscis allows innoculation of the next host on which the fly feeds with the Leishmania parasite. Crushing the sand fly on the skin of a mammal can allow percutaneous transmission. Once inside the vertebrate host the Leishmania will invade the hosts macrophages and having done this revert to the amastigote form.
Pathogenesis
Infection with Leishmania can produce either cutaneous or viscreal disease as the infected macrophages proliferate in foci. There is a very long incubation period from infection to pathology, which can take years and therefore many infected dogs either never become symptomatic or remain so for a long period of time.
The cutaneous form of the disease produces areas of ulceration on the pinnae of the ears, eyelids or on the lips. These ucerations can also be seen between the digits of the dogs paw. This is a parasitic infection of the skin. The viscreal form causes a chronic wasting condition where generalised excema can be seen. Hair is lossed from around the eyes giving the animal a 'spectacled' appearance. These symptoms are accompanied by an intermitted fever and some generalized lymphadenopathy.
Even once an animal has been treated for leishmaniasis it is not uncommon for clinical symptoms to recur after a lengthy period of remission.
Epidemiology
The spread of the disease relies on the presence of the sand flyas a vector. Therfore the regions in which it is found commonly are those in which conditions are suitable for the flies such as the Mediteranean coast, southern Europe as well as in central America and northern Africa. As these flies are very common in these regions controlling there numbers has limited success, however due to control of mosquitos to prevent the spread of malaria the number of sand flies has also been reduced and a reduction in the number of cases of leishmania has been noted. Although this parasite is of primary veterinary importance in dogs, large reservoirs exist in wild animals and stray dogs. This reservoir is easily accessed by the sand fly vector and compounds the issue of controlling the spread of the disease.
Although the UK is not home to any species of sand fly, leishmaniasis is being observed more frequently in the domestic dog population. This is largely due to the increase in the number of animals that travel to areas of
- Mechanisms of transmission
- sand fly bite
- Rarely through direct contact
- Leishmaniasis in British dogs
- Susceptible to infection if exposed whilst abroad in endemic areas as have no immunity
- No sand flies in Britain but dogs have become infected whilst in contact with infected imported animals
Diagnosis
- Demonstrate Leishmania organisms
- In skin scraping or smears
- In joint fluid, lymph node or bone marrow biopsies
Treatment and Control
- Chemotherapy
- Prolonged treatment, expensive, suppresses infection
- Does not cure infection
- Prevent sand flies biting
- Collars, sprays containing insecticide with repellent effect
- Destruction of infected and stray dogs
- Sand flies biting infected dogs may spread the disease to other dogs, humans and wildlife
- There is a slight possibility of transmission to humans by direct contact
In dogs
- disseminated disease of the monocyte-macrophage system
- protozoa; genus Leishmania
- increased travel means clinincal disease may be acquired in endemic areas but now presents to veterinarians in non-endemic areas
- lymph node aspirates contain macrophages with organisms