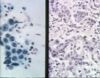
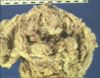
Adenocarcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- Adenocarcinoma is the most common gastric neoplasm in small animals.
- This is a tumour of the mucosal epithelium.
- These are genreally found in the fundus (particularly along the lesser curvature), and in the pylorus.
- There are two main internal appearances of gastric adenocarcinoma, both of which show thickened, oedematous, pale and firm tissue:
- A diffuse infiltration of gastric mucosa by neoplastic glandular epithelial cells.
- Causes a diffuse rugal thickening.
- A more solitary lesion that is seen as a thick plaque-like lesion
- Generally has a central erosion/ulceration of the tumour tissue.
- Distinguishable from a peptic ulcer as the edges of the eroded area are raised and thickened (tumour tissue).
- Generally has a central erosion/ulceration of the tumour tissue.
- A diffuse infiltration of gastric mucosa by neoplastic glandular epithelial cells.
- The external appearance of an affected stomach can include thickening of the draining lymphoid vessels due to tumour infiltration ('cording of the lymphatics') and evidence of a scirrhous reaction to the carcinoma.
- Adenocarcinomas are locally aggressive and spread via the lymphatics to the lymph nodes, lung, liver and adrenal glands.
Intestinal
- An intestinal adenocarcinoma is a malignancy of epithelial cells from the intestinal mucosa.
- Found in both the small and large intestines
- Common in the canine rectum.
- Species affected:
- Fairly common in dog and cat.
- Seen related to bracken ingestion in the older sheep.
- Occasionally occur in horses.
- These tumours usually grow away from the mucosa, down through the muscularis mucosae and into the submucosa, muscular layers and the serosa.
- They may, however, project into the lumen.
- Intestinal adeocarcinomas may take an annular form.
- This may result in stenosis of lumen
- Muscle proximal to the lesion becomes hypertrophied and dilated.
- This may result in stenosis of lumen
- Spread may be
- Via the lympahtics.
- To the lymph nodes, lung and liver.
- Transcoelomic spread
- Small, white plaques on serosa and adjacent tissues e.g. diaphragm.
- Via the lympahtics.