Difference between revisions of "Lymphatic System Overview - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{toplink |
| + | |thispagetable = Lymphatic System (Table) - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |thispagemap = Lymphatic System (Content Map) - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |pagetype =Anatomy | ||
| + | }} | ||
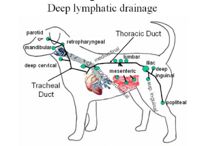
[[Image:Deep Lymphatic Drainage Diagram.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Deep Lymphatic drainage - Copyright B.Catchpole RVC]] | [[Image:Deep Lymphatic Drainage Diagram.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Deep Lymphatic drainage - Copyright B.Catchpole RVC]] | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 6: | Line 10: | ||
==Lymphatic Vessels and Lymph== | ==Lymphatic Vessels and Lymph== | ||
| − | Due to their structure lymphatic capillaries are more permeable than vascular capillaries | + | Due to their structure lymphatic capillaries are more permeable than vascular capillaries and this means that they can not only more effectively remove fluid from tissue but they can also take up large molecules as well as chylomicrons for the transport of fats. Chylomicrons enter the [[Lymph - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph]] to eventually join the blood via the thoracic duct; this enables the lipid soluble [[Small Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology#Triacylglycerol Digestion and Absorption |triacylglycerol (TAG)]] to be transported into the blood. The interstitial fluid or lymph within the lymphatic vessels passes through lymph nodes and is surveyed by immune cells before returning to the blood, ensuring that antigens/pathogens from tissues are removed. |
| − | == | + | ==Lymphoreticular system== |
The lymphoreticular system produces [[Immunology|immune cells]] and removes senescent cells. | The lymphoreticular system produces [[Immunology|immune cells]] and removes senescent cells. | ||
| − | Primary (or central) lymphoid tissues can also be referred to as primary lymphoid organs. Maturation of [[Lymphocytes | + | Primary (or central) lymphoid tissues can also be referred to as primary lymphoid organs. Maturation of [[Lymphocytes|lymphocytes]] and [[Leukopoiesis#Lymphopoiesis|lymphopoiesis]] occurs in the primary lymphoid tissues, with different tissues responsible for maturing different types of lymphocyte. The primary lymphoid tissues are: |
*[[Bone Marrow - Anatomy & Physiology|Bone marrow]] | *[[Bone Marrow - Anatomy & Physiology|Bone marrow]] | ||
*[[Bursa of Fabricius - Anatomy & Physiology|The Bursa of Fabricius]] | *[[Bursa of Fabricius - Anatomy & Physiology|The Bursa of Fabricius]] | ||
*[[Thymus - Anatomy & Physiology|The Thymus]] | *[[Thymus - Anatomy & Physiology|The Thymus]] | ||
| − | *[[Haematopoiesis | + | *[[Haematopoiesis#Hepatic Phase|The Foetal Liver]] |
| − | Secondary (or peripheral) lymphoid tissues or secondary lymphoid organs provide a site for immune responses to occur and are populated by relatively mature [[Lymphocytes#T cells|T cells]] and [[Lymphocytes#B cells|B cells]], [[Macrophages|macrophages]] and dendritic cells; each tissue seems to be preferentially populated by lymphocyte types that specialise in the antigens that are most | + | Secondary (or peripheral) lymphoid tissues or secondary lymphoid organs provide a site for immune responses to occur and are populated by relatively mature [[Lymphocytes#T cells|T cells]] and [[Lymphocytes#B cells|B cells]], [[Macrophages|macrophages]] and dendritic cells; each tissue seems to be preferentially populated by lymphocyte types that specialise in the antigens that are most likley to be presented at that site. The secondary lymphoid tissues are: |
*[[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|The Lymph nodes]] | *[[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|The Lymph nodes]] | ||
*[[Spleen - Anatomy & Physiology|The Spleen]] | *[[Spleen - Anatomy & Physiology|The Spleen]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 29: | ||
*[[Regional Lymphoid Tissue - Anatomy & Physiology|Regional lymphoid tissue]] | *[[Regional Lymphoid Tissue - Anatomy & Physiology|Regional lymphoid tissue]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Test yourself on the lymphoreticular flash cards== |
| − | + | [[Lymphoreticular System Flashcards - Wikiblood|Lymphoreticular Flashcards]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 49: | Line 45: | ||
*<div id="Nance">{{citation|initiallast = Nance|initialfirst = D.M|finallast = Sanders|finalfirst = V.M|year = 2007|jtitle = Autonomic innervation and regulation of the immune system (1987-2007)|jor = Brain, Behavior, and Immunity|vol = 21(6)|range = 736-745}}</div> | *<div id="Nance">{{citation|initiallast = Nance|initialfirst = D.M|finallast = Sanders|finalfirst = V.M|year = 2007|jtitle = Autonomic innervation and regulation of the immune system (1987-2007)|jor = Brain, Behavior, and Immunity|vol = 21(6)|range = 736-745}}</div> | ||
| − | + | ==Creator== | |
| − | + | [[Asher Allison]] | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
Revision as of 15:07, 1 July 2010
|
|
Introduction
The lymphatic system can be divided into two anatomical and functional subsets: lymphatic vessels that carry lymph around the body, and the lymphoreticular system which describes the lymphoid tissues. The lymphatic system has three functions - immune defence, removal of interstitial fluid from tissues and the transport of fats.
Lymphatic Vessels and Lymph
Due to their structure lymphatic capillaries are more permeable than vascular capillaries and this means that they can not only more effectively remove fluid from tissue but they can also take up large molecules as well as chylomicrons for the transport of fats. Chylomicrons enter the lymph to eventually join the blood via the thoracic duct; this enables the lipid soluble triacylglycerol (TAG) to be transported into the blood. The interstitial fluid or lymph within the lymphatic vessels passes through lymph nodes and is surveyed by immune cells before returning to the blood, ensuring that antigens/pathogens from tissues are removed.
Lymphoreticular system
The lymphoreticular system produces immune cells and removes senescent cells. Primary (or central) lymphoid tissues can also be referred to as primary lymphoid organs. Maturation of lymphocytes and lymphopoiesis occurs in the primary lymphoid tissues, with different tissues responsible for maturing different types of lymphocyte. The primary lymphoid tissues are:
Secondary (or peripheral) lymphoid tissues or secondary lymphoid organs provide a site for immune responses to occur and are populated by relatively mature T cells and B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells; each tissue seems to be preferentially populated by lymphocyte types that specialise in the antigens that are most likley to be presented at that site. The secondary lymphoid tissues are:
- The Lymph nodes
- The Spleen
- Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue or MALT
- The Tonsils
- The Appendix/caecal pouch
- The Ileal Peyer's Patch
- Regional lymphoid tissue
Test yourself on the lymphoreticular flash cards
References
Texts:
- Dyce, K.M., Sack, W.O. and Wensing, C.J.G. (2002) Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.
- Janeway, C.A., Travers, P., Walport, M. and Shlomchik, M.J. (2005) Immunobiology: The immune system in health and disease. 6th ed. New York: Garland Science Publishing.
- McGeady, T.A., Quinn, P.J., FitzPatrick, E.S. and Ryan, M.T. (2006) Veterinary Embryology. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
- Ross, M.H. and Pawlina, W. (2006) Histology: A text and atlas. 5th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Sjaastad, O.V., Hove, K. and Sand, O. (2004) Physiology of Domestic Animals. Oslo: Scandinavian Veterinary Press.
- Tizard, I.R. (2004) Veterinary Immunology: An Introduction. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.
Literature:
- Dasso, J.F., Obiakor, H., Bach, H., Anderson, and Mage, R.G. (2000) A morphological and immunohistological study of the human and rabbit appendix for comparison with the avian bursa. Developmental & Comparative Immunology 24(8): pp.797-814.
- Metcalfe, D.D., Baram, D. and Mekori, Y. (1997) Mast Cells. Physiological Reviews 77(4): pp.1033-1064.
- Nance, D.M. and Sanders, V.M. (2007) Autonomic innervation and regulation of the immune system (1987-2007). Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 21(6): pp.736-745.