Difference between revisions of "Small Animal Emergency and Critical Care Medicine Q&A 03"
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Template:Manson | ||
| + | |book = Small Animal Emergency and Critical Care Medicine Q&A}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[[Image:ECC 03.jpg|centre|500px]] | [[Image:ECC 03.jpg|centre|500px]] | ||
| Line 11: | Line 15: | ||
|a1= | |a1= | ||
If the cat is dyspneic, oxygen supplementation is warranted. Thoracocentesis is indicated due to the muffled lung and heart sounds. | If the cat is dyspneic, oxygen supplementation is warranted. Thoracocentesis is indicated due to the muffled lung and heart sounds. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1=Thoracocentesis |
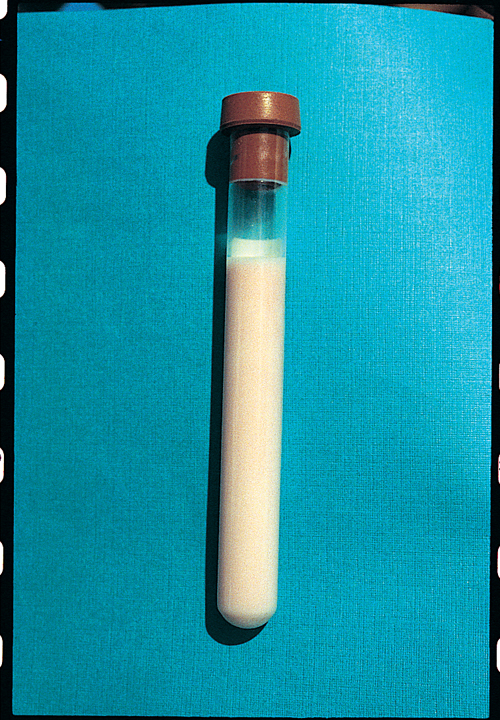
|q2=Thoracocentesis initially relieves the cat’s distress and yields the fluid shown. What is the most likely character of this fluid, and how would you confirm this? | |q2=Thoracocentesis initially relieves the cat’s distress and yields the fluid shown. What is the most likely character of this fluid, and how would you confirm this? | ||
|a2= | |a2= | ||
| Line 17: | Line 21: | ||
The fluid should be analyzed for triglyceride and cholesterol content and low cholesterol content when compared to serum. The cellular components are predominantly small lymphocytes and some neutrophils. Chyle does not settle upon centrifugation, but clears partially when mixed with ether. | The fluid should be analyzed for triglyceride and cholesterol content and low cholesterol content when compared to serum. The cellular components are predominantly small lymphocytes and some neutrophils. Chyle does not settle upon centrifugation, but clears partially when mixed with ether. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2=Chylous Effusion |
|q3=What is your differential diagnosis for conditions associated with this type of fluid production? | |q3=What is your differential diagnosis for conditions associated with this type of fluid production? | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
Chylothorax in cats has been associated with mediastinal lymphoma, heartworm disease, cardiomyopathy and trauma, although the majority are not found to have an obvious underlying cause and are termed idiopathic. | Chylothorax in cats has been associated with mediastinal lymphoma, heartworm disease, cardiomyopathy and trauma, although the majority are not found to have an obvious underlying cause and are termed idiopathic. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3=Chylous Effusion |
|q4=How would you proceed to determine the underlying disease process? | |q4=How would you proceed to determine the underlying disease process? | ||
|a4= | |a4= | ||
The diagnostic approach to determine an underlying cause should include thoracic radiographs (following fluid evacuation by thoracocentesis or tube thoracostomy), CBC, serum biochemistry, heartworm test, FeLV and FIV tests, and echocardiography. | The diagnostic approach to determine an underlying cause should include thoracic radiographs (following fluid evacuation by thoracocentesis or tube thoracostomy), CBC, serum biochemistry, heartworm test, FeLV and FIV tests, and echocardiography. | ||
| − | |l4= | + | |l4=Chylous Effusion#Diagnosis |
|q5=What are the therapeutic options and the prognosis for successful long-term management? | |q5=What are the therapeutic options and the prognosis for successful long-term management? | ||
|a5= | |a5= | ||
| Line 35: | Line 39: | ||
The prognosis is guarded as chylous effusion may not resolve and constrictive pleuritis may develop. | The prognosis is guarded as chylous effusion may not resolve and constrictive pleuritis may develop. | ||
| − | |l5= | + | |l5=Chylous Effusion#Treatment |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:37, 30 September 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Small Animal Emergency and Critical Care Medicine Q&A. |
A five-year-old, castrated male domestic shorthair cat is presented after a 2 month history of slowly progressive dyspnea and anorexia. The owner is concerned today because the cat is coughing. On presentation the cat is tachypneic, with a RR of 60 bpm. Lung sounds are not auscultated in the ventral fields and the heart is muffled. The cat has a choppy, dysynchrous breathing pattern.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is your initial emergency therapeutic plan? | If the cat is dyspneic, oxygen supplementation is warranted. Thoracocentesis is indicated due to the muffled lung and heart sounds. |
Link to Article | |
| Thoracocentesis initially relieves the cat’s distress and yields the fluid shown. What is the most likely character of this fluid, and how would you confirm this? | The appearance of the fluid is consistent with chylous effusion. The fluid should be analyzed for triglyceride and cholesterol content and low cholesterol content when compared to serum. The cellular components are predominantly small lymphocytes and some neutrophils. Chyle does not settle upon centrifugation, but clears partially when mixed with ether. |
Link to Article | |
| What is your differential diagnosis for conditions associated with this type of fluid production? | Chylothorax in cats has been associated with mediastinal lymphoma, heartworm disease, cardiomyopathy and trauma, although the majority are not found to have an obvious underlying cause and are termed idiopathic. |
Link to Article | |
| How would you proceed to determine the underlying disease process? | The diagnostic approach to determine an underlying cause should include thoracic radiographs (following fluid evacuation by thoracocentesis or tube thoracostomy), CBC, serum biochemistry, heartworm test, FeLV and FIV tests, and echocardiography. |
Link to Article | |
| What are the therapeutic options and the prognosis for successful long-term management? | Treatment of the underlying disease process (e.g. improved cardiac function for cardiomyopathy, chemotherapy for lymphosarcoma) often leads to resolution of chylothorax. Medical management involves tube thoracostomy to allow continued drainage, and dietary management with a low fat diet and supplementation with short- or medium-chain fatty acids. Surgical options for therapy include thoracic duct ligation or the implantation of diaphragmatic mesh, pleuroperitoneal or pleurovenous shunts and pleurodesis. The prognosis is guarded as chylous effusion may not resolve and constrictive pleuritis may develop. |
Link to Article | |