Difference between revisions of "Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology"
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | The oral cavity is the first section of the alimentary tract that | + | The oral cavity is the first section of the alimentary tract that receives food. It provides the digestive functions of prehension, [[Mastication|mastication]] and in salivation and also plays a role in the [[Cardiorespiratory System Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|respiratory system]] through oral breathing when the nasopharynx is impaired. The oral cavity or mouth, consists of accessory structures (the [[Salivary Glands - Anatomy & Physiology|salivary glands]]), projecting structures, (the [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]] and the [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]]) and the walls enclosing the oral cavity. |
[[Image:Anatomy of the Oral Cavity.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Oral Cavity Anatomy - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | [[Image:Anatomy of the Oral Cavity.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Oral Cavity Anatomy - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Inside the dental arches, the palate borders dorsally and the [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]], gums and jaw margins laterally. The [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] margins ventrally. The size can be altered by raising or lowering the [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] and the floor of the oral cavity when the mouth is closed. | Inside the dental arches, the palate borders dorsally and the [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]], gums and jaw margins laterally. The [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] margins ventrally. The size can be altered by raising or lowering the [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]] and the floor of the oral cavity when the mouth is closed. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Origin and Innervation== |
The oral cavity originates from ectoderm. It is innervated by the '''trigeminal nerve''' ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V]]). | The oral cavity originates from ectoderm. It is innervated by the '''trigeminal nerve''' ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V]]). | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{OpenPages}} | {{OpenPages}} | ||
[[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:42, 31 August 2014
Introduction
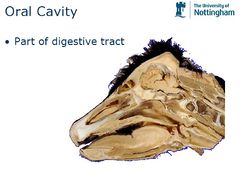
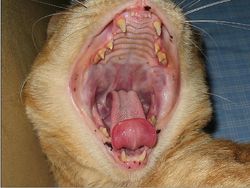
The oral cavity is the first section of the alimentary tract that receives food. It provides the digestive functions of prehension, mastication and in salivation and also plays a role in the respiratory system through oral breathing when the nasopharynx is impaired. The oral cavity or mouth, consists of accessory structures (the salivary glands), projecting structures, (the teeth and the tongue) and the walls enclosing the oral cavity.
Anatomical Boundaries
The oral cavity is bordered rostrally by the lips and caudally by the pharynx at the level of the palatoglossal arches.
Outer Vestibule
The teeth and jaw margins medially and the lips and cheeks laterally. The ramus of the mandible and masseter muscle caudally.
Oral Cavity Proper
Inside the dental arches, the palate borders dorsally and the teeth, gums and jaw margins laterally. The tongue margins ventrally. The size can be altered by raising or lowering the tongue and the floor of the oral cavity when the mouth is closed.
Origin and Innervation
The oral cavity originates from ectoderm. It is innervated by the trigeminal nerve (CN V).
| Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Oral Cavity anatomy Oral Cavity pathology |
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology tutorials about the oral cavity |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662c5506e48488_40123456 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662c5506e7c3c0_22025433 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662c5506eaabb1_58388299
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |