Difference between revisions of "Tritrichomonas foetus"
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
|kingdom =Protista | |kingdom =Protista | ||
| Line 24: | Line 23: | ||
The protozoa resides on the surface and in the lumen of the female reproductive tract and in the crypt of penile epithelial cells. Transmission is achieved from infected individuals during mating and direct contact. | The protozoa resides on the surface and in the lumen of the female reproductive tract and in the crypt of penile epithelial cells. Transmission is achieved from infected individuals during mating and direct contact. | ||
| − | ''T. foetus'' has no known cyst stage, although carrier cows occur very rarely and the pathogenesis of the carrier state is unknown. Therefore, trophozoites replicate simply by binary fission. It is thought that ''T. foetus'' feeds from host lipids and fatty acids <ref>Beach DH, Holz GGJr, Singh BN, Lindmark DG, 1991. '''Phospholipid metabolism of cultured ''Trichomonas vaginalis'' and | + | ''T. foetus'' has no known cyst stage, although carrier cows occur very rarely and the pathogenesis of the carrier state is unknown. Therefore, trophozoites replicate simply by binary fission. It is thought that ''T. foetus'' feeds from host lipids and fatty acids <ref>Beach DH, Holz GGJr, Singh BN, Lindmark DG, 1991. '''Phospholipid metabolism of cultured ''Trichomonas vaginalis'' and Tritrichomonas foetus'''. ''Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology'', 44(1:97-108;19)</ref> |
''T. foetus'' is sometimes isolated from foetal gut and lung but this is unlikely to be due to invasion and more likely due to swallowing or inhalation of amniotic fluid in utero. | ''T. foetus'' is sometimes isolated from foetal gut and lung but this is unlikely to be due to invasion and more likely due to swallowing or inhalation of amniotic fluid in utero. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 38: | ||
''T. foetus'' mainly causes [[Diarrhoea|diarrhoea]] by colonisation of the large intestine. Recovery is slow but longterm prognosis is good. Reports of resistance and success are available for most anthelmintic and antibiotic therapies. | ''T. foetus'' mainly causes [[Diarrhoea|diarrhoea]] by colonisation of the large intestine. Recovery is slow but longterm prognosis is good. Reports of resistance and success are available for most anthelmintic and antibiotic therapies. | ||
| − | ==Other | + | ==Other ''Tritrichomonas'' spp.== |
| − | + | Others such as ''Trichomonas suis'' and ''Trichomonas vaginalis'' reside as commensals, usually in the gastrointestinal tract of other species such as pigs and guinea pigs respectively. ''[[Trichomonas gallinae]]'' occurs in birds. | |
| Line 53: | Line 52: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Animal Health & Production Compendium, '''Tritrichomonas datasheet''', accessed 02/06/2011 @ http://www.cabi.org/ahpc/ | ||
Feline Advisory Bureau, '''Tritrichomonas infection in cats''', accessed 02/06/2011 @ http://www.fabcats.org/breeders/infosheets/tritrichomonas/ | Feline Advisory Bureau, '''Tritrichomonas infection in cats''', accessed 02/06/2011 @ http://www.fabcats.org/breeders/infosheets/tritrichomonas/ | ||
| Line 58: | Line 59: | ||
Wright, I.(2010) '''Tritrichomonas foetus: Jumping the Species Barrier''', ''UK Vet'', Vol 15, 1-3. | Wright, I.(2010) '''Tritrichomonas foetus: Jumping the Species Barrier''', ''UK Vet'', Vol 15, 1-3. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
[[Category:Miscellaneous_Protozoa]] | [[Category:Miscellaneous_Protozoa]] | ||
| − | [[Category:CABI Expert Review | + | [[Category:CABI Expert Review]] |
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:25, 19 June 2011
| Tritrichomonas foetus | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Protista |
| Phylum | Protozoa |
| Family | Trichomonadidae |
| Genus | Tritrichomonas |
| Species | T. foetus and more |
Also known as: Trichomonas foetus — Trichomonas fetus
Introduction
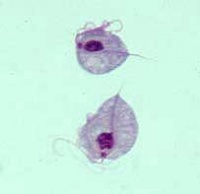
Tritrichomonas foetus is a protozoal pathogen causing disease primarily in cattle and felids. It is identifiable by its pear-like shape, three anterior flagellae (recurrent flagellum) and an undulating membrane on one side.
Lifecycle and Transmission
Cattle
Tritrichomonas foetus is a venereal disease in cattle causing early embryonic death and abortion.
The protozoa resides on the surface and in the lumen of the female reproductive tract and in the crypt of penile epithelial cells. Transmission is achieved from infected individuals during mating and direct contact.
T. foetus has no known cyst stage, although carrier cows occur very rarely and the pathogenesis of the carrier state is unknown. Therefore, trophozoites replicate simply by binary fission. It is thought that T. foetus feeds from host lipids and fatty acids [1]
T. foetus is sometimes isolated from foetal gut and lung but this is unlikely to be due to invasion and more likely due to swallowing or inhalation of amniotic fluid in utero.
Cats
Tritrichomonas foetus is transmitted via the faecal: oral route in cats. Behaviours such as grooming may aid transmission by direct contact. The venereal route is unproven in cats.
Pathogenesis
Cattle
Proteinases secreted by T. foetus degrade substrates such as fibrinogen, albumin and immunoglobulins, thus altering the biological environment and resulting in embryonic death. Pyometra is occasionally observed in females but males show no clinical signs. For more information see Trichomonosis - Cattle.
Cats
T. foetus mainly causes diarrhoea by colonisation of the large intestine. Recovery is slow but longterm prognosis is good. Reports of resistance and success are available for most anthelmintic and antibiotic therapies.
Other Tritrichomonas spp.
Others such as Trichomonas suis and Trichomonas vaginalis reside as commensals, usually in the gastrointestinal tract of other species such as pigs and guinea pigs respectively. Trichomonas gallinae occurs in birds.
Relevant Links: Trichomonosis - Cattle
| Tritrichomonas foetus Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Protozoa Flashcards Tritrichomonas foetus Flashcards |
References
- ↑ Beach DH, Holz GGJr, Singh BN, Lindmark DG, 1991. Phospholipid metabolism of cultured Trichomonas vaginalis and Tritrichomonas foetus. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 44(1:97-108;19)
The Animal Health & Production Compendium, Tritrichomonas datasheet, accessed 02/06/2011 @ http://www.cabi.org/ahpc/
Feline Advisory Bureau, Tritrichomonas infection in cats, accessed 02/06/2011 @ http://www.fabcats.org/breeders/infosheets/tritrichomonas/
Wright, I.(2010) Tritrichomonas foetus: Jumping the Species Barrier, UK Vet, Vol 15, 1-3.
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |