Difference between revisions of "Yeast-like fungi"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Candidosis) |
m (→Cryptococcosis) |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
*May be a primary pathogen or opportunistic | *May be a primary pathogen or opportunistic | ||
| − | *Targets the respiratory system | + | *Targets the [[Cardiorespiratory System - Anatomy & Physiology|respiratory system]] |
| − | **Including the paranasal sinuses | + | **Including the [[Paranasal sinuses - Anatomy & Physiology|paranasal sinuses]] |
**Also can be systemic, cutaneous, visceral, skeletal or ocular | **Also can be systemic, cutaneous, visceral, skeletal or ocular | ||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
**Can spread within the herd | **Can spread within the herd | ||
| − | *Affects the CNS of dogs and cats | + | *Affects the [[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology|CNS]] of dogs and cats |
| − | **Paranasal sinuses and pharynx can be infected with dissemination to the CNS and other tissues | + | **[[Paranasal sinuses - Anatomy & Physiology|paranasal sinuses]] and [[Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|pharynx]] can be infected with dissemination to the [[Nervous System - CNS - Anatomy & Physiology|CNS]] and other tissues |
| − | ***E.g. Lungs, kidneys and joints | + | ***E.g. [[Lungs - Anatomy & Physiology|Lungs]], [[Urinary System - Anatomy & Physiology#The Kidney|kidneys]] and [[Joints - Anatomy & Physiology|joints]] |
**Also causes subcutaneous granulomas | **Also causes subcutaneous granulomas | ||
**The tip of the nose is a common site of infection in cats | **The tip of the nose is a common site of infection in cats | ||
***See [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#In Cats|here]] | ***See [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#In Cats|here]] | ||
| − | *Causes myxoma-like lesions of the lung and lip in horses | + | *Causes myxoma-like lesions of the [[Lungs - Anatomy & Physiology|lung]] and [[Lips - Anatomy & Physiology|lip]] in horses |
*Causes cryptococcal meningitis in humans | *Causes cryptococcal meningitis in humans | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
*Gram positive | *Gram positive | ||
| − | *Grows on blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar forming white, granular colonies which become slimy, mucoid and turn | + | *Grows on blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar forming white, granular colonies which become slimy, mucoid and turn creamy/brown within a week |
*Species identified by carbohydrate assimilation tests | *Species identified by carbohydrate assimilation tests | ||
| − | *Antigen and antibody should be tested for as antibody formed by the body is soon overwhelmed and neutralised by abundent polysaccharide antigen from the capsule | + | *Antigen and antibody should be tested for as [[Immunoglobulins - WikiBlood|antibody]] formed by the body is soon overwhelmed and neutralised by abundent polysaccharide antigen from the capsule in active, systemic infections |
| − | **Latex agglutination for antigen, complement fixation, ELISA and IFAT can be used | + | **Latex agglutination for [[Adaptive Immune System - WikiBlood#Actions of the Adaptive Immune System|antigen]], complement fixation, ELISA and IFAT can be used |
==Geotrichosis== | ==Geotrichosis== | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 28 April 2009
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Candidosis
- Candidia albicans is the most important species
- C. tropicalis and C. pelliculosa are other important species
- World wide distribution
- Usually an endogenous mycoses
- Immunocompromised animals may show symptoms
- Usually lesions on mucous membranes and at mucocutaneous junctions
- Many species have been implicated in bovine mastitis
- C. albicans has been isolated in porcine stomach ulcers
- C. rugosa has been implicated in pyometra in mares
- Infection of the crop, oesophagus and mouth occur in poultry and other birds leading to sour crop
- Causes thrush in humans
- C. albicans causes metritis and vaginitis in mares and genital candidiosis in stallions (and bulls)
- Skin scrapings in 20% KOH for microscopy
