Difference between revisions of "Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
Also known as: '''''RAAS''''' | Also known as: '''''RAAS''''' | ||
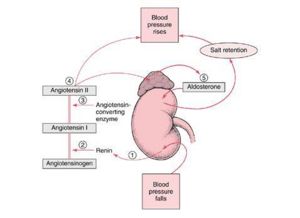
[[Image:RAS.jpg|right|thumb|300px|<small><center> Schematic of the RAAS ©RVC 2008</center></small>]] | [[Image:RAS.jpg|right|thumb|300px|<small><center> Schematic of the RAAS ©RVC 2008</center></small>]] | ||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | + | The RAAS is activated whenever blood flow through the kidneys is reduced and when there are sodium losses in conditions such as diarrhoes, vomiting or excessive sweating. These losses reduce extracellular fluid volume and this in turn reduces arterial blood pressure, which triggers the RAAS system through several different mechanisms. | |
| − | The RAAS is activated whenever blood flow through the kidneys is reduced | ||
==RAAS Activation== | ==RAAS Activation== | ||
| − | |||
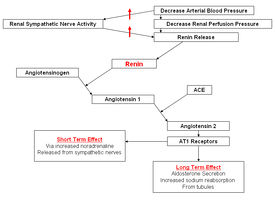
[[Image:raasflowdefap.jpg|right|thumb|275px|<small><center>The Mechanism Behind the RAAS </center></small>]] | [[Image:raasflowdefap.jpg|right|thumb|275px|<small><center>The Mechanism Behind the RAAS </center></small>]] | ||
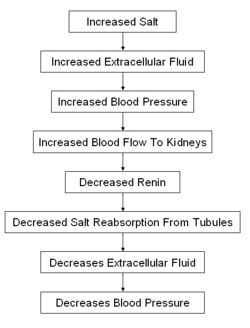
[[Image:raasflowsumap.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center>Summary of the purpose of the RAAS</center></small>]] | [[Image:raasflowsumap.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center>Summary of the purpose of the RAAS</center></small>]] | ||
| − | + | In the event of blood pressure dropping [[Kidney Endocrine Function - Anatomy & Physiology#Renin|Renin]] is secreted due to the decreased stretch of the [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology#Juxtaglomerular Cells|'''juxtaglomerular cells''']] and an increased sympathetic stimulation triggered by the decreased activation of arterial baroreceptors. This enzyme cleaves the alpha glycoprotein '''Angiotensinogen''' which is released from the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]]. This produces '''Angiotensin 1''' which is further converted by [[Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) - Anatomy & Physiology|'''Angiotensin Converting Enzyme''' (ACE)]] to '''Angiotensin II''' mainly in the lungs but to a much lesser extent locally in the kidneys. Angiotensin 2 then works to restore blood pressure by inducing constriction of arterioles, which increases vascular resistance, and constricting veins which reduces vascular volume. In this section we cover its effects on and through the kidneys. | |
| − | In the event of blood pressure dropping | ||
==Effects of Angiotensin II on Blood Pressure== | ==Effects of Angiotensin II on Blood Pressure== | ||
| − | + | '''Angiotensin II''' acts on '''AT1 receptors''' to stimulate the release of '''[[Aldosterone|aldosterone]]''' from the [[Adrenal Glands - Anatomy & Physiology#Adrenal Glands|zona glomerulosa]] of the adrenal glands. This mineralocorticoid increases the reabsorption of sodium and therefore water and chloride from the distal tubule of the kidney, thus helping to increase blood pressure and volume. It also stimulates the thirst center and increases the secretion of [[Pituitary Gland - Anatomy & Physiology #Posterior Pituitary Gland |anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)]] to help increase blood volume. The RAAS allows pressure to return to 50% of baseline within 15 minutes of a significant haemorrhage occuring. | |
| − | '''Angiotensin II''' acts on '''AT1 receptors''' to stimulate the release of '''[[Aldosterone|aldosterone]]''' from the [[Adrenal Glands - Anatomy & Physiology#Adrenal Glands|zona glomerulosa]] of the adrenal glands. This mineralocorticoid increases | ||
==Effects of Angiotensin II on GFR== | ==Effects of Angiotensin II on GFR== | ||
| − | + | If blood pressure drops then [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Glomerular Filtration Rate|glomerular filtration rate (GFR)]] also drops due to reduced blood flow through the kidneys. To restore homeostasis, contraction of the efferent arteriole occurs in response to angiotensin II and the pressure difference between the afferent and efferent arterioles increases, creating greater filtration pressure. When blood pressure falls, therefore there is minimum alteration of GFR. The increased renal resistance to blood flow and the maintained GFR has many advantageous effects. | |
| − | If blood pressure drops then [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Glomerular Filtration Rate|glomerular filtration rate (GFR)]] also drops | ||
===Advantages of Angiotensin II induced Vasoconstriction=== | ===Advantages of Angiotensin II induced Vasoconstriction=== | ||
| − | + | * Increased total peripheral resistance helps to return blood pressure towards normal. (Angiotensin II also has vasoconstrictive effects in multiple organs.) | |
| − | Increased total peripheral resistance helps to return blood pressure towards normal. (Angiotensin II also has vasoconstrictive effects in multiple organs.) The reduced perfusion of the kidneys allows blood to be diverted to the brain and heart. The constriction of the efferent arterioles also reduces hydrostatic pressure in the [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Pressure in the Peritubular Capillaries|peritubular capillaries]], increasing reabsorption of water and salt and helping to restore the extracellular fluid | + | * The reduced perfusion of the kidneys allows blood to be diverted to the brain and heart. |
| + | * The constriction of the efferent arterioles also reduces hydrostatic pressure in the [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Pressure in the Peritubular Capillaries|peritubular capillaries]], increasing reabsorption of water and salt and helping to restore the extracellular fluid ECF and normalising blood pressure. | ||
| + | * The amount of waste excreted is linked to the GFR. Maintaining GFR permits the excretion of waste products such as urea to be maintained. | ||
==Effects of Angiotensin II On Sodium== | ==Effects of Angiotensin II On Sodium== | ||
| − | + | * Induces insertion of Na<sup>+</sup> channels into renal tubules via stimulation of AT<sub>1</sub> receptors. These occur in: | |
| − | Induces insertion of Na<sup>+</sup> channels into renal tubules via stimulation of AT<sub>1</sub> receptors. These occur in: | + | *The proximal tubule, with the addition of: |
| − | + | ** Apical - Na<sup>+</sup>/H<sup>+</sup> exchangers | |
| − | + | ** Basolateral Na<sup>+</sup>(HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup>)<sub>3</sub> and Na<sup>+</sup>K<sup>+</sup>ATPase | |
| − | + | *The thick ascending limb, with the addition of: | |
| − | Apical - Na<sup>+</sup>/H<sup>+</sup> exchangers | + | ** Apical Na<sup>+</sup>/H<sup>+</sup> exchangers and Na<sup>+</sup>K<sup>+</sup>2Cl<sup>-</sup> symporter |
| − | + | *The collecting ducts, with the addition of: | |
| − | + | ** Epithelial Na<sup>+</sup> channels | |
| − | |||
| − | Apical Na<sup>+</sup>/H<sup>+</sup> exchangers and Na<sup>+</sup>K<sup>+</sup>2Cl<sup>-</sup> symporter | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Epithelial Na<sup>+</sup> channels | ||
Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of '''Aldosterone'''. | Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of '''Aldosterone'''. | ||
| − | + | ==Test yourself with the Renal Flashcards== | |
| − | + | [[Important Hormonal Regulators of the Kidney - Renal Flash Cards - Anatomy & Physiology|Hormonal Regulators of the Kidney flashcard]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Kidney Hormonal Regulators]][[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Kidney Hormonal Regulators]][[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
[[Category:Blood Pressure]] | [[Category:Blood Pressure]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:25, 10 December 2010
Also known as: RAAS
Introduction
The RAAS is activated whenever blood flow through the kidneys is reduced and when there are sodium losses in conditions such as diarrhoes, vomiting or excessive sweating. These losses reduce extracellular fluid volume and this in turn reduces arterial blood pressure, which triggers the RAAS system through several different mechanisms.
RAAS Activation
In the event of blood pressure dropping Renin is secreted due to the decreased stretch of the juxtaglomerular cells and an increased sympathetic stimulation triggered by the decreased activation of arterial baroreceptors. This enzyme cleaves the alpha glycoprotein Angiotensinogen which is released from the liver. This produces Angiotensin 1 which is further converted by Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) to Angiotensin II mainly in the lungs but to a much lesser extent locally in the kidneys. Angiotensin 2 then works to restore blood pressure by inducing constriction of arterioles, which increases vascular resistance, and constricting veins which reduces vascular volume. In this section we cover its effects on and through the kidneys.
Effects of Angiotensin II on Blood Pressure
Angiotensin II acts on AT1 receptors to stimulate the release of aldosterone from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal glands. This mineralocorticoid increases the reabsorption of sodium and therefore water and chloride from the distal tubule of the kidney, thus helping to increase blood pressure and volume. It also stimulates the thirst center and increases the secretion of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) to help increase blood volume. The RAAS allows pressure to return to 50% of baseline within 15 minutes of a significant haemorrhage occuring.
Effects of Angiotensin II on GFR
If blood pressure drops then glomerular filtration rate (GFR) also drops due to reduced blood flow through the kidneys. To restore homeostasis, contraction of the efferent arteriole occurs in response to angiotensin II and the pressure difference between the afferent and efferent arterioles increases, creating greater filtration pressure. When blood pressure falls, therefore there is minimum alteration of GFR. The increased renal resistance to blood flow and the maintained GFR has many advantageous effects.
Advantages of Angiotensin II induced Vasoconstriction
- Increased total peripheral resistance helps to return blood pressure towards normal. (Angiotensin II also has vasoconstrictive effects in multiple organs.)
- The reduced perfusion of the kidneys allows blood to be diverted to the brain and heart.
- The constriction of the efferent arterioles also reduces hydrostatic pressure in the peritubular capillaries, increasing reabsorption of water and salt and helping to restore the extracellular fluid ECF and normalising blood pressure.
- The amount of waste excreted is linked to the GFR. Maintaining GFR permits the excretion of waste products such as urea to be maintained.
Effects of Angiotensin II On Sodium
- Induces insertion of Na+ channels into renal tubules via stimulation of AT1 receptors. These occur in:
- The proximal tubule, with the addition of:
- Apical - Na+/H+ exchangers
- Basolateral Na+(HCO3-)3 and Na+K+ATPase
- The thick ascending limb, with the addition of:
- Apical Na+/H+ exchangers and Na+K+2Cl- symporter
- The collecting ducts, with the addition of:
- Epithelial Na+ channels
Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of Aldosterone.