Difference between revisions of "Bacterial skin infections - Pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
====Ovine fleece rot==== | ====Ovine fleece rot==== | ||
| − | *Caused by [[Pseudomonas | + | *Caused by [[:Category:Pseudomonas and Burkholderia species|''Pseudomonas'']] and excessive moisture |
*Prediscposes to [[Parasitic skin infections - Pathology#Myiasis|myiasis]] | *Prediscposes to [[Parasitic skin infections - Pathology#Myiasis|myiasis]] | ||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
*May involve a foreign bodey reaction to follicular contents and draining sinuses develop | *May involve a foreign bodey reaction to follicular contents and draining sinuses develop | ||
*If chronic, scarring and loss of adnexa | *If chronic, scarring and loss of adnexa | ||
| − | *Bacteria often isolated include [[Staphylococcus spp.|''Staphylococcus'' spp.]], especially ''S. intermedius'' in dogs, [[Streptococci|''Streptococcus'' spp.]], ''[[Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis]]'', [[Pseudomonas | + | *Bacteria often isolated include [[Staphylococcus spp.|''Staphylococcus'' spp.]], especially ''S. intermedius'' in dogs, [[Streptococci|''Streptococcus'' spp.]], ''[[Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis]]'', [[:Category:Pseudomonas and Burkholderia species|''Pseudomonas'']], [[:Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species|''Pasteurella'']], [[Proteus|''Proteus'']], [[Escherichia coli|''E.coli'']] |
====Staphylococcal folliculitis and furunculosis==== | ====Staphylococcal folliculitis and furunculosis==== | ||
Revision as of 19:47, 14 May 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
Cutaneous bacterial infections tend to be called pyodermas. They are superficial, deep and are common in dogs, but less common in other species.
Superficial pyoderma
- Affects epidermis and upper infundibulum of hair follicles
- No scarring when healed
- Grossly:
- Erythema
- Alopecia
- Papules and pustules
- Crusts
- Epidermal collarettes
- Microscopically:
- Intraepidermal pustular dermatitis
- Superficial suppurative folliculitis
- Bacteria commonly not seen
Impetigo
- = Superficial pustular dermatitis
- Caused by coagulase-positive Staphylococcus spp.
- Associated with:
- Abrasions
- Poor nutrition
- Viral infections
- Immunosuppression (often due to hyperadrenocorticism)
- Grossly:
- Pustules -> crusts, mostly in hairless skin
- Microscopically:
- Interfollicular neutrophilic subcorneal pustule
Dermatophilosis
- Caused by Dermatophilus congolensis
- Affects cattle, horses, sheep mainly
- More common in wet and warm weather
- Transmotted from animal to animal
- Lesions tend to form on dorsal back and extremities
- Associated with skin trauma, prolonged wetting or parasites
- -> penetration of zoospores
- Bacteria proliferate in outer sheath of hair follicles and superficial epidermis
- Gram-positive, filamentous branching organisms, subdivided longitudinally and transversly
- Causing:
- Acute inflammatory response -> neutrophil migration through dermis and epidermis -> formation of microabscesses
- Further penetration of bacteria is thus prevented
- Regenerated epidermis is invaded again by remaining organisms
- Repeated reinfection -> multilaminated pustular crusts
- Grossly:
- Papules, pustules, crusts may coalesce and mat the coat
- Microscopically:
- Hyperplastic superficial perivascular dermatitis
- Multilaminated crusts, alternating keratin and inflammatory cell layers
Greasy pig disease
- = Exudative epidermitis of pigs
- Caused by Staphylococcus hyicus
- Affects neonatal piglets - often fatal, older piglets - milder disease
- Focal erosion of stratum corneum
- Brown exudate
- Dermatitis around eyes, ears, snout, chin and medial legs, may spread to ventral abdomen and thorax
- Rapidly becomes generalised -> greasy exudate over red skin -> hardened, cracked exudate
- In older piglets, milder localised disease develops around eyes, ears and face
- Grossly:
- Thickened epidermis, scaling
- Microscopically:
- Early - subcorneal pustular dermatitis extending to hair follicles -> superficial suppurative folliculitis
- Late - hyperplastic epidermis, thick keratin crusts with cocci, microabscesses
Ovine fleece rot
- Caused by Pseudomonas and excessive moisture
- Prediscposes to myiasis
Equine pastern folliculitis
- = Greasy heel
- Secondary pyoderma
- Affects caudal pastern and fetlock
Deep pyoderma
- Less common than superficial pyoderma
- Occurs mainly in dogs
- Affects infundibulum, isthmic portion of hair follicles and surrounding dermis and subcutis
- Heals with scarring
- Local lymph nodes are often affected
- Often secondary to immunosuppression, follicular hyperkeratosis or demodicosis
- May also be a sequele to superficial pyoderma
- Grossly:
- Microscopically:
- Pyogranulomatous folliculitis and furunculosis
- Nodular or diffuse dermatitis
- Panniculitis
- May involve a foreign bodey reaction to follicular contents and draining sinuses develop
- If chronic, scarring and loss of adnexa
- Bacteria often isolated include Staphylococcus spp., especially S. intermedius in dogs, Streptococcus spp., Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, Pseudomonas, Pasteurella, Proteus, E.coli
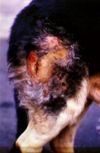
Staphylococcal folliculitis and furunculosis
- Occurs in dogs, horses, sheep and goats
- Dogs:
- Localised or generalised lesions
- Affected areas include: muzzle, chin, bridge of nose, pressure points and interdigital areas
- German Shepherd deep pyoderma
- Genetically predisposed
- Dorsal lumosacral, ventral adbomen and thigh areas
- Horses:
- Areas under tack ususlly involved
- Goats:
- Extremities, ventral abdomen, udder, medial thigh, perineum tend to be affected
- Sheep:
- Adults: face, limbs and teats
- Lambs: lips and perineum
Subcutaneous abscesses
- Purulent exudate within dermis and subcutis
- Commonly occurs in cats due to contamination of penetrating wounds
- Surrounding wall of collagen and fibroblasts may develop
- Common bacteria (often normal mouth flora)
Bacterial granulomatous dermatitis
- Usually due to saprophytes
- Grossly:
- Diffuse or nodular lesions
- May ulcerate and form drainage fistulas
- Microscopically:
- Macrophages +/- multinucleated giant cells
- Caseous necrosis and neutrophils
- Mycobacterial granulomatous or pyogranulomatous lesions
- Usually caused by Mycobacterium lepraemurium (feline leprosy) or other Mycobacteria
- Most commonly lesions appear on head, neck and legs
- Botryomycosis
- Granulomatous dermatitis caused by nonfilamentous bacteria
- Usually Staphylococcus aureus
- Small, yellow granules are formed - sulfur granules
- Central bacteria surrounded by homogeneous eosinophilic material
- Filamentous bacteria can also cause granulomas
Bacterial pododermatitis
- Digital infections in ruminants
- Contagious footrot
- Usually caused by Bacteroides nodosus together with Fusobacterium necrophorum
- Moisture and trauma allow B. nodosus to enter -> aids bacterial penetration of epidermis -> F. necrophorum invades -> necrosis and inflammation
- Grossly:
- Early lesions - red, moist, swollen, eroded interdigital skin
- Spreads to epidermal matrix of hoof -> separation of horn + malodorous exudate
- Regeneration attempted as germinal epithelium is not destroyed
- Chronic infections -> long , misshapen hoof
- Benign footrot (scald)- only interdigital ski affected, slight separation of heel horn
- Mostly the type occuring in cattle
- Necrobacillosis of the foot
- Usually caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum with other bacteria
- In sheep:
- Ovine interdigital dermatitis
- Acute necrotising dermatitis similar to benign footrot
- Foot abscesses
- Bulbular or lamellar
- Mostly in wet conditions and in heavy sheep
- Ovine interdigital dermatitis
- In cattle:
- Interdigital dermatitis and cellulitis
- Caused by F. necrophorum and Bacteroides melaninogenicus
- Predisposed by trauma
- Grossly:
- Fissures, necrotic swollen edges in interdigital spaces
- Inflammation may spread to joint spaces
Systemic bacterial infections
- Salmonellosis
- Capillary dilatation and congestion -> cyanosis of external ears and abdoman
- Thrombosis -> necrosis of extremities
- Erysipelas in pigs
- Caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
- Vasculitis, thrombosis, ischaemia -> cutaneous lesions - firm, raises, rhomboidal pink to dark purple areas
- Clostridium novyi
- Severe cellulitis, toxaemia and death of young rams during breeding season (due to traumatised heads) - 'big head'
- Streptococcus equi
- In horses
- Immune complex vasculitis -> purpura