Difference between revisions of "Causes of colic - Donkey"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - '{{review}}' to '') |
m (Text replace - '|rspace={{Donkey}} |pagetype=Donkey }}' to '|pagetype=Donkey }} {{infotable |Maintitle = This section was sponsored and content provided by '''THE DONKEY SANCTUARY''' |Maintitlebackcolour = B4CDCD }} [[Cat) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
[[Image:Causes of colic.jpg|center]] | [[Image:Causes of colic.jpg|center]] | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
** colitis | ** colitis | ||
** ovarian disease | ** ovarian disease | ||
| − | ** | + | ** gastric ulceration |
** nephritis | ** nephritis | ||
** hepatopathy | ** hepatopathy | ||
** chronic [[Hyperlipaemia - Donkey|hyperlipaemia]] | ** chronic [[Hyperlipaemia - Donkey|hyperlipaemia]] | ||
** pedunculated lipoma | ** pedunculated lipoma | ||
| − | ** | + | ** lower respiratory tract infection |
** peritonitis | ** peritonitis | ||
** fracture | ** fracture | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[Category:Donkey]] | [[Category:Donkey]] | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 10:18, 25 February 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
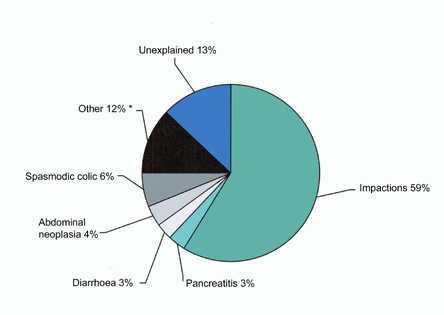
- *Included in the 12% of ‘other’ causes are:
- gastroenteritis
- sand colic
- colitis
- ovarian disease
- gastric ulceration
- nephritis
- hepatopathy
- chronic hyperlipaemia
- pedunculated lipoma
- lower respiratory tract infection
- peritonitis
- fracture
- intestinal torsion
- intestinal displacement
References
- Duffield, H. (2008) Colic In Svendsen, E.D., Duncan, J. and Hadrill, D. (2008) The Professional Handbook of the Donkey, 4th edition, Whittet Books, Chapter 3
|
|
This section was sponsored and content provided by THE DONKEY SANCTUARY |
|---|