Motor Pathways - Anatomy & Physiology
Introduction
Motor pathways carry signals from the brain to the skeletal muscle and smooth muscle such as those contained in glands. The system consists of upper and lower motor neurones. The information provided below is primarily focussed on the motor pathways that coordinate skeletal muscle movement, i.e. motor pathways related to voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
Motor Pathways
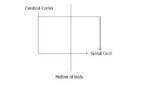
The connections between the motor cortex in the forebrain and motor neurons within the spinal cord are made up of two pyramidal tracts; the Pyramidal System and the Extrapyramidal System. These motor pathways are transmitted via ventral horns within the spine. Upper motor neurones are located mainly within the neopallium of the cerebellum. They govern the excitation or inhibition of lower motor neurones.
Pyramidal System (Corticospinal)
- Produces fine movements associated with skill, e.g. writing and playing a musical instrument.
- Most developed in primates, although may exist in other species such as the cat, where it aids in grooming.
- Nerve fibres of the pyramidal system originate in the cerebral cortex and then pass to the thalamus, and medulla oblongata.
- Some fibres decussate in the medulla oblongata, whilst others remain ipsilateral until they leave the spinal cord where they cross the midline of the body.
- Nevertheless, all fibres cross the midline at some point, so that the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body and vice versa.
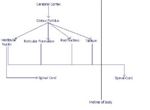
Extrapyramidal System
- Distinguishable from the pyramidal system as tracts do not run within the pyramids of the medulla.
- Earlier evolutionary development than the pyramidal system, so is a feature of lower animals and is the most important system in domestic species.
- More complex than the pyramidal system as involves various multisynaptic pathways that relay within several nuclei in the brain.
- Nuclei are dispersed from the telencephalon to the medulla oblongata and may be visible grossly.
- Parts of it take origin from the motor cortex, others from the tectum and reticular formation.
- Neurones then relay within nuclei which include:
- Red nucleus
- Substantia nigra
- Caudate nucleus
- Subthalamic nuclei
- Olive in the medulla oblongata
- Reticular formation
- Neurones that relay in the red nucleus and reticular formation relay directly onto LMNs, others relay to other nuclei.
- The main descending motor tracts from these two nuclei are:
- Rubrospinal tract - important in carnivores and ungulates. Modulates pattern generators in the spinal cord.
- Reticospinal tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
- Tectospinal tract