Difference between revisions of "Immunoglobulin A"
(→Links) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
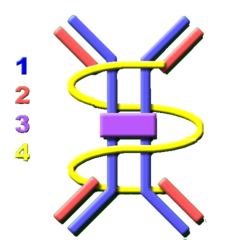
[[Image:LH sIgA.png|thumb|right|250px|<p>1 = Heavy Chain</p><p>2 = Light chain</p><p>3 = J chain</p><p>4 = Secretory component</p>]] | [[Image:LH sIgA.png|thumb|right|250px|<p>1 = Heavy Chain</p><p>2 = Light chain</p><p>3 = J chain</p><p>4 = Secretory component</p>]] | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
IgA is a dimeric immunoglobulin that is produced by the joining of two IgA monomers by a ‘J’ chain. Its heavy chain is type alpha(α). There are two types of IgA: | IgA is a dimeric immunoglobulin that is produced by the joining of two IgA monomers by a ‘J’ chain. Its heavy chain is type alpha(α). There are two types of IgA: | ||
| − | '''Type 1''' - Non-secretory and found in blood. | + | :'''Type 1''' - Non-secretory and found in blood. |
| − | + | :'''Type 2''' – Secretory and secreted on mucosal surfaces. | |
| − | '''Type 2''' – Secretory and secreted on mucosal surfaces. | ||
Only Type 2 contains the secretory component, a glycoprotein, which protects IgA from digestion and mediates its active transport across mucosal epithelium. The secretory component is added to salivary IgA by mucosal epithelial cells in the salivary glands, while in the alimentary tract, the secretory component is produced by the enterocytes. | Only Type 2 contains the secretory component, a glycoprotein, which protects IgA from digestion and mediates its active transport across mucosal epithelium. The secretory component is added to salivary IgA by mucosal epithelial cells in the salivary glands, while in the alimentary tract, the secretory component is produced by the enterocytes. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| − | IgA is preferentially produced at mucosal surfaces by plasma cells. | + | IgA is preferentially produced at mucosal surfaces by plasma cells. IL-4 produced by T cells (T<sub>H</sub>2) and mast cells, signals B cells to differentiate into plasma cells. IL-10 and CD40 interaction with T<sub>H</sub>2 cells then causes class switching to produce IgA. |
Salivary IgA is produced by plasma cells in connective tissue around salivary glands. IgA in the alimentary system is produced by plasma cells in the lamina propria. It is the only Ig that can cross into the lumen of the alimentary tract. During lactation, the levels of IgA increase so that it becomes the predominant immunoglobulin in the milk (more than [[IgG]]). Mucosal epithelium have a “poly Ig receptor” and this bind to the J chain on the IgA, and allows IgA to travel across the cell. IgA crosses the cell in a transport vesicle and is released by exocytosis. | Salivary IgA is produced by plasma cells in connective tissue around salivary glands. IgA in the alimentary system is produced by plasma cells in the lamina propria. It is the only Ig that can cross into the lumen of the alimentary tract. During lactation, the levels of IgA increase so that it becomes the predominant immunoglobulin in the milk (more than [[IgG]]). Mucosal epithelium have a “poly Ig receptor” and this bind to the J chain on the IgA, and allows IgA to travel across the cell. IgA crosses the cell in a transport vesicle and is released by exocytosis. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
[[Immunoglobulin M|Immunoglobulin M]] | [[Immunoglobulin M|Immunoglobulin M]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | {{Jim Bee 2007}} | ||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
[[Category:Immunoglobulins]] | [[Category:Immunoglobulins]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:A&P Done]] |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 16:04, 2 July 2012
Overview
Shortened to IgA.
IgA is present at low concentrations in plasma, and has minimal function inside the body. However, it is specially adapted for action at mucosal surfaces and as such, is present in high concentrations in mucosal secretions and in colostrum (and milk). In many species (dogs, cats and pigs), it is the major antibody in mucosal secretions.
Structure
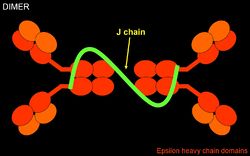
IgA is a dimeric immunoglobulin that is produced by the joining of two IgA monomers by a ‘J’ chain. Its heavy chain is type alpha(α). There are two types of IgA:
- Type 1 - Non-secretory and found in blood.
- Type 2 – Secretory and secreted on mucosal surfaces.
Only Type 2 contains the secretory component, a glycoprotein, which protects IgA from digestion and mediates its active transport across mucosal epithelium. The secretory component is added to salivary IgA by mucosal epithelial cells in the salivary glands, while in the alimentary tract, the secretory component is produced by the enterocytes.
Production
IgA is preferentially produced at mucosal surfaces by plasma cells. IL-4 produced by T cells (TH2) and mast cells, signals B cells to differentiate into plasma cells. IL-10 and CD40 interaction with TH2 cells then causes class switching to produce IgA.
Salivary IgA is produced by plasma cells in connective tissue around salivary glands. IgA in the alimentary system is produced by plasma cells in the lamina propria. It is the only Ig that can cross into the lumen of the alimentary tract. During lactation, the levels of IgA increase so that it becomes the predominant immunoglobulin in the milk (more than IgG). Mucosal epithelium have a “poly Ig receptor” and this bind to the J chain on the IgA, and allows IgA to travel across the cell. IgA crosses the cell in a transport vesicle and is released by exocytosis.
Function
IgA binds to antigens and prevents agents from adhering to the epithelium, and as adhesion is a prerequisite to establishing infection, it prevents infection. Agents include toxins, bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. As IgA resists proteolytic digestion, it is able to function well in the gut, although some bacteria have proteases to overcome this resistance. IgA is a "non-inflammatory" isotype, as it does not activate complement by the classical pathway, and has no role in opsonisation. This helps to preserve the mucosal integrity and function. Ruminant mucosal IgG subclass similarly is also a poor complement activator.
Links
| Originally funded by the RVC Jim Bee Award 2007 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6940441b1035c1_64888101 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6940441b19af05_58512222 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6940441b1fd780_45771236
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |