Difference between revisions of "Periodontal Surgery - Small Animal"
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | Periodontal surgery is the term used for certain specific surgical techniques aimed at '''preserving the periodontium'''. Periodontal surgery techniques include closed curettage, gingivoplasty, various flap techniques, osseous surgery, guided tissue regeneration and, of course, implants. The techniques create accessibility for professional [[ | + | Periodontal surgery is the term used for certain specific surgical techniques aimed at '''preserving the periodontium'''. Periodontal surgery techniques include closed curettage, gingivoplasty, various flap techniques, osseous surgery, guided tissue regeneration and, of course, implants. The techniques create accessibility for professional [[scaling and polishing]], and establish a gingival morphology that facilitates plaque control by home care regimes. Some techniques are aimed at regeneration of periodontal attachment lost, e.g. guided tissue regeneration. |
| − | Periodontal surgery is never | + | Periodontal surgery is never first-line treatment for [[Periodontal Disease|periodontal disease]]. Conservative management of periodontal disease (i.e. thorough supra- and subgingival scaling, rootplaning and polishing), in combination with [[Oral Hygiene - Small Animal|daily meticulous home care]], is always the first step. If a client cannot maintain good dental hygiene for their pet then, in the interest of the well being of the animal, there is no indication for periodontal surgery. |
The main objective of periodontal surgery is to contribute to the preservation of the periodontium by facilitating plaque removal and plaque control. Periodontal surgery can help achieve this by: | The main objective of periodontal surgery is to contribute to the preservation of the periodontium by facilitating plaque removal and plaque control. Periodontal surgery can help achieve this by: | ||
| − | #Creating accessibility for professional scaling and root planing | + | #Creating accessibility for professional scaling and root planing |
| − | #Establishing a [[Gingiva|gingival]] morphology that facilitates plaque control by home care regimes | + | #Establishing a [[Gingiva|gingival]] morphology that facilitates plaque control by home care regimes |
| − | #In addition, periodontal surgery may aim to regenerate | + | #In addition, periodontal surgery may aim to regenerate lost periodontal attachment |
==Gingivoplasty== | ==Gingivoplasty== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
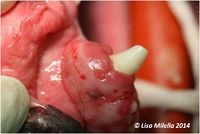
Gingivoplasty is the '''removal of gingival pockets''' by excision of the gingiva, or recontouring the gingiva to its proper anatomical form. It is indicated for the management of [[Gingival Hyperplasia|gingival hyperplasia]]. In this situation the excessive gingival tissue should be excised, leaving a normal depth of healthy gingiva. | Gingivoplasty is the '''removal of gingival pockets''' by excision of the gingiva, or recontouring the gingiva to its proper anatomical form. It is indicated for the management of [[Gingival Hyperplasia|gingival hyperplasia]]. In this situation the excessive gingival tissue should be excised, leaving a normal depth of healthy gingiva. | ||
| − | The procedure for | + | The procedure for gingivoplasty is as follows: |
#Pocket depths are measured with a graduated [[Periodontal Probe|periodontal probe]]. The probe is withdrawn from the pocket and held against the outer surface of the gingiva to show the depth of the pocket and a bleeding point made. This is repeated along the circumference of the tooth. | #Pocket depths are measured with a graduated [[Periodontal Probe|periodontal probe]]. The probe is withdrawn from the pocket and held against the outer surface of the gingiva to show the depth of the pocket and a bleeding point made. This is repeated along the circumference of the tooth. | ||
#A beveled incision, using either a scalpel blade (No. 11 or 15) or electrosurgery is made, joining the bleeding points and recreating the scalloped edge of the normal gingival anatomy. The beveled incision is directed towards the base of the pocket or to a level slightly coronal to the apical extension of the junctional epithelium. When using electrosurgery the operator should allow for a 1 mm slough postoperatively. The electrode should be activated at the minimal effective setting in cut mode and stroked across the [[gingiva]] at the required angle. The cut surface should be pink and not bleeding if the setting is correct. Blanched tissue indicates that the setting is too high and should be reduced. To avoid overheating the tooth the electrode should not be applied to the gingiva around the same tooth for more than 5 seconds. | #A beveled incision, using either a scalpel blade (No. 11 or 15) or electrosurgery is made, joining the bleeding points and recreating the scalloped edge of the normal gingival anatomy. The beveled incision is directed towards the base of the pocket or to a level slightly coronal to the apical extension of the junctional epithelium. When using electrosurgery the operator should allow for a 1 mm slough postoperatively. The electrode should be activated at the minimal effective setting in cut mode and stroked across the [[gingiva]] at the required angle. The cut surface should be pink and not bleeding if the setting is correct. Blanched tissue indicates that the setting is too high and should be reduced. To avoid overheating the tooth the electrode should not be applied to the gingiva around the same tooth for more than 5 seconds. | ||
