Candida spp.
- Candidia albicans is the most important species
- C. tropicalis and C. pelliculosa are other important species
- World wide distribution
- Usually an endogenous mycoses
- Immunocompromised animals may show symptoms
- Usually lesions on mucous membranes and at mucocutaneous junctions
- Many species have been implicated in bovine mastitis
- C. albicans has been isolated in porcine stomach ulcers
- C. rugosa has been implicated in pyometra in mares
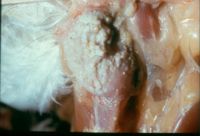
- Infection of the crop, oesophagus and mouth occur in poultry and other birds leading to sour crop
- Causes thrush in humans
- Affects the tongue
- C. albicans causes metritis and vaginitis in mares and genital candidiosis in stallions (and bulls)
- Skin scrapings in 20% KOH for microscopy
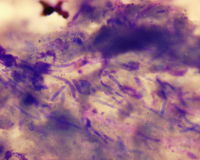
- Diphtheritic membranes, pus and fluids can be examined by Lactophenol Cotton Blue and stained by Gram or Methylene Blue stain
- Gram positive, oval, thin-walled budding cells with hyphal fragments
- Grow on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar producing soft, creamy colonies in 24-48 hours
- Grossly:
- Exudative, papular, pustular to ulcerative dermatitis
- Stomatitis and otitis externa may develop
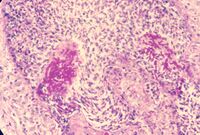
- Microscopically:
- Spongiotic neutrophilic pustular inflammation
- Parakeratosis
- Ulcerations
- Superficial exudate containing organisms
- Candida spp. in candidiasis