Difference between revisions of "Snake Urinary System"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{review}} | {{review}} | ||
| − | [[Image:Burmese_python_kidneys2.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Kidneys of a [[Burmese Python|Burmese python]]''' | + | [[Image:Burmese_python_kidneys2.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Kidneys of a [[Burmese Python|Burmese python]]''' © RVC]] |
The urinary system of snakes consists of paired lobulated [[Kidney - Anatomy & Physiology|kidneys]] and ureters that empty into the dorsal urodeum. | The urinary system of snakes consists of paired lobulated [[Kidney - Anatomy & Physiology|kidneys]] and ureters that empty into the dorsal urodeum. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Paired kidneys are located in the dorsal caudal coelomic cavity with the right kidney cranial to the left. They are elongated, lobulated and somewhat triangular in cross section. All reptiles have metanephric kidneys that are simpler than the mammalian counterpart. There are decreased number of glomeruli (some species are aglomerular) and there is no loop of Henle. They may have one or more renal arteries, and in some [[:Category:Snake Species|species]], there is a separate branch of the ureter draining each lobule. There may be a sexual segment in the caudal kidney that follows up the distal part of each tubule and empties into a collecting duct. Since no urinary bladder is present, urine is not stored and ureters empty directy into the [[Cloaca|cloaca]]. | Paired kidneys are located in the dorsal caudal coelomic cavity with the right kidney cranial to the left. They are elongated, lobulated and somewhat triangular in cross section. All reptiles have metanephric kidneys that are simpler than the mammalian counterpart. There are decreased number of glomeruli (some species are aglomerular) and there is no loop of Henle. They may have one or more renal arteries, and in some [[:Category:Snake Species|species]], there is a separate branch of the ureter draining each lobule. There may be a sexual segment in the caudal kidney that follows up the distal part of each tubule and empties into a collecting duct. Since no urinary bladder is present, urine is not stored and ureters empty directy into the [[Cloaca|cloaca]]. | ||
| + | * '''For more information on excretion in reptiles, see''' [[Lizard and Snake Excretion|here]]. | ||
==Uric acid== | ==Uric acid== | ||
[[Uric acid]] is the main form of nitrogenous waste with lesser amounts of ammonia and urea depending on the species, the natural environment and degree of water conservation required. [[Uric acid]] is [[Lizard and Snake Excretion|excreted]] by tubular secretion rather than urea by glomerular filtration | [[Uric acid]] is the main form of nitrogenous waste with lesser amounts of ammonia and urea depending on the species, the natural environment and degree of water conservation required. [[Uric acid]] is [[Lizard and Snake Excretion|excreted]] by tubular secretion rather than urea by glomerular filtration | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
==Ureters and Cloaca== | ==Ureters and Cloaca== | ||
Snakes have no bladder. The ureter enters the urodeum at a urogenital papilla and urine refluxes into the [[Snake Digestive System|colon]] for fluid conservation. | Snakes have no bladder. The ureter enters the urodeum at a urogenital papilla and urine refluxes into the [[Snake Digestive System|colon]] for fluid conservation. | ||
| − | * | + | * '''For a definition of cloaca, see''' [[Cloaca|here]]. |
| − | *For | + | * '''For information on renal diseases, see''' [[Lizard and Snake Renal Disease]]. |
[[Category:Snake_Anatomy]] | [[Category:Snake_Anatomy]] | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
Mader, D.R. (2005). Reptile Medicine and Surgery. Saunders. pp. 49. ISBN 072169327X | Mader, D.R. (2005). Reptile Medicine and Surgery. Saunders. pp. 49. ISBN 072169327X | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 10 May 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
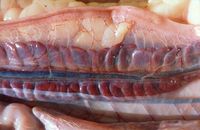
The urinary system of snakes consists of paired lobulated kidneys and ureters that empty into the dorsal urodeum.
Kidney
Paired kidneys are located in the dorsal caudal coelomic cavity with the right kidney cranial to the left. They are elongated, lobulated and somewhat triangular in cross section. All reptiles have metanephric kidneys that are simpler than the mammalian counterpart. There are decreased number of glomeruli (some species are aglomerular) and there is no loop of Henle. They may have one or more renal arteries, and in some species, there is a separate branch of the ureter draining each lobule. There may be a sexual segment in the caudal kidney that follows up the distal part of each tubule and empties into a collecting duct. Since no urinary bladder is present, urine is not stored and ureters empty directy into the cloaca.
- For more information on excretion in reptiles, see here.
Uric acid
Uric acid is the main form of nitrogenous waste with lesser amounts of ammonia and urea depending on the species, the natural environment and degree of water conservation required. Uric acid is excreted by tubular secretion rather than urea by glomerular filtration
Ureters and Cloaca
Snakes have no bladder. The ureter enters the urodeum at a urogenital papilla and urine refluxes into the colon for fluid conservation.
- For a definition of cloaca, see here.
- For information on renal diseases, see Lizard and Snake Renal Disease.
Reference
Mader, D.R. (2005). Reptile Medicine and Surgery. Saunders. pp. 49. ISBN 072169327X