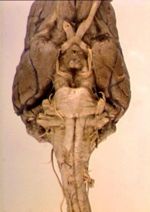
Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Introduction
Cranial nerves are those nerves which arise from the brain and brain stem rather than the spinal cord. Nerves arising from the spinal cord are the peripheral nerves. There are 12 cranial nerves, although the trigeminal nerve (V) has 3 branches. These are:
Opthalmic (V1)
Maxillary (V2)
Mandibular (V3)
Cranial Nerve Location and Routes
A summary of the cranial nerves is shown below:
| Nerve | Attatchment to brain | Exit Foramen | Fibre Type | Location of cell bodies | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I - Olfactory | Olfactory bulb | Cribriform plate | SVS | Olfactory epithelium | Olfactory epithelium |
| II - Optic | Optic chiasma | Optic canal | SSS | Retina | Retina |
| III - Occulomotor | Midbrain | Orbital fissure and Round Foramen | GSM + GVM | Nuculi III
parasympathetic nuculi III |
Extraoccular mm.
Constrictor pupulli |
| IV - Trochlear | Midbrain (dorsal) | Round Foramen | GSM | Nuc IV | Dorsal oblique mm. |
| V - Trigeminal | Pons | V1 - Orbital fissure
V2 - Round Foramen and Orbital Fissure V3 - Oval Foramen |
V1 - GSS
V2 - GSS V3 - SVM |
V1 - Trigeminal gangion
V2 - Trigeminal ganglion V3 - Nuculi V |
V1 - Eye region
V2 - Upper jaw inc. teeth V3 - mm. of arch 1 |
| VI - Abducens | Medulla oblongata | Orbital fissure | GSM | Nuc IV | Lateral rectus and retractor bulbi mm. |
| VII - Facial | Medulla oblongata | Stylomastoid foramen | SVM + GVM + SVS | Nuc III
(Taste - gleniailate ganglion) |
mm. of arch 2
Submaxillary and sublingual glands Rostral 2/3 taste |
| VIII - Vestibulocochlear | Medulla oblongata | Inner accoustic meatus | SSS | Vestibular ganglion | Maculae and cristae |
| IX - Glossopharyngeal | Medulla oblongata | Jugular foramen | G/S V M/S | Ganglia IX - SVM
Nuculi ambiguous - mm. arch 3 |
Carotid gland
Caudal 1/3 taste mm. of arch 3 Carotid body |
| X - Vagus | Medulla oblongata | Jugular foramen | GVM + SUM + GVS + GSS | Ganglion X - (amongst others) | Thoracic and abdominal organs
mm. of arches 4-6 Pharynx and larynx External ear |
| XI - Accessory | Medulla oblongata | Jugular foramen | GSM | Cervical spinal cord | Trapezius m. etc |
| XII - Hypoglossal | Medulla oblongata | Hypoglossal canal | GSM | Medulla nuculi XII | Tongue mm. |
Cranial Nerve Fibre Types
Cranial nerves are best explained by function:
- General Somatic Motor (GSM)
Motor cortex —→ Motor nuculi —→ Muscle
- General Visceral Motor (GVM)
Brainstem —→ Parasympathetic nuculi —→ Parasympathetic ganglion —→ Gland etc
- "Branchial motor" - Special Visceral Motor (SVM)
Motor cortex —→ Motor nuculi —→ Muscle
- General Somatic Sensory (GSS) and General Visceral Sensory (GVS)
Sensory cortex —→ Thalamus —→ Trigeminal nuculi —→ Trigeminal ganglion —→ Skin etc
Special sensory fibres (SSS + SVS):
Smell SVS
Priform cortex —→ Olfactory tubercle —→ Olfactory Bulb —→ SMELL
Vision SSS
Occipital cortex —→ Thalamus MGN —→ Rostral colliculus/Retinal ganglion cell —→ Bipolar cell —→ VISION
Hearing/Balance SSS
Temporal cortex —→ Thalamus MGN —→ Caudal colliculus and hindbrain —→ Spiral ganglion —→ HEARING
Taste SVS
Sensory cortex —→ Thalamus —→ Hindbrain (VII, IX, X) —→ Ganglion —→ TASTE
Cranial Nerves and their Functions
| # | Name | Nuclei | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Olfactory nerve | Anterior olfactory nucleus | Transmits the sense of smell |
| II | Optic nerve | Lateral geniculate nucleus | Transmits visual information to the brain |
| III | Oculomotor nerve | Oculomotor nucleus, Edinger-Westphal nucleus | Innervates the dorsal rectus, medial rectus, ventral rectus, and ventral oblique, which collectively perform most eye movements |
| IV | Trochlear nerve | Trochlear nucleus | Innervates the superior oblique muscle, which depresses, pulls laterally, and intorts the eyeball |
| V | Trigeminal nerve | Principal sensory trigeminal nucleus, Spinal trigeminal nucleus, Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus, Trigeminal motor nucleus | Receives sensation from the face and innervates the muscles of mastication |
| VI | Abducens nerve | Abducens nucleus | Innervates the lateral rectus, which abducts the eye and the retractor bulbi which forces the third eyelid across the surface of the cornea as a protective mechanism. |
| VII | Facial nerve | Facial nucleus, Solitary nucleus, Superior salivary nucleus | Provides motor innervation to the muscles of facial expression and stapedius, receives the special sense of taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue, and provides secretomotor innervation to the salivary glands (except parotid) and the lacrimal gland |
| VIII | Vestibulocochlear nerve | Vestibular nuclei, Cochlear nuclei | Senses sound, rotation and gravity (essential for balance & movement) |
| IX | Glossopharyngeal nerve | Nucleus ambiguus, Inferior salivary nucleus, Solitary nucleus | Receives taste from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue, provides secretomotor innervation to the parotid gland, and provides motor innervation to the stylopharyngeus |
| X | Vagus nerve | Nucleus ambiguus, Dorsal motor vagal nucleus, Solitary nucleus | Supplies branchiomotor innervation to most laryngeal and pharyngeal muscles; provides parasympathetic fibers to nearly all thoracic and abdominal viscera down to the splenic flexure; and receives the special sense of taste from the epiglottis |
| XI | Accessory nerve | Nucleus ambiguus, Spinal accessory nucleus | Controls muscles of the neck and overlaps with functions of the vagus |
| XII | Hypoglossal nerve | Hypoglossal nucleus | Provides motor innervation to the intrinsic muscles of the tongue and other glossal muscles |