Difference between revisions of "Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
TestStudent (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{review}} |
| − | == | + | {{toplink |
| + | |backcolour = | ||
| + | |linkpage =Cardiology - WikiClinical | ||
| + | |linktext =Cardiology | ||
| + | |sublink1=Cardiovascular Conditions - WikiClinical | ||
| + | |subtext1=CARDIOVASCULAR CONDITIONS | ||
| + | |maplink1= Cardiovascular Conditions (Content Map) - WikiClinical | ||
| + | |pagetype=Clinical | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:cat-logo.png|right|40px]] | ||
| + | [[Image:dog-logo.png|right|40px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Rare in dogs | ||
| − | + | *Common in cats | |
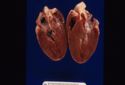
| + | [[Image:hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.jpg|right|thumb|125px|<small><center>'''Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (cat)'''. Courtesy of T. Scase</center></small>]] | ||
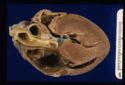
| + | [[Image:hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 2.jpg|right|thumb|125px|<small><center>'''Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (cat)'''. Courtesy of T. Scase</center></small>]] | ||
| + | ===Signalment=== | ||
| − | == | + | Dogs: Rare |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Cats: Pedigrees (e.g. Persians, Maine Coons) & mixed breeds; Occurs in young pedigrees and young to old mixed breeds; Male>Female | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Description=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy without an identifiable cause is known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The ventricular myocardium becomes so thick that the lumen is reduced to a size that is not compatible with maintaining the heart's function as a pump. The left ventricle no longer has the capacity to hold normal volumes of blood during diastole. As a result, the left atrium dilates from the increased pressure and volume of blood backing up into the lungs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Diagnosis=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====History & Clinical Signs==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | -Asymptomatic | ||
| + | |||
| + | -Hindlimb paresis or weakness (saddle thrombus see in cats) | ||
| + | |||
| + | -Signs of left-sided heart failure | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Physical Exam:==== | ||
| − | + | -Systolic murmur | |
| − | + | -Ventricular arrhythmias | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Radiography==== | |
| − | |||
| − | + | -Left atrial enlargement | |
| − | + | -Enlarged heart | |
| − | + | -Pulmonary congestion & edema | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Electrocardiography (ECG)==== | |
| + | -Tall R wave | ||
| − | + | -Wide QRS | |
| − | + | -Ventricular arrhythmias | |
| − | + | -Conduction disturbances | |
| + | -Sinus tachycardia | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====Echocardiography==== | |
| + | -Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy | ||
| − | + | -Left atrial enlargement | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | -Mitral valve insufficiency | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Treatment=== | |
| − | + | -Treat the individual symptoms | |
| + | Contraindications: Arterial Vasodilators; Positive Inotrops | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Prognosis=== | |
| − | + | -Poor for symptomatic cats | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 10:58, 6 October 2008
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
- Rare in dogs
- Common in cats
Signalment
Dogs: Rare
Cats: Pedigrees (e.g. Persians, Maine Coons) & mixed breeds; Occurs in young pedigrees and young to old mixed breeds; Male>Female
Description
- Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy without an identifiable cause is known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The ventricular myocardium becomes so thick that the lumen is reduced to a size that is not compatible with maintaining the heart's function as a pump. The left ventricle no longer has the capacity to hold normal volumes of blood during diastole. As a result, the left atrium dilates from the increased pressure and volume of blood backing up into the lungs.
Diagnosis
History & Clinical Signs
-Asymptomatic
-Hindlimb paresis or weakness (saddle thrombus see in cats)
-Signs of left-sided heart failure
Physical Exam:
-Systolic murmur
-Ventricular arrhythmias
Radiography=
-Left atrial enlargement
-Enlarged heart
-Pulmonary congestion & edema
Electrocardiography (ECG)=
-Tall R wave
-Wide QRS
-Ventricular arrhythmias
-Conduction disturbances
-Sinus tachycardia
Echocardiography
-Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy
-Left atrial enlargement
-Mitral valve insufficiency
Treatment
-Treat the individual symptoms
Contraindications: Arterial Vasodilators; Positive Inotrops
Prognosis
-Poor for symptomatic cats