#The incised tissues are removed using a [[Dental Scaling Equipment|curette or a scaler]]. Remaining tissue tags are cut with a curette or a pair of scissors. | #The incised tissues are removed using a [[Dental Scaling Equipment|curette or a scaler]]. Remaining tissue tags are cut with a curette or a pair of scissors. | ||
| − | #Hemorrhage is controlled with gauze swabs and digital pressure. The [[ | + | #Hemorrhage is controlled with gauze swabs and digital pressure. The [[Enamel Organ#Crown|crown]] and exposed [[Enamel Organ#Root|root]] surfaces are then scaled and polished. |
The postoperative phase is uncomfortable and [[Analgesia for Oral Disease|analgesics]] are indicated for the first few days. The healing of a gingivoplasty wound is similar to that of a simple soft tissue wound. Plaque control is important to ensure adequate healing. | The postoperative phase is uncomfortable and [[Analgesia for Oral Disease|analgesics]] are indicated for the first few days. The healing of a gingivoplasty wound is similar to that of a simple soft tissue wound. Plaque control is important to ensure adequate healing. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
The advantages of flap operations include: | The advantages of flap operations include: | ||
| − | * | + | *Existing keratinized [[gingiva]] is preserved. |
| − | * | + | *There is increased visualization of the defect and enabling thorough debridement of dental deposits and inflamed soft tissues. |
| − | * | + | *The marginal bone is exposed, whereby the morphology of bony defects can be identified and the proper treatment carried out. |
*The flap can either be replaced at its original position or shifted [[Dental Terminology|apically or coronally]], thereby making it possible to adjust the gingival margin to the local conditions. | *The flap can either be replaced at its original position or shifted [[Dental Terminology|apically or coronally]], thereby making it possible to adjust the gingival margin to the local conditions. | ||
*The flap procedure preserves the oral epithelium. | *The flap procedure preserves the oral epithelium. | ||
| − | + | The design of the periodontal flap will depend on the type of pocket. The most common flap used in veterinary oral surgery is usually a full flap, or one with vertical releasing incisions allowing for increased exposure, but considered more invasive. Another commonly used flap for periodontal surgery is the envelope flap. This is created along the arcade, without vertical incisions. Periodontal flaps are typically made full thickness, which means the periosteum is released from the underlying hard tissue and kept with the flap. | |
| − | '''Envelope | + | '''Envelope flap:''' The sulcal incision is different from any other incision used in the oral cavity because the incision not only releases the gingiva from the underlying hard tissues but also excises the diseased pocket epithelium and granulation tissue. Furthermore, the sum of these incisions used to create the flap, creates a sharp marginal edge of the resulting flap, which allows for better apposition when it is replaced. |
| − | The extent of the flap should always be determined prior to any incision and all [[Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]] in the area affected and needing treatment should be involved from the beginning to allow for a smooth incision. In most cases, carrying the incision a little mesial and distal | + | The extent of the flap should always be determined prior to any incision and all [[Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]] in the area affected and needing treatment should be involved from the beginning to allow for a smooth incision. In most cases, carrying the incision a little mesial and distal of the target tooth is necessary for adequate visualization and access . |
| − | The '''full flap''' is created when further exposure is necessary or the flap is to be repositioned (coronally, apically, or laterally). It is a more invasive procedure with increased complication potential (e.g. hemorrhage and dehiscence) and therefore should not be performed when an envelope flap is sufficient. | + | The '''full flap''' is created when further exposure is necessary or the flap is to be repositioned (coronally, apically, or laterally). It is a more invasive procedure with increased complication potential (e.g., hemorrhage and dehiscence) and therefore should not be performed when an envelope flap is sufficient. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {{ | + | {{unfinished}} |
| − | + | [[Category:Dental Surgical Procedures]][[Category:To Do - Dentistry preMars]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Dental Surgical Procedures]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 10 April 2014
Introduction
Periodontal surgery is the term used for certain specific surgical techniques aimed at preserving the periodontium. Periodontal surgery techniques include closed curettage, gingivoplasty, various flap techniques, osseous surgery, guided tissue regeneration and, of course, implants. The techniques create accessibility for professional scaling and polishing, and establish a gingival morphology that facilitates plaque control by home care regimes. Some techniques are aimed at regeneration of periodontal attachment lost, e.g. guided tissue regeneration.
Periodontal surgery is never first-line treatment for periodontal disease. Conservative management of periodontal disease (i.e. thorough supra- and subgingival scaling, rootplaning and polishing), in combination with daily meticulous home care, is always the first step. If a client cannot maintain good dental hygiene for their pet then, in the interest of the well being of the animal, there is no indication for periodontal surgery.
The main objective of periodontal surgery is to contribute to the preservation of the periodontium by facilitating plaque removal and plaque control. Periodontal surgery can help achieve this by:
- Creating accessibility for professional scaling and root planing
- Establishing a gingival morphology that facilitates plaque control by home care regimes
- In addition, periodontal surgery may aim to regenerate lost periodontal attachment
Gingivoplasty
Gingivoplasty is the removal of gingival pockets by excision of the gingiva, or recontouring the gingiva to its proper anatomical form. It is indicated for the management of gingival hyperplasia. In this situation the excessive gingival tissue should be excised, leaving a normal depth of healthy gingiva.
The procedure for gingivoplasty is as follows:
- Pocket depths are measured with a graduated periodontal probe. The probe is withdrawn from the pocket and held against the outer surface of the gingiva to show the depth of the pocket and a bleeding point made. This is repeated along the circumference of the tooth.
- A beveled incision, using either a scalpel blade (No. 11 or 15) or electrosurgery is made, joining the bleeding points and recreating the scalloped edge of the normal gingival anatomy. The beveled incision is directed towards the base of the pocket or to a level slightly coronal to the apical extension of the junctional epithelium. When using electrosurgery the operator should allow for a 1 mm slough postoperatively. The electrode should be activated at the minimal effective setting in cut mode and stroked across the gingiva at the required angle. The cut surface should be pink and not bleeding if the setting is correct. Blanched tissue indicates that the setting is too high and should be reduced. To avoid overheating the tooth the electrode should not be applied to the gingiva around the same tooth for more than 5 seconds.
- The incised tissues are removed using a curette or a scaler. Remaining tissue tags are cut with a curette or a pair of scissors.
- Hemorrhage is controlled with gauze swabs and digital pressure. The crown and exposed root surfaces are then scaled and polished.
The postoperative phase is uncomfortable and analgesics are indicated for the first few days. The healing of a gingivoplasty wound is similar to that of a simple soft tissue wound. Plaque control is important to ensure adequate healing.
These animals are unlikely to accept toothbrushing immediately postoperatively, so chemical plaque control is indicated. Apply chlorhexidine gluconate gel on a piece of gauze twice daily for the first week, then once-daily in combination with toothbrushing for the second week.
Plaque control by means of daily toothbrushing and removing any predisposing causes if possible, e.g. cyclosporine administration, are necessary to prevent recurrence.
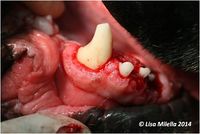
Flap Operations With or Without Osseous Surgery
Flap procedures can be used in all cases where surgical treatment of periodontal disease is indicated. These procedures can be performed with or without osseous surgery. Flap procedures are particularly useful where periodontal pockets extend beyond the mucogingival junction, the furcation is involved and/or recontouring of bony lesions is required.
The advantages of flap operations include:
- Existing keratinized gingiva is preserved.
- There is increased visualization of the defect and enabling thorough debridement of dental deposits and inflamed soft tissues.
- The marginal bone is exposed, whereby the morphology of bony defects can be identified and the proper treatment carried out.
- The flap can either be replaced at its original position or shifted apically or coronally, thereby making it possible to adjust the gingival margin to the local conditions.
- The flap procedure preserves the oral epithelium.
The design of the periodontal flap will depend on the type of pocket. The most common flap used in veterinary oral surgery is usually a full flap, or one with vertical releasing incisions allowing for increased exposure, but considered more invasive. Another commonly used flap for periodontal surgery is the envelope flap. This is created along the arcade, without vertical incisions. Periodontal flaps are typically made full thickness, which means the periosteum is released from the underlying hard tissue and kept with the flap.
Envelope flap: The sulcal incision is different from any other incision used in the oral cavity because the incision not only releases the gingiva from the underlying hard tissues but also excises the diseased pocket epithelium and granulation tissue. Furthermore, the sum of these incisions used to create the flap, creates a sharp marginal edge of the resulting flap, which allows for better apposition when it is replaced.
The extent of the flap should always be determined prior to any incision and all teeth in the area affected and needing treatment should be involved from the beginning to allow for a smooth incision. In most cases, carrying the incision a little mesial and distal of the target tooth is necessary for adequate visualization and access .
The full flap is created when further exposure is necessary or the flap is to be repositioned (coronally, apically, or laterally). It is a more invasive procedure with increased complication potential (e.g., hemorrhage and dehiscence) and therefore should not be performed when an envelope flap is sufficient.
| This article is still under construction. |