- Diphtheritic membranes, pus and fluids can be examined by Lactophenol Cotton Blue and stained by Gram or Methylene Blue stain
- Gram positive, oval, thin-walled budding cells with hyphal fragments
- Grow on Blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar producing soft, creamy colonies in 24-48 hours
- Grossly:
- Exudative, papular, pustular to ulcerative dermatitis
- Stomatitis and otitis externa may develop
- Microscopically:
- Spongiotic neutrophilic pustular inflammation
- Parakeratosis
- Ulcerations
- Superficial exudate containing organisms
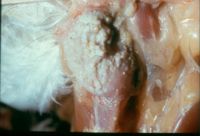
- Candida spp. in candidiasis
Cryptococcosis
- Over 19 species
- C. neoformans only major pathogen
- Worldwide
- Occurs in high concentrations in pigeon droppings (high creatinine concentration)
- The pigeon is not infected
- C. neoformis colonise the droppings after they have been excreted
- Also found in fruit, milk and soil
- Exogenous, inhaled infection which is generally sporadic (non-contageous)
- Can also be absorbed via skin penetration and ingestion
- May be a primary pathogen or opportunistic
- Targets the respiratory system
- Including the paranasal sinuses
- Also can be systemic, cutaneous, visceral, skeletal or ocular
- Causes sporadic mastitis in cattle
- Can spread within the herd
- Affects the CNS of dogs and cats
- Causes cryptococcal meningitis in humans
- Also affects dolphins, foxes, ferrets, monkeys, birds, cheetahs and guinea-pigs
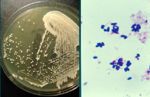
- Large yeast with capsule seen using India ink stain
- Stains with PAS (Periodic acis Schiff)
- Gram positive
- Grows on blood agar and Sabouraud's Dextrose agar forming white, granular colonies which become slimy, mucoid and turn creamy/brown within a week
- Species identified by carbohydrate assimilation tests
- Antigen and antibody should be tested for as antibody formed by the body is soon overwhelmed and neutralised by abundent polysaccharide antigen from the capsule in active, systemic infections
- Latex agglutination for antigen, complement fixation, ELISA and IFAT can be used
Geotrichosis
- G. candidum
- Rare
- Two forms: the yeast-like (glaborous) and fluffy
- Affects a wide range of species
- Usually diagnosed post-mortem
- Affects the mucous membranes, udder, bronchi and lungs
- Usually mild, causing suppurative granulomas
- Can be recovered from otitis externa infections in dogs
- Organisms appear as rectangular or spherical arthrospores on wet mounts
- Thick walled, non-budding, gram positive
- Grow on Sabouraud's Dextrose agar
- Membranous colonies
- Does not grow well on blood agar
Malassezia pachydermidis
- Caused by Malassezia pachydermatis
- Normally present in oily areas on the external ear canal and skin in dogs
- Some strains have been recovered from the ear canal of cats
- Bottle-shaped, small budding cells, non-mycelial
- Gram stain shows purple yeast cells with a very wide base
- Grow on Sabouraud's Dextrose agar in 2 weeks of incubation at room temperature
- Greenish discolouration on blood agar
- Clinical disease may cause yeast to proliferate and cause infection
- Grossly:
- Regional lesions: muzzle, ears, interdigital, perianal
- Or generalised disease
- Erythematous, hyperpigmented, lichenified and scaly lesions with alopecia
- Microscopically:
- hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis
- Spongiotic pustular dermatitis
- Acanthosis
- Organisms are usually present, minimum 3-5 yeasts per high-power field must be found to imply cause of disease
- Malassezia pachydermis in malassezia dermatitis
Rhodotorula
- Rhodotorula minuta and R. rubra
- Canine ear infections
- Equine uterus
- Seldom seen in animal infections
Torulopsis glabrata
- Commensal in animals and is found in the soil
- Implicated in cases of:
- Pyelonephritis, pneumonia, septicaemia and meningitis (humans)
- Mastitis and abortion in cattle
- Systemic infection of monkeys and dogs
Trichosporonosis
- Found in soil
- Deuteromycetes yeast
- Trichosporonosis beigelii
- Implicated in feline nasal granuloma, skin infections in horses and monkeys, mastitis in cattle and sheep and in feline bladder infections
- T. capitum implicated in bovine mastitis