Difference between revisions of "IGF-1 - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
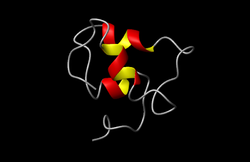
2007 '''Schematic structure of Insulin-like growth factor-1.''']] | 2007 '''Schematic structure of Insulin-like growth factor-1.''']] | ||
| − | IGF-1 is one of a number of | + | IGF-1 is one of a number of insulin-like growth factors. Insulin-like growth factors are produced by many different tissues and have local paracrine and autocrine effects. (see [[Hormones - Anatomy & Physiology|hormones]] for further details). They bind to carrier proteins to extend their half life in the blood. The '''liver''' is the main source of IGF-1. |
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:A&P Done]] |
Revision as of 13:21, 10 January 2011
Overview
IGF-1 is one of a number of insulin-like growth factors. Insulin-like growth factors are produced by many different tissues and have local paracrine and autocrine effects. (see hormones for further details). They bind to carrier proteins to extend their half life in the blood. The liver is the main source of IGF-1.
Actions of IGF-1
Increased protein synthesis and increased chondrogenesis, both promoting growth.