Difference between revisions of "Piroplasmida"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Piroplasmida) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | {{review}} |
| + | {{toplink | ||
| + | |backcolour = | ||
| + | |linkpage =Parasites | ||
| + | |linktext =PARASITES | ||
| + | |pagetype=Bugs | ||
| + | |sublink1=Protozoa | ||
| + | |subtext1=PROTOZOA | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''piroplasms''' are a group of blood-bourne protozoa which are transmitted by [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|ticks]]. The two species most of veterinary importance are ''Babesia'', ''Cytauxzoon'' and ''Theileria''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Piroplasms are apicomplexan protozoa which inhabit [[Erythrocytes - WikiBlood|erythrocytes]], and sometimes other cells of vertebrates, but do not form pigment from haemoglobin. All piroplasms are small and round or pear-shaped (erythrocyte forms) and are parasitic on fish, amphibians, birds and mammals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==''Babesia''== | ||
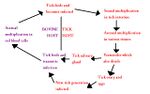
| + | [[Image:Babesia Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Babesia'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | ||
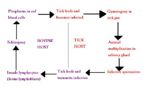
| + | [[Image:Alternative Babesia life cycle diagram.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Babesia'' Life Cycle - Mariana Ruiz Villarreal]] | ||
| + | *Infects a wide range of host species in different areas of the world | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Babesiosis has severe effects on cattle production in parts of the world | ||
| + | **Prevents European breeds from being successful in tropical regions where [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|ticks]] are endemic. | ||
| + | **Occurs sporadically in the UK and Ireland causing losses of around £8 million per year | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life Cycle''' | ||
| + | *Both [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Disease Transmission|trans-stadial]] and [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Disease Transmission|trans-ovarian]] occurs | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Each female [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|tick]] produces 3000 eggs | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|tick]] is the definitive host | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Babesia'' multiplies in the red blood cells by '''budding''' | ||
| + | **Forms 2-4 daughter cells (species dependent) | ||
| + | **Giemsa blood smears can differentiate between species using 'Diffquik' stain | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Babesia'' species are either small or large depending on the size of the daughter cells | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Small ''Babesia'' | ||
| + | **E.g. ''B. divergens'' | ||
| + | **E.g. ''B. gibsoni'' | ||
| + | **Peripheral nucleus | ||
| + | **Obtuse angle | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Large ''Babesia'' | ||
| + | **E.g. ''B. major'' | ||
| + | **E.g. ''B. canis-complex'' | ||
| + | **Central nucleus | ||
| + | **Acute angle | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Daughter cells disrupt the red blood cell and are released | ||
| + | **Spread and infect other red blood cells | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Antigen is released which absorbs onto other red blood cells | ||
| + | **Causes haemolysis and [[General Pathology - Pigmentation and Calcification#Haemoglobin|haemoglobin pigmentation]] | ||
| + | **Causes haemolytic anaemia, haemoglobinuria and fever | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cattle | ||
| + | **Sudden onset | ||
| + | **Often fatal if untreated | ||
| + | **Causes 'pipestem' faeces | ||
| + | **Clumping of red blood cells in brain capillaries can occur causing neurological signs | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Epidemiology''' | ||
| + | *Determined by: | ||
| + | **Number of infected [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|ticks]] seeking a blood mean ('''tick pressure''') | ||
| + | **Calves under 9 months are refractory to disease | ||
| + | ***Can develop immunity if exposed without showing clinical signs | ||
| + | **Premunity developes quickly in infected cattle which causes a 'carrier state' | ||
| + | **Immunity can wane in the absense of re-infection | ||
| + | **Uninfected cattle remain susceptible | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Predisposing factors: | ||
| + | **Sucseptible animals introduced into an infected area | ||
| + | **Infected [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|ticks]] are intorduced into a clean area | ||
| + | **Infected cattle are introduced into an area with clean [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|ticks]] | ||
| + | **Temporary reduction in the [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|tick]] population decreasing the transmission rate (causing enzootic instability) | ||
| + | **Infected are transported or stressed in other ways, e.g. parturition | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In the UK | ||
| + | **Sporadic disease | ||
| + | **Enzootic instability | ||
| + | **Occurs mostly during the spring and autumn during periods of greatest [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|tick]] activity | ||
| + | **Occurs mostly in stressed cattle under 2 years old on rough grazing | ||
| + | **''B. divergens'' the most common species | ||
| + | **[[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Ixodes spp.|''Ixodes ricinus'']] is the vector | ||
| + | **[[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Disease Transmission|Trans-ovarial]] transmission to the next generation occurs | ||
| + | **''B. major'' occurs in South East England but is not pathogenic | ||
| + | ***Vector is [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Important Hard Ticks|''Haemaphysalis'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Overseas | ||
| + | **''B. bovis'' causes considerable losses in cattle throughout many tropical and sub-tropical areas | ||
| + | ***In Australia an attenuated vaccine is used | ||
| + | ***Vector is [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Important Hard Ticks|''Boophilus'']] | ||
| + | **''B. bigemina'' causes problems in Africa and South America | ||
| + | ***Vector is [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Important Hard Ticks|''Boophilus'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Dogs | ||
| + | **Complex epidemiology | ||
| + | **Recognised species are extending their endemic ranges due to the disovery of the small ''Babesia'' species, pet passport scheme and increased overseas travel | ||
| + | **Large species comprises 3 subspecies | ||
| + | ***''B. canie canis'' is the msot important | ||
| + | ****[[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Important Hard Ticks|''Dermacentor'']] vector | ||
| + | ****Largely confined to southern Europe but is spreading | ||
| + | ***''B. canis'' uses [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Important Hard Ticks|''Rhipicephalus'']] as a vector and is spreading northwards through Europe | ||
| + | ***''B. gibsoni'' is now established in the USA and South-East Asia | ||
| + | **British dogs have no immunity as no species are endemic to the UK so are highly suceptible if taken abroad | ||
| + | **Prevent [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|tick]] bites by a 'Amitraz' collar is currently the best method of protection | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Horses | ||
| + | **2 species occur | ||
| + | **''B. equi'' is the most pathogenic | ||
| + | **Not endemic to the UK | ||
| + | **Serology using ELISA or IFAT to diagnose | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Sheep and goats | ||
| + | **Several species | ||
| + | **Little clincial significance | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Enzootic Instability=== | ||
| + | *Low rate of transmission | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Few infected [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|ticks]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Infrequent exposure | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Immunity wanes or is completely absent in many individuals | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Low levels of herd immunity | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Higher''' incidence of disease | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Enzootic Stability=== | ||
| + | *High rate of transmission | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Many infected ticks | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Frequent exposure boosts immunity | ||
| + | |||
| + | *High level of herd immunity | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Lower''' incidence of disease | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==''Theileria''== | ||
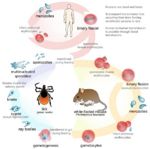
| + | [[Image:Theileria parva life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Theileria parva'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | ||
| + | *Main species of veterinary importance is ''Theileria parva'' | ||
| + | **Causes '''East Coast Fever''' | ||
| + | ***Severe, proliferative lymphatic disease of cattle | ||
| + | ***Central and Eastern Africa | ||
| + | ***Transmitted by [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Ticks of Veterinary Importance|''Rhipicephalus appendiculatus'']] | ||
| + | ***[[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Disease Transmission|Trans-stadial]] transmission | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Other ''Theileria'' species causes production losses in cattle and sheep in the Middle East, Mediterranean and in Northern Africa | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life Cycle''' | ||
| + | *Incubation phase lasts 1 week | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lymphoblast proliferation | ||
| + | **Local [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] first infected then spreads through body | ||
| + | **Occurs in week two | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Lymphoid depletion | ||
| + | **[[Lymphocytes - WikiBlood|Lymphocytes]] killed | ||
| + | **Decreases lymphopoiesis | ||
| + | **Occurs in week 3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Total incubation period takes about 18 days | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Diagnosis''' | ||
| + | *Clinical signs | ||
| + | **Pyrexia | ||
| + | **Enlarged local [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] | ||
| + | ***Usually parotid [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] as [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks#Ticks of Veterinary Importance|''Rhipicephalus appendiculatus'']] feeds in the ear | ||
| + | **Loss of condition | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Examine Giemsa stained smears of: | ||
| + | **Local [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] aspirated for schizonts | ||
| + | **Blood smears for pioplasms in red blood cells | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Post-mortem | ||
| + | **Pulmonary oedema | ||
| + | **Gut mucosal haemorrhages | ||
| + | **[[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|Lymph node]] and [[Spleen - Anatomy & Physiology|spleen]] cellular atrophy | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Control''' | ||
| + | *Integrated control of both the [[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|tick]] and vector | ||
| + | **[[Vaccines - WikiBlood|Vaccination]] and [[ectoparasiticides]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Current [[Vaccines - WikiBlood|vaccination]] is live unattentuated | ||
| + | **Contains frozen stabilate of ground up tick gut containing infective sporozoites | ||
| + | **Long lasting oxytetracycline administered at the same time to slow down schizogony giving the immune response time to develop | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==''Cytauxzoon felis''== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Cytauxzoon is classified in the order ''Piroplasmida'' and family ''Theileriidae'' | ||
| + | **This family has both an erythrocytic and a tissue (leukocytic) phase | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The ''Babesiidae'', a related family, is characterized by having a primarily erythrocytic phase in the mammalian host | ||
| + | **Its morphological features are indistinguishable from the erythrocytic form of Cytauxzoon | ||
| + | |||
| + | *''Cytauxzoon felis'', ''B. equi'', and ''B. rodhaini'' have been linked to both the babesias and theilerias by RNA gene sequence analysis | ||
| + | **It has been suggested that these organisms be reclassified within a separate family | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Life Cycle''' | ||
| + | *Large schizonts of ''C. felis'' develop in [[Macrophages - WikiBlood|macrophages]] | ||
| + | **In Theileria the exoerythrocytic stage occurs primarily within [[Lymphocytes - WikiBlood|lymphocytes]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In ''C. felis'', schizonts develop within mononuclear phagocytes, initially as indistinct vesicular structures and later as large, distinct nucleated schizonts that actively undergo division by true schizogony and binary fission | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Later in the course of the disease, schizonts develop buds (merozoites) that separate and eventually fill the entire host cell | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Each schizont may contain numerous merozoites | ||
| + | **Ultrastructurally, schizonts lack a parasitophorous vacuole, and individual merozoites possess rhoptries | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The host cell ruptures, releasing merozoites into the tissue fluid and blood | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Merozoites are then believed to enter erythrocytes to form the intraerythrocytic stage | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Merozoites appear in [[Macrophages - WikiBlood|macrophages]] one to three days before they are observed in [[Erythrocytes - WikiBlood|erythrocytes]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Pathogenicity''' | ||
| + | *[[Suborder: Metastigmata, ticks|Ticks]] are implicated as the natural vector for ''Cytauxzoon'' | ||
| + | **Most cases of infection have been associated with the presence of these parasites on the hosts | ||
| + | **Experimentally, ''Dermacentor variabilis'' can transmit the organism from bobcats to domestic cats. In a white tiger that developed a natural, fatal infection in Florida, two female Lone Star ticks (''Amblyomma americanum'') were present on the inguinal skin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Clinically, the disease in cats is characterized by fever, depression, dyspnea, anorexia, lymphadenopathy, anaemia, and icterus leading to death in three to six days | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Gross findings include pale or icteric mucous membranes, petechiae and ecchymoses in the [[Lungs - Anatomy & Physiology|lung]], [[Heart - Anatomy & Physiology|heart]], [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph nodes]] and on mucous membranes, splenomegaly, lymphadenomegaly, and hydropericardium | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Microscopically, numerous large schizonts are present within the cytoplasm of endothelial-associated [[Macrophages - WikiBlood|macrophages]] | ||
| + | **Infected macrophages become markedly enlarged (up to 75μm) and may occlude the lumens of numerous vessels of many tissues, especially the [[Lungs - Anatomy & Physiology|lungs]] | ||
| + | **Minimal inflammatory reaction is present in tissues | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Diagnosis''' | ||
| + | *Merozoites within [[Erythrocytes - WikiBlood|erythrocytes]], best seen on peripheral blood or tissue impressions, are variable in morphology and can occur as round, oval, or signet ring-shaped bodies | ||
| + | **Are 1-5 micrometers in diameter | ||
| + | **Small, peripherally placed basophilic nucleus | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Organisms that must be distinguished from the intraerythrocytic phase of ''C. felis'' include ''Babesia'' and ''Hemobartonella'' | ||
| + | **The blood stage may appear similar to the ring forms of ''Hemobartonella'' and to the piriforms of ''Babesia'' | ||
| + | **Unlike ''Cytauxzoon'', ''babesiosis'' and ''hemobartonellosis'' do not have a tissue stage of infection | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Differential diagnosis for the tissue phase of ''cytauxzoonosis'' includes other small (less than 5 μm), intrahistiocytic organisms such as ''Toxoplasma'', ''Leishmania'' and ''Histoplasma'' | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 22 November 2008
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Introduction
The piroplasms are a group of blood-bourne protozoa which are transmitted by ticks. The two species most of veterinary importance are Babesia, Cytauxzoon and Theileria.
Piroplasms are apicomplexan protozoa which inhabit erythrocytes, and sometimes other cells of vertebrates, but do not form pigment from haemoglobin. All piroplasms are small and round or pear-shaped (erythrocyte forms) and are parasitic on fish, amphibians, birds and mammals.
Babesia
- Infects a wide range of host species in different areas of the world
- Babesiosis has severe effects on cattle production in parts of the world
- Prevents European breeds from being successful in tropical regions where ticks are endemic.
- Occurs sporadically in the UK and Ireland causing losses of around £8 million per year
Life Cycle
- Both trans-stadial and trans-ovarian occurs
- Each female tick produces 3000 eggs
- The tick is the definitive host
- Babesia multiplies in the red blood cells by budding
- Forms 2-4 daughter cells (species dependent)
- Giemsa blood smears can differentiate between species using 'Diffquik' stain
- Babesia species are either small or large depending on the size of the daughter cells
- Small Babesia
- E.g. B. divergens
- E.g. B. gibsoni
- Peripheral nucleus
- Obtuse angle
- Large Babesia
- E.g. B. major
- E.g. B. canis-complex
- Central nucleus
- Acute angle
- Daughter cells disrupt the red blood cell and are released
- Spread and infect other red blood cells
- Antigen is released which absorbs onto other red blood cells
- Causes haemolysis and haemoglobin pigmentation
- Causes haemolytic anaemia, haemoglobinuria and fever
- Cattle
- Sudden onset
- Often fatal if untreated
- Causes 'pipestem' faeces
- Clumping of red blood cells in brain capillaries can occur causing neurological signs
Epidemiology
- Determined by:
- Number of infected ticks seeking a blood mean (tick pressure)
- Calves under 9 months are refractory to disease
- Can develop immunity if exposed without showing clinical signs
- Premunity developes quickly in infected cattle which causes a 'carrier state'
- Immunity can wane in the absense of re-infection
- Uninfected cattle remain susceptible
- Predisposing factors:
- Sucseptible animals introduced into an infected area
- Infected ticks are intorduced into a clean area
- Infected cattle are introduced into an area with clean ticks
- Temporary reduction in the tick population decreasing the transmission rate (causing enzootic instability)
- Infected are transported or stressed in other ways, e.g. parturition
- In the UK
- Sporadic disease
- Enzootic instability
- Occurs mostly during the spring and autumn during periods of greatest tick activity
- Occurs mostly in stressed cattle under 2 years old on rough grazing
- B. divergens the most common species
- Ixodes ricinus is the vector
- Trans-ovarial transmission to the next generation occurs
- B. major occurs in South East England but is not pathogenic
- Vector is Haemaphysalis
- Overseas
- Dogs
- Complex epidemiology
- Recognised species are extending their endemic ranges due to the disovery of the small Babesia species, pet passport scheme and increased overseas travel
- Large species comprises 3 subspecies
- B. canie canis is the msot important
- Dermacentor vector
- Largely confined to southern Europe but is spreading
- B. canis uses Rhipicephalus as a vector and is spreading northwards through Europe
- B. gibsoni is now established in the USA and South-East Asia
- B. canie canis is the msot important
- British dogs have no immunity as no species are endemic to the UK so are highly suceptible if taken abroad
- Prevent tick bites by a 'Amitraz' collar is currently the best method of protection
- Horses
- 2 species occur
- B. equi is the most pathogenic
- Not endemic to the UK
- Serology using ELISA or IFAT to diagnose
- Sheep and goats
- Several species
- Little clincial significance
Enzootic Instability
- Low rate of transmission
- Few infected ticks
- Infrequent exposure
- Immunity wanes or is completely absent in many individuals
- Low levels of herd immunity
- Higher incidence of disease
Enzootic Stability
- High rate of transmission
- Many infected ticks
- Frequent exposure boosts immunity
- High level of herd immunity
- Lower incidence of disease
Theileria
- Main species of veterinary importance is Theileria parva
- Causes East Coast Fever
- Severe, proliferative lymphatic disease of cattle
- Central and Eastern Africa
- Transmitted by Rhipicephalus appendiculatus
- Trans-stadial transmission
- Causes East Coast Fever
- Other Theileria species causes production losses in cattle and sheep in the Middle East, Mediterranean and in Northern Africa
Life Cycle
- Incubation phase lasts 1 week
- Lymphoblast proliferation
- Local lymph node first infected then spreads through body
- Occurs in week two
- Lymphoid depletion
- Lymphocytes killed
- Decreases lymphopoiesis
- Occurs in week 3
- Total incubation period takes about 18 days
Diagnosis
- Clinical signs
- Pyrexia
- Enlarged local lymph node
- Usually parotid lymph node as Rhipicephalus appendiculatus feeds in the ear
- Loss of condition
- Examine Giemsa stained smears of:
- Local lymph node aspirated for schizonts
- Blood smears for pioplasms in red blood cells
- Post-mortem
- Pulmonary oedema
- Gut mucosal haemorrhages
- Lymph node and spleen cellular atrophy
Control
- Integrated control of both the tick and vector
- Current vaccination is live unattentuated
- Contains frozen stabilate of ground up tick gut containing infective sporozoites
- Long lasting oxytetracycline administered at the same time to slow down schizogony giving the immune response time to develop
Cytauxzoon felis
- Cytauxzoon is classified in the order Piroplasmida and family Theileriidae
- This family has both an erythrocytic and a tissue (leukocytic) phase
- The Babesiidae, a related family, is characterized by having a primarily erythrocytic phase in the mammalian host
- Its morphological features are indistinguishable from the erythrocytic form of Cytauxzoon
- Cytauxzoon felis, B. equi, and B. rodhaini have been linked to both the babesias and theilerias by RNA gene sequence analysis
- It has been suggested that these organisms be reclassified within a separate family
Life Cycle
- Large schizonts of C. felis develop in macrophages
- In Theileria the exoerythrocytic stage occurs primarily within lymphocytes
- In C. felis, schizonts develop within mononuclear phagocytes, initially as indistinct vesicular structures and later as large, distinct nucleated schizonts that actively undergo division by true schizogony and binary fission
- Later in the course of the disease, schizonts develop buds (merozoites) that separate and eventually fill the entire host cell
- Each schizont may contain numerous merozoites
- Ultrastructurally, schizonts lack a parasitophorous vacuole, and individual merozoites possess rhoptries
- The host cell ruptures, releasing merozoites into the tissue fluid and blood
- Merozoites are then believed to enter erythrocytes to form the intraerythrocytic stage
- Merozoites appear in macrophages one to three days before they are observed in erythrocytes
Pathogenicity
- Ticks are implicated as the natural vector for Cytauxzoon
- Most cases of infection have been associated with the presence of these parasites on the hosts
- Experimentally, Dermacentor variabilis can transmit the organism from bobcats to domestic cats. In a white tiger that developed a natural, fatal infection in Florida, two female Lone Star ticks (Amblyomma americanum) were present on the inguinal skin.
- Clinically, the disease in cats is characterized by fever, depression, dyspnea, anorexia, lymphadenopathy, anaemia, and icterus leading to death in three to six days
- Gross findings include pale or icteric mucous membranes, petechiae and ecchymoses in the lung, heart, lymph nodes and on mucous membranes, splenomegaly, lymphadenomegaly, and hydropericardium
- Microscopically, numerous large schizonts are present within the cytoplasm of endothelial-associated macrophages
- Infected macrophages become markedly enlarged (up to 75μm) and may occlude the lumens of numerous vessels of many tissues, especially the lungs
- Minimal inflammatory reaction is present in tissues
Diagnosis
- Merozoites within erythrocytes, best seen on peripheral blood or tissue impressions, are variable in morphology and can occur as round, oval, or signet ring-shaped bodies
- Are 1-5 micrometers in diameter
- Small, peripherally placed basophilic nucleus
- Organisms that must be distinguished from the intraerythrocytic phase of C. felis include Babesia and Hemobartonella
- The blood stage may appear similar to the ring forms of Hemobartonella and to the piriforms of Babesia
- Unlike Cytauxzoon, babesiosis and hemobartonellosis do not have a tissue stage of infection
- Differential diagnosis for the tissue phase of cytauxzoonosis includes other small (less than 5 μm), intrahistiocytic organisms such as Toxoplasma, Leishmania and Histoplasma