Difference between revisions of "Actinobacillosis - Cattle"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Also known as: '''''Wooden tongue''' | Also known as: '''''Wooden tongue''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Caused by: '''''Actinobacillus lignieresii''''' | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 11: | ||
==Signalment== | ==Signalment== | ||
Occurs in cattle and sheep of all ages but particularly seen in young beef breeds especially sucklers on poor forage. | Occurs in cattle and sheep of all ages but particularly seen in young beef breeds especially sucklers on poor forage. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Clinical Signs== | ==Clinical Signs== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
In contrast to foot and mouth cases are nearly always sporadic. | In contrast to foot and mouth cases are nearly always sporadic. | ||
| − | Occasionally generalised infections occur and the bacteria may affect soft tissue anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract including the [[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]], [[Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] and [[Oesophageal Groove|oesophageal groove]]. | + | Occasionally generalised infections occur and the bacteria may affect soft tissue anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract including the [[Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology|rumen]], [[Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]] and [[Oesophageal Groove|oesophageal groove]]. The lungs may become affected due to aspiration of the agent. The bacteria often spread from the site of infection to lymphatics, and may cause pyogranulomatous lymphadenitis. |
Additionally a cutaneous form of the disease has been reported where ulcers and nodules are present in the subcutaneous tissue containing yellow-green pus. | Additionally a cutaneous form of the disease has been reported where ulcers and nodules are present in the subcutaneous tissue containing yellow-green pus. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sheep produce abscesses with thick walls. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Feeding is impaired causing loss of condition. Infection in the oesophageal groove can cause tympany and enlargement of the retropharyngeal lymph node, causing difficulty in swallowing and breathing. | ||
==Pathology== | ==Pathology== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 32: | ||
This type of lesion is caused by the host response to the pathogen, rather than directly a pathogen effect. | This type of lesion is caused by the host response to the pathogen, rather than directly a pathogen effect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contamination of the environment occurs via ulcerating lesions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| + | A diagnosis can be made on history and clinical signs, including induration of the tongue. Tissue sections may demonstrate pyogranulomatous foci containing club colonies. Gram negative rods may be present in smears from exudates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The organism can be cultured on blood agar and MacConkey agar, incubated for 24-72 hours. The bacteria on blood agar form small, sticky, non-haemolytic colonies. The MacConkey agar allows slow lactose fermentation. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| − | [[Antibiotics|Antibiotics]] are effective and [[Aminoglycosides#Streptomycin|streptomycin]] is recommended | + | [[Antibiotics|Antibiotics]] are effective and [[Aminoglycosides#Streptomycin|streptomycin]] is recommended intramuscularly for 10 days. Animals that do not respond to treatment in two weeks should be slaughtered. Potentiated sulphonamides or a penicillin/streptomycin combination can be used. |
| + | |||
| + | Sodium iodide parenterally, or potassium iodide orally have also been successful. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rough feed should be avoided | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 61: | ||
Andrews, A.H, Blowey, R.W, Boyd, H and Eddy, R.G. (2004) '''Bovine Medicine''' (Second edition), ''Blackwell Publishing'' | Andrews, A.H, Blowey, R.W, Boyd, H and Eddy, R.G. (2004) '''Bovine Medicine''' (Second edition), ''Blackwell Publishing'' | ||
| − | [[Category:Tongue_-_Pathology]][[Category:Cattle]] | + | [[Category:Tongue_-_Pathology]][[Category:Alimentary Diseases - Cattle]] |
[[Category:Sheep]] | [[Category:Sheep]] | ||
[[Category:Expert_Review]] | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 10 January 2011
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Also known as: Wooden tongue
Caused by: Actinobacillus lignieresii
Description
An infectious disease caused by the gram-negative coccobacilli Actinobacillus lignieresii. Characterised by inflammation of the soft tissues of the head especially the tongue and pharangeal lymph nodes of cattle and sheep. The causal agent is widespread in the environment and part of the normal commensal flora of the gastrointestinal mucosa, it gains access to the tongue via small abrasions. It can be a progressive disease of low virulence but high persistence so the animal may stop eating and eventually die if not treated.
Signalment
Occurs in cattle and sheep of all ages but particularly seen in young beef breeds especially sucklers on poor forage.
Clinical Signs
Often begins like foot and mouth disease. Animals are dull, have difficulty masticating, are inappetent and salivate profusely. The tongue is inflammed, hard and painful with small areas of ulceration along its sides. Often the tongue is described like a lump of wood hence the name and may increase in size by up to 50%.
In contrast to foot and mouth cases are nearly always sporadic.
Occasionally generalised infections occur and the bacteria may affect soft tissue anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract including the rumen, reticulum and oesophageal groove. The lungs may become affected due to aspiration of the agent. The bacteria often spread from the site of infection to lymphatics, and may cause pyogranulomatous lymphadenitis.
Additionally a cutaneous form of the disease has been reported where ulcers and nodules are present in the subcutaneous tissue containing yellow-green pus.
Sheep produce abscesses with thick walls.
Feeding is impaired causing loss of condition. Infection in the oesophageal groove can cause tympany and enlargement of the retropharyngeal lymph node, causing difficulty in swallowing and breathing.
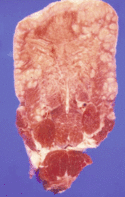
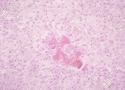
Pathology
The tongue becomes fibrous with raised red nodules (2-3mm across) along the surface. This lesion is a pyogenic granuloma containing large numbers of the bacterial microcolonies surrounded by clublike spicules of calcium phosphate which look like sulphur granules.
This type of lesion is caused by the host response to the pathogen, rather than directly a pathogen effect.
Contamination of the environment occurs via ulcerating lesions.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis can be made on history and clinical signs, including induration of the tongue. Tissue sections may demonstrate pyogranulomatous foci containing club colonies. Gram negative rods may be present in smears from exudates.
The organism can be cultured on blood agar and MacConkey agar, incubated for 24-72 hours. The bacteria on blood agar form small, sticky, non-haemolytic colonies. The MacConkey agar allows slow lactose fermentation.
Treatment
Antibiotics are effective and streptomycin is recommended intramuscularly for 10 days. Animals that do not respond to treatment in two weeks should be slaughtered. Potentiated sulphonamides or a penicillin/streptomycin combination can be used.
Sodium iodide parenterally, or potassium iodide orally have also been successful.
Rough feed should be avoided
Prognosis
If treatment is initiated early it is often successful however if treatment is delayed beyond 2 weeks the prognosis is much poorer.
Literature Search
Use these links to find recent scientific publications via CAB Abstracts (log in required unless accessing from a subscribing organisation).
Actinobacillosis/wooden tongue publications
References
Andrews, A.H, Blowey, R.W, Boyd, H and Eddy, R.G. (2004) Bovine Medicine (Second edition), Blackwell Publishing