Difference between revisions of "Avian Liver - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
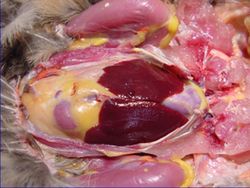
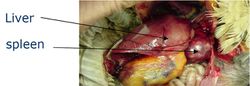
| − | The liver has | + | The liver has 2 lobes. It is dark brown coloured (except just after hatching where it is yellow). The right lobe larger than left lobe. It is positioned ventral and caudal to the [[Heart - Anatomy & Physiology|heart]] (as there is no diaphragm). It is closely associated to the '''[[Proventriculus - Anatomy & Physiology|proventriculus]]''' and [[Spleen - Anatomy & Physiology|spleen]]. It has a thin capsule and indistinct lobation. 2 bile ducts enter the distal '''[[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]]''', one from each lobe of the liver. The duct from the right lobe is connected to the '''[[Gall Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology|gallbladder]]'''. Hepatic lobules are indistinct (except near hilus) due to a lack of '''perilobular connective tissue'''. Avian bile aids the emulsification of fats and contains amylase and lipase. |
[[Image:Anatomy of the Avian Liver.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Anatomy of the Liver(Avian)- Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Anatomy of the Avian Liver.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Anatomy of the Liver(Avian)- Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
| − | + | *Polyhedral and angular cells | |
| − | + | *Larger cells than in mammals | |
| + | |||
| + | *Large, spherical nucleus | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Base of cell forms a wall of the sinusoid | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cell apices communicate with the bile canaliculi | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Granular cytoplasm | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Liver cords form columns around the interlobular bile capillary. The cell arrangement is simpler than in mammals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Sinusoids anastamose freely | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Kupfer cells present | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reticular fibres support the liver cords | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Elastic fibres in the capsule and vessels | ||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Test yourself with the [[The Avian Alimentary Tract - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards|Avian Alimentary Tract Flashcards]]''' | ||
'''Click here for more information on [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology]]''' | '''Click here for more information on [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology]]''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Avian Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Avian Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:To Do - AimeeHicks]][[Category:To Do - AP Review]] |
Revision as of 18:27, 10 December 2010
Structure
The liver has 2 lobes. It is dark brown coloured (except just after hatching where it is yellow). The right lobe larger than left lobe. It is positioned ventral and caudal to the heart (as there is no diaphragm). It is closely associated to the proventriculus and spleen. It has a thin capsule and indistinct lobation. 2 bile ducts enter the distal duodenum, one from each lobe of the liver. The duct from the right lobe is connected to the gallbladder. Hepatic lobules are indistinct (except near hilus) due to a lack of perilobular connective tissue. Avian bile aids the emulsification of fats and contains amylase and lipase.
Function
See liver function.
Vasculature
See liver vasculature.
Innervation
See liver innervation.
Lymphatics
See liver lymphatics.
Gallbladder- Species Differences
Pigeons and parrots lack a gall bladder.
Histology
- Polyhedral and angular cells
- Larger cells than in mammals
- Large, spherical nucleus
- Base of cell forms a wall of the sinusoid
- Cell apices communicate with the bile canaliculi
- Granular cytoplasm
- Liver cords form columns around the interlobular bile capillary. The cell arrangement is simpler than in mammals.
- Sinusoids anastamose freely
- Kupfer cells present
- Reticular fibres support the liver cords
- Elastic fibres in the capsule and vessels
Links
Test yourself with the Avian Alimentary Tract Flashcards
Click here for more information on Liver - Anatomy & Physiology