Difference between revisions of "Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
Thepollycat (talk | contribs) m (→Links: Videos added) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | A function of the omasum is absorption. Food enters omasum at second biphasic reticular contraction. The omasum itself has biphasic contractions. The first contraction expels fluid by squeezing the ingesta from the omasal canal between the lamellae. The second contraction expels solids by mass contraction of the omasum. Contractions are slower than the rumenoreticular contractions (see [[Rumination|rumination]]). Food is squeezed between lamellae. | + | A function of the omasum is absorption. Food enters omasum at second biphasic reticular contraction. The omasum itself has biphasic contractions. The first contraction expels fluid by squeezing the ingesta from the omasal canal between the lamellae. The second contraction expels solids by mass contraction of the omasum. Contractions are slower than the rumenoreticular contractions (see [[Rumination - Anatomy & Physiology|rumination]]). Food is squeezed between lamellae. |
==Vasculature== | ==Vasculature== | ||
| − | The blood supply to the omasum includes the '''cranial mesenteric artery''', the '''left gastric''' and | + | The blood supply to the omasum includes the '''cranial mesenteric artery''', the '''caudal mesenteric artery''' and the '''left gastric''' and '''left gastroepiploic arteries'''. |
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | {{OpenPages}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Stomach - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
[[Category:A&P Done]] | [[Category:A&P Done]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:03, 21 August 2012
Introduction
The omasum is the third chamber in the ruminant stomach. It lies within the intrathoracic part of the abdomen so cannot be palpated manually. Instead it is examined by ausculation. The omasum has biphasic contractions which squeeze fluid out of the food before allowing the ingesta to continue into the abomasum. Absorption of volatile fatty acids continues in the omasum.
Structure
The omasum is right of the midline. The Rumen and reticulum are located to the left and the liver and body wall to the right. The omasum is covered by lesser omentum and is bilaterally flattened. It is located at ribs 8-11. The lower pole has an extensive connection to the fundic region of the abomasum. The omasal canal is formed between the end of the laminae and the omasal groove, part of the gastric groove between the cardia and the pyloric sphincter. The omasal canal passes between the reticulum and the abomasum. Its mucosa is smooth except for particularly large papillae around the reticulo-omasal opening. The omaso-abomasal opening is a large and oval, partly covered by overhanging abomasal folds.
Function
A function of the omasum is absorption. Food enters omasum at second biphasic reticular contraction. The omasum itself has biphasic contractions. The first contraction expels fluid by squeezing the ingesta from the omasal canal between the lamellae. The second contraction expels solids by mass contraction of the omasum. Contractions are slower than the rumenoreticular contractions (see rumination). Food is squeezed between lamellae.
Vasculature
The blood supply to the omasum includes the cranial mesenteric artery, the caudal mesenteric artery and the left gastric and left gastroepiploic arteries.
Innervation
The omasum is innervated by the dorsal vagus nerve (CN X) (most important) and the ventral vagus nerve.
Lymphatics
There are numerous small lymph nodes that are scattered in the omasal curvatures. The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the cardia and the omasum, then to the cistera chyli.
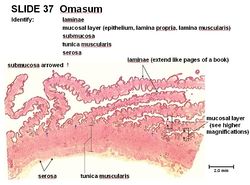
Histology
The omasum has a keratinised stratified squamous epithelium. It is firm in texture and can vary in size. Lamellae thrown into leaves divide the lumen into narrow and uniform recesses. It contains no glands.
The papillae of the omasum are mostly small and lenticular, although some can be large and conical. The circular tunica muscularis extends into papillae of long laminae and the lamina muscualris extends into papillae encircling the tunica muscularis. The omasum has 3 smooth muscle layers in the papillae therefore they are very motile.
Species Differences
Small Ruminant
The small ruminants have a smaller omasum, which is bean shaped.
Bovine
The lower pole of the omasum contacts the abdominal floor below the costal arch.
Links
Click here for information on rumen
Click here for information on reticulum
Click here for information on abomasum
| Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Omasum Flashcards |
 Selection of relevant videos |
Bovine omasum potcast Ovine omasum and abomasum potcast Sections of the interior of the complex ruminant stomach potcast Ruminant forestomach structure dissection |
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology of the ruminant gastrointestinal tract |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a519c2dc1ba6_01840458 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a519c2e77c02_07889912 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a519c2f1ecc5_96856805
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |