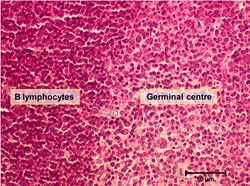
B cells
Also known as B lymphocytes
So named as they were initially found in the Bursa of Fabricius, B cells produce antibodies (Ig’s) and are associated with humoral immunity (T cells are part of the cell-mediated immune response), and are an integral part of the adaptive immune system. They represent 20-30% of circulating lymphocytes. B cells have B cell receptors (BCRs), or antigen binding sites which combine as the antibody IgM when the B cell is immature, changing to IgD when the cell is mature. IgM has a large molecular mass and can bind up to 10 antigens simultaneously. B cells also express MHC II, CD9, CD,19, CD20 and CD24.
Under antigenic stimulation B cells differentiate into plasma cells and memory cells.
B-cells also act as Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs) by presenting digested fragments to T cells on MHC